\(\left(x+3\right)\sqrt{x+4}+\left(x+9\right)\sqrt{x+11}=x^2+9x+10\)
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Câu b bạn có bị lỗi dấu căn không mà sao nó kéo dài cả 2 vế pt vậy :v
\(a,\sqrt{x^2-6x+9}+x=11\\ \Leftrightarrow\sqrt{\left(x-3\right)^2}=11-x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left|x-3\right|=11-x\\ TH_1:x\ge3\\ x-3=11-x\\ \Leftrightarrow2x=14\\ \Leftrightarrow x=7\left(tm\right)\)
\(TH_2:x< 3\\ -x+3=11-x\\ \Leftrightarrow-x+x=11-3\\ \Leftrightarrow0=8\left(VL\right)\)
Vậy \(S=\left\{7\right\}\)
\(c,\sqrt{16\left(x+1\right)}-\sqrt{9\left(x+1\right)}=4\) \(\left(dk:x\ge-1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{4^2}.\sqrt{\left(x+1\right)}-\sqrt{3^2}.\sqrt{\left(x+1\right)}=4\left(1\right)\)
Đặt \(a=\sqrt{x+1}\left(a\ge0\right)\)
Pt trở thành : \(4a-3a=4\Leftrightarrow a=4\left(tmdk\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow\sqrt{x+1}=4\\ \Rightarrow\left(\sqrt{x+1}\right)^2=16\\ \Rightarrow\left|x+1\right|=16\)
\(TH_1:x\ge-1\\ x+1=16\Leftrightarrow x=15\left(tm\right)\\ TH_2:x< -1\\ -x-1=16\Leftrightarrow x=-17\left(tm\right)\)
Nhưng loại TH2 vì dk ban đầu là \(x\ge-1\)
Vậy \(S=\left\{15\right\}\)
\(d,\sqrt{9x+9}+\sqrt{4x+4}=\sqrt{x+1}\left(dk:x\ge-1\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow\sqrt{9}.\sqrt{x+1}+\sqrt{4}.\sqrt{x+1}-\sqrt{x+1}=0\)
Đặt \(\sqrt{x+1}=a\left(a\ge0\right)\)
Tới đây bạn làm tương tự câu c nha.

a: ĐKXĐ: \(x\in R\)
\(\sqrt{\left(2x+3\right)^2}=5\)
=>|2x+3|=5
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x+3=5\\2x+3=-5\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x=2\\2x=-8\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\left(nhận\right)\\x=-4\left(nhận\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
b: ĐKXĐ: \(x\in R\)
\(\sqrt{9\left(x-2\right)^2}=18\)
=>\(\sqrt{9}\cdot\sqrt{\left(x-2\right)^2}=18\)
=>\(3\cdot\left|x-2\right|=18\)
=>\(\left|x-2\right|=6\)
