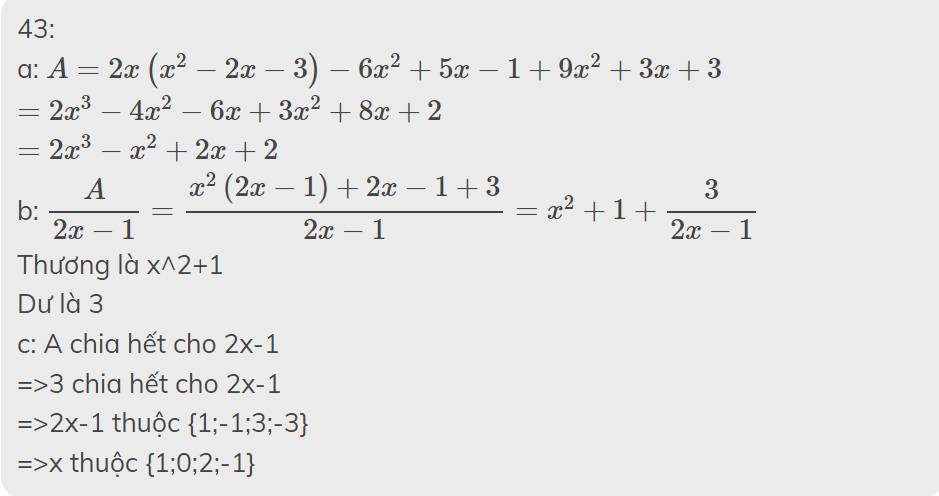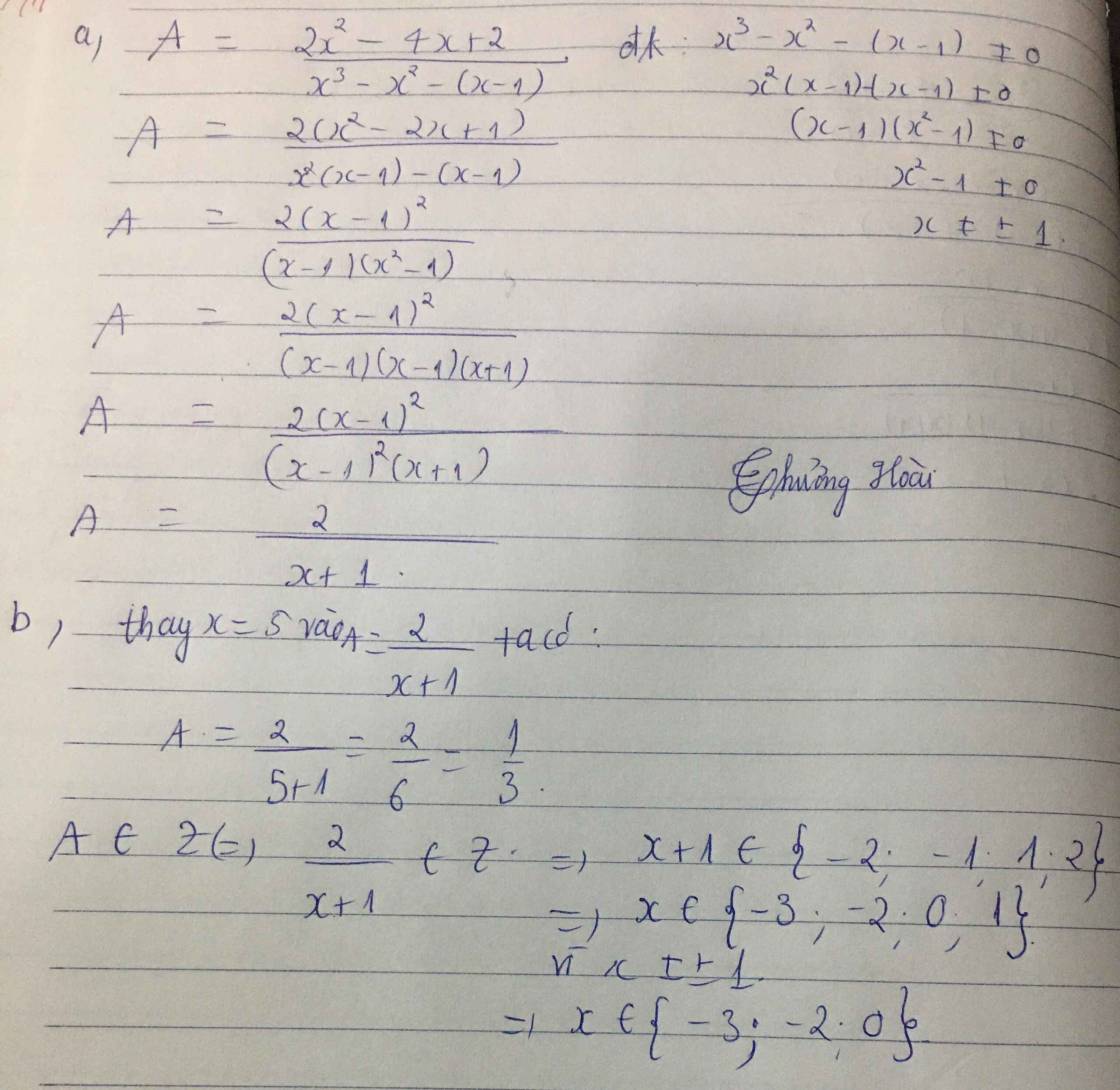cho biểu thức M=2x-3/x+1 tìm x có giá trị nguyên
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