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-2=6\\x-2=-6\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=8\left(nhận\right)\\x=-4\left(nhận\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
c: ĐKXĐ: x>=2
\(\sqrt{9x-18}-\sqrt{4x-8}+3\sqrt{x-2}=40\)
=>\(3\sqrt{x-2}-2\sqrt{x-2}+3\sqrt{x-2}=40\)
=>\(4\sqrt{x-2}=40\)
=>\(\sqrt{x-2}=10\)
=>x-2=100
=>x=102(nhận)
d: ĐKXĐ: \(x\in R\)
\(\sqrt{4\left(x-3\right)^2}=8\)
=>\(\sqrt{\left(2x-6\right)^2}=8\)
=>|2x-6|=8
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x-6=8\\2x-6=-8\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x=14\\2x=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=7\left(nhận\right)\\x=-1\left(nhận\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
e: ĐKXĐ: \(x\in R\)
\(\sqrt{4x^2+12x+9}=5\)
=>\(\sqrt{\left(2x\right)^2+2\cdot2x\cdot3+3^2}=5\)
=>\(\sqrt{\left(2x+3\right)^2}=5\)
=>|2x+3|=5
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x+3=5\\2x+3=-5\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x=2\\2x=-8\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\left(nhận\right)\\x=-4\left(nhận\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
f: ĐKXĐ:x>=6/5
\(\sqrt{5x-6}-3=0\)
=>\(\sqrt{5x-6}=3\)
=>\(5x-6=3^2=9\)
=>5x=6+9=15
=>x=15/5=3(nhận)

\(a,ĐK:1\le x\le3\)
Đặt \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{x-1}=a\\\sqrt{3-x}=b\end{matrix}\right.\left(a,b\ge0\right)\)
\(PT\Leftrightarrow a+b-ab=1\Leftrightarrow a+b-ab-1=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(a-1\right)\left(1-b\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}a=1\\b=1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-1=1\\3-x=1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow x=2\left(tm\right)\)