\(\dfrac{2x^3+x^2+2x+2}{2x+1}\left(đk:x\ne-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)=\dfrac{\left(2x+1\right)\left(x^2+1\right)}{2x+1}+\dfrac{1}{2x+1}=x^2+1+\dfrac{1}{2x+1}\)
Do x nguyên nên để biểu thức trên có giá trị nguyên thì :
\(1⋮2x+1\Rightarrow2x+1\inƯ\left(1\right)=\left\{1;-1\right\}\)
\(\Rightarrow x\in\left\{0;-1\right\}\)
\(\dfrac{2x^3+x^2+2x+2}{2x+1}\)
\(=\dfrac{2x^3+x^2+2x+1+1}{2x+1}\)
\(=x^2+1+\dfrac{1}{2x+1}\)
Để đó là số nguyên thì \(1⋮2x+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x+1\in\left\{1;-1\right\}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x\in\left\{0;-2\right\}\)
hay \(x\in\left\{0;-1\right\}\)

a) \(M=\frac{x}{x+1}+\frac{1}{x-1}-\frac{2x}{1-x^2}\left(x\ne\pm1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow M=\frac{x}{x+1}+\frac{1}{x-1}+\frac{2x}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow M=\frac{x^2-x}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}+\frac{x+1}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}+\frac{2x}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow M=\frac{x^2-x+x+1+2x}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow M=\frac{x^2+2x+1}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}=\frac{\left(x+1\right)^2}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}=\frac{x+1}{x-1}\)
Vậy \(M=\frac{x+1}{x-1}\left(x\ne\pm1\right)\)
b) \(M=\frac{x+1}{x-1}\left(x\ne\pm1\right)\)
x-2=1
<=> x=3 (tmđk)
Thay x=3 vào M ta có: \(M=\frac{3+1}{3-1}=\frac{4}{2}=2\)
Vậy M=2 khi x-2=1
c) \(M=\frac{x+1}{x-1}\left(x\ne\pm1\right)\)
M nguyên khi x+1 chia hết cho x-1
=> x-1+2 chia hết cho x-1
x nguyên => x-1 nguyên => x-1 thuộc Ư (2)={-2;-1;1;2}
Ta có bảng
| x-1 | -2 | -1 | 1 | 2 |
| x | -1 | 0 | 2 | 3 |
| ĐCĐK | ktm | tm | tm | tm |
Vậy x={0;2;3}