\(b,ĐK:0\le x\le9\\ PT\Leftrightarrow9+2\sqrt{x\left(9-x\right)}=-x^2+9x+9\\ \Leftrightarrow2\sqrt{-x^2+9x}-\left(-x^2+9x\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\sqrt{-x^2+9x}\left(2-\sqrt{-x^2+9x}\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}-x^2+9x=0\\\sqrt{-x^2+9x}=2\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=9\\x^2-9x+4=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\left(n\right)\\x=9\left(n\right)\\x=\dfrac{9+\sqrt{65}}{2}\left(n\right)\\x=\dfrac{9-\sqrt{65}}{2}\left(n\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)

6:ĐKXĐ: x>=0; x<>1/25
BPT=>\(\dfrac{3\sqrt{x}}{5\sqrt{x}-1}+3< =0\)
=>\(\dfrac{3\sqrt{x}+15\sqrt{x}-5}{5\sqrt{x}-1}< =0\)
=>\(\dfrac{18\sqrt{x}-5}{5\sqrt{x}-1}< =0\)
=>\(\dfrac{1}{5}< \sqrt{x}< =\dfrac{5}{18}\)
=>\(\dfrac{1}{25}< x< =\dfrac{25}{324}\)
7:
ĐKXĐ: x>=0
BPT \(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\sqrt{x}+1}{2\sqrt{x}+3}>\dfrac{8}{3}:\dfrac{8}{3}=1\)
=>\(\dfrac{\sqrt{x}+1}{2\sqrt{x}+3}-1>=0\)
=>\(\dfrac{\sqrt{x}+1-2\sqrt{x}-3}{2\sqrt{x}+3}>=0\)
=>\(-\sqrt{x}-2>=0\)(vô lý)
8:
ĐKXĐ: x>=0; x<>9/4
BPT \(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\sqrt{x}-2}{2\sqrt{x}-3}+4< 0\)
=>\(\dfrac{\sqrt{x}-2+8\sqrt{x}-12}{2\sqrt{x}-3}< 0\)
=>\(\dfrac{9\sqrt{x}-14}{2\sqrt{x}-3}< 0\)
TH1: 9căn x-14>0 và 2căn x-3<0
=>căn x>14/9 và căn x<3/2
=>14/9<căn x<3/2
=>196/81<x<9/4
TH2: 9căn x-14<0 và 2căn x-3>0
=>căn x>3/2 hoặc căn x<14/9
mà 3/2<14/9
nên trường hợp này Loại
9:
ĐKXĐ: x>=0
\(BPT\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{2\sqrt{x}+3}{5\sqrt{x}+7}< =-\dfrac{1}{3}\)
=>\(\dfrac{2\sqrt{x}+3}{5\sqrt{x}+7}+\dfrac{1}{3}< =0\)
=>\(\dfrac{6\sqrt{x}+9+5\sqrt{x}+7}{3\left(5\sqrt{x}+7\right)}< =0\)
=>\(\dfrac{11\sqrt{x}+16}{3\left(5\sqrt{x}+7\right)}< =0\)(vô lý)
10:
ĐKXĐ: x>=0; x<>1/49
\(BPT\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{6\sqrt{x}-2}{7\sqrt{x}-1}+6>0\)
=>\(\dfrac{6\sqrt{x}-2+42\sqrt{x}-6}{7\sqrt{x}-1}>0\)
=>\(\dfrac{48\sqrt{x}-8}{7\sqrt{x}-1}>0\)
=>\(\dfrac{6\sqrt{x}-1}{7\sqrt{x}-1}>0\)
TH1: 6căn x-1>0 và 7căn x-1>0
=>căn x>1/6 và căn x>1/7
=>căn x>1/6
=>x>1/36
TH2: 6căn x-1<0 và 7căn x-1<0
=>căn x<1/6 và căn x<1/7
=>căn x<1/7
=>0<=x<1/49

c) \(\sqrt[]{8+\sqrt[]{x}}+\sqrt{5-\sqrt[]{x}}=5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(\sqrt[]{8+\sqrt[]{x}}+\sqrt{5-\sqrt[]{x}}\right)^2=25\left(1\right)\left(đkxđ:0\le x\le25\right)\)
Áp dụng Bất đẳng thức Bunhiacopxki cho 2 cặp số dương \(\left(1;\sqrt[]{8+\sqrt[]{x}}\right);\left(1;\sqrt{5-\sqrt[]{x}}\right)\)
\(\left(1.\sqrt[]{8+\sqrt[]{x}}+1.\sqrt{5-\sqrt[]{x}}\right)^2\le\left(1^2+1^2\right)\left(8+\sqrt[]{x}+5-\sqrt[]{x}\right)=26\)
\(\left(1\right)\Leftrightarrow26=25\left(vô.lý\right)\)
Vậy phương trình đã cho vô nghiệm
b) \(\sqrt[]{1+4x}+2\sqrt[]{2-x}+2\sqrt[]{\left(1+4x\right)\left(2-x\right)}=3\) \(\left(đkxđ:-\dfrac{1}{4}\le x\le2\right)\)
\(\)\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt[]{1+4x}+2\sqrt[]{2-x}=3-2\sqrt[]{\left(1+4x\right)\left(2-x\right)}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(\sqrt[]{1+4x}+2\sqrt[]{2-x}\right)^2=\left[3-2\sqrt[]{\left(1+4x\right)\left(2-x\right)}\right]^2\left(1\right)\)
Áp dụng Bất đẳng thức Bunhiacopxki :
\(\left(1.\sqrt[]{1+4x}+2\sqrt[]{2-x}\right)^2\le\left(1^2+2^2\right)\left(1+4x+2-x\right)=5\left(3x+3\right)\)
Áp dụng Bất đẳng thức Cauchy :
\(2\sqrt[]{\left(1+4x\right)\left(2-x\right)}\le1+4x+2-x=3x+3\)
Dấu "=" xảy ra khi và chỉ khi
\(1+4x=2-x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{1}{5}\left(thỏa.đk\right)\)
\(pt\left(1\right)\Leftrightarrow5\left(4x+3\right)=4x+3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4\left(4x+3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-\dfrac{3}{4}\left(k.thỏa.x=\dfrac{1}{5}.vô.lý\right)\)
Vậy phương trình đã cho vô nghiệm
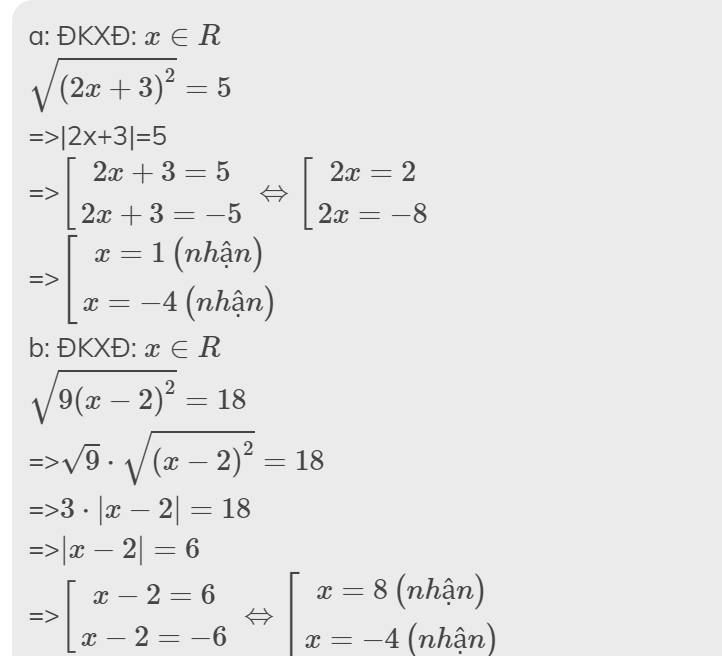
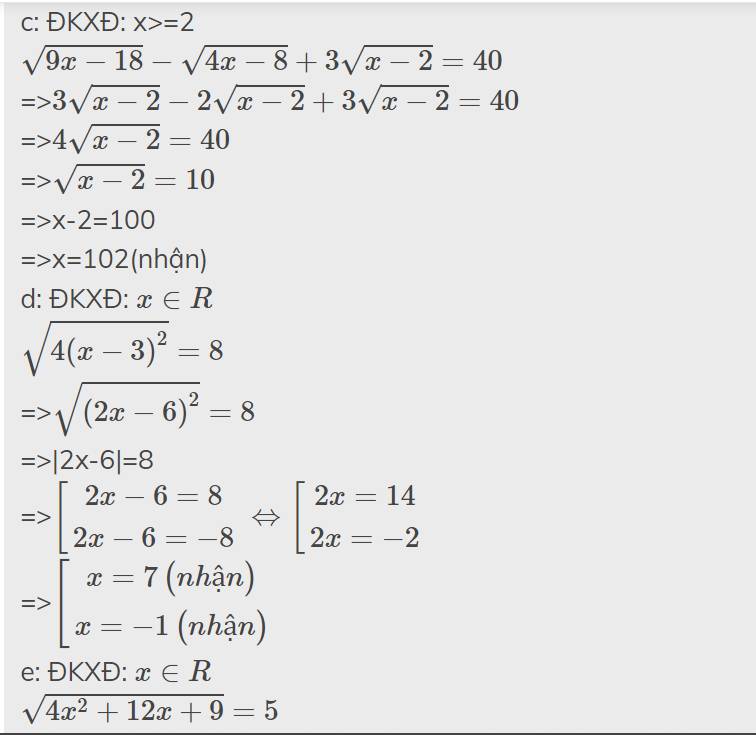
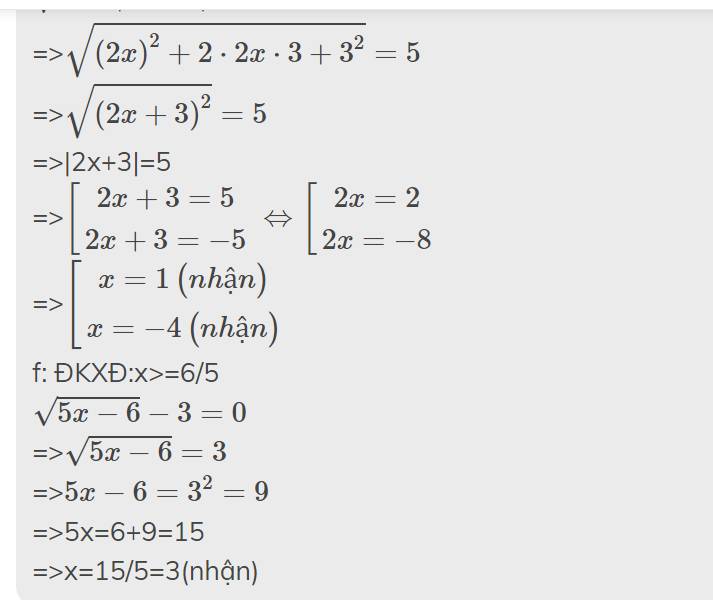
ai giúp mình tìm x với !!
bài này có cho điều kiện hay gì ko bạn