\(\Leftrightarrow x+1\in\left\{1;-1;3;-3\right\}\)
hay \(x\in\left\{0;-2;2;-4\right\}\)
⇔x+1∈{1;−1; 3 ;−3}⇔x+1∈{1 ;− 1 ; 3 ;−3}
hay x∈{0;−2; 2;−4}

A = \(\dfrac{2x-1}{x+2}\)
a, A là phân số ⇔ \(x\) + 2 # 0 ⇒ \(x\) # -2
b, Để A là một số nguyên thì 2\(x-1\) ⋮ \(x\) + 2
⇒ 2\(x\) + 4 - 5 ⋮ \(x\) + 2
⇒ 2(\(x\) + 2) - 5 ⋮ \(x\) + 2
⇒ 5 ⋮ \(x\) + 2
⇒ \(x\) + 2 \(\in\) { -5; -1; 1; 5}
⇒ \(x\) \(\in\) { -7; -3; -1; 3}
c, A = \(\dfrac{2x-1}{x+2}\)
A = 2 - \(\dfrac{5}{x+2}\)
Với \(x\) \(\in\) Z và \(x\) < -3 ta có
\(x\) + 2 < - 3 + 2 = -1
⇒ \(\dfrac{5}{x+2}\) > \(\dfrac{5}{-1}\) = -5 ⇒ - \(\dfrac{5}{x+2}\)< 5
⇒ 2 - \(\dfrac{5}{x+2}\) < 2 + 5 = 7 ⇒ A < 7 (1)
Với \(x\) > -3; \(x\) # - 2; \(x\in\) Z ⇒ \(x\) ≥ -1 ⇒ \(x\) + 2 ≥ -1 + 2 = 1
\(\dfrac{5}{x+2}\) > 0 ⇒ - \(\dfrac{5}{x+2}\) < 0 ⇒ 2 - \(\dfrac{5}{x+2}\) < 2 (2)
Với \(x=-3\) ⇒ A = 2 - \(\dfrac{5}{-3+2}\) = 7 (3)
Kết hợp (1); (2) và(3) ta có A(max) = 7 ⇔ \(x\) = -3

Answer:
\(M=\left(\frac{x}{x-3}+\frac{3x^2+3}{9-x^2}+\frac{2x}{x+3}\right):\frac{x+1}{3-x}\)
ĐKXĐ:
\(x-3\ne0\)
\(9-x^2\ne0\)
\(x+3\ne0\)
\(x+1\ne0\)
(Ý này trình bày trong vở bạn xếp vào vào cái ngoặc "và" nhé!)
\(\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x\ne\pm3\\x\ne-1\end{cases}}\)
\(=\frac{-x\left(3+x\right)+3x^2+3+2x\left(3-x\right)}{\left(3-x\right)\left(3+x\right)}.\frac{\left(3-x\right)}{x+1}\)
\(=\frac{9x+3}{\left(3+x\right)\left(x+1\right)}\)
\(=\frac{3}{x+1}\)
Có: \(x^2+x-6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+6x-x-6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x+6\right)-\left(x+6\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+6\right)\left(x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x+6=0\\x-1=0\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=-6\\x=1\end{cases}}\) (Thoả mãn)
Trường hợp 1: \(x=1\Leftrightarrow M=\frac{3}{1+1}=\frac{3}{2}\)
Trường hợp 2: \(x=-6\Leftrightarrow M=\frac{3}{-6+1}=\frac{-3}{5}\)
Để cho biểu thức M nguyên thì \(\frac{3}{x+1}\inℤ\)
\(\Rightarrow x+1\inƯ\left(3\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x+1=1\\x+1=3\end{cases}\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=0\\x=2\end{cases}}}\) (Thoả mãn)