Tìm x: \(\left(2x-1\right)^8=\left(2x-1\right)^{10}\)
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


a: \(P=\left(\dfrac{3x+6}{2\left(x^2+4\right)}-\dfrac{2x^2-x-10}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x^2+1\right)}\right):\left(\dfrac{10\left(x^2-1\right)+3\left(x^2+1\right)\left(x-1\right)-6\left(x+1\right)\left(x^2+1\right)}{\left(x^2+1\right)\left(x+1\right)\left(x-1\right)\cdot2}\right)\cdot\dfrac{2}{x-1}\)
\(=\left(\dfrac{\left(3x+6\right)\left(x^3+x^2+x+1\right)-\left(2x^2+8\right)\left(2x^2-x-10\right)}{2\left(x^2+4\right)\left(x+1\right)\left(x^2+1\right)}\right)\cdot\dfrac{\left(x^2+1\right)\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)\cdot2}{-3x^3+x^2-3x-13}\cdot\dfrac{2}{x-1}\)
\(=\dfrac{-x^4+11x^3+13x^2+17x+16}{\left(x^2+4\right)}\cdot\dfrac{2}{-3x^3+x^2-3x-13}\)

(2x+9)/(x+1)(x+8)-(2x+15)/(x+8)(x+7)+(2x+10)/(x+7)(x+3)=4/3
(x+1+x+8)/(x+1)(x+8)-(x+8+x+7)/(x+8)(x+7)+(x+7+x+3)/(x+7)(x+3)=4/3
1/(x+8)+1/(x+1)-1/(x+7)-1/(x+8)+1/(x+7)+1/(x+3)=4/3
1/(x+1)+1/(x+3)=4/3
(x+3+x+1)/(x+3)(x+1)=4/3
(2x+4)/(x+3)(x+1)=4/3
=>(2x+4).3=(x+3)(x+1).4
6(x+2)=4(x+3)(x+1)
3(x+2)=2(x+3)(x+1)
3x+6=2(x^2+4x+3)
3x+6=2x^2+8x+6
2x^2+8x+6-3x-6=0
2x^2+5x=0
x(2x+5)=0
=> x=0 hoac 2x+5=0
=> x=0 hoac x=-5/2

1) (x−1):0,16=−9:(1−x)
\(\Rightarrow\)(x-1):0,16= 9:(-1):(x-1)
\(\Rightarrow\)(x-1):0,16=9:(x-1)
\(\Rightarrow\)(x-1).(x-1)= 9. 0,16
\(\Rightarrow\)(x-1)\(^2\)= 1,44=1,2\(^2\)=(-1,2)\(^2\)
\(\Rightarrow\)x-1=1,2\(\Rightarrow\)x=2,2
hoặc x-1= -1,2\(\Rightarrow\)x= -0,2
Vậy x =2,2 ; x=0,2
...............................

a: ta có: \(\dfrac{\left(x+2\right)^2}{2}+\dfrac{\left(2x+1\right)^2}{4}+\dfrac{\left(2x-1\right)^2}{8}-\left(x+1\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4\left(x^2+4x+4\right)+2\left(4x^2+4x+1\right)+4x^2-4x+1-8\left(x+1\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x^2+16x+16+8x^2+8x+2+4x^2-4x+1-8\left(x^2+2x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow16x^2+20x+19-8x^2-16x-8=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow8x^2+4x+11=0\)
\(\text{Δ}=4^2-4\cdot8\cdot11=-336< 0\)
Vì Δ<0 nên phương trình vô nghiệm
b.
PT \(\Leftrightarrow \frac{x^2+2x+1}{2}-\frac{4x^2-4x+1}{3}+\frac{4x^2+4x+1}{4}-\frac{x^2-10x+25}{6}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow \left(\frac{x^2+2x+1}{2}+\frac{4x^2+4x+1}{4}\right)-\left(\frac{4x^2-4x+1}{3}+\frac{x^2-10x+25}{6}\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow \frac{6x^2+8x+3}{4}-\frac{9x^2-18x+27}{6}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow \frac{3(6x^2+8x+3)-2(9x^2-18x+27)}{12}=0\)
$\Leftrightarrow 5x-\frac{15}{4}=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x=\frac{3}{4}$

\(8,1-\left(x-6\right)=4\left(2-2x\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow1-x+6=8-8x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-x+8x=8-1-6\)
\(\Leftrightarrow7x=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{1}{7}\)
\(9,\left(3x-2\right)\left(x+5\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}3x-2=0\\x+5=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{2}{3}\\x=-5\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(10,\left(x+3\right)\left(x^2+2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+3=0\\x^2+2=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-3\\x=\varnothing\end{matrix}\right.\)
`8)1-(x-5)=4(2-2x)`
`<=>1-x+5=8-6x`
`<=>5x=2<=>x=2/5`
`9)(3x-2)(x+5)=0`
`<=>[(x=2/3),(x=-5):}`
`10)(x+3)(x^2+2)=0`
Mà `x^2+2 > 0 AA x`
`=>x+3=0`
`<=>x=-3`
`11)(5x-1)(x^2-9)=0`
`<=>(5x-1)(x-3)(x+3)=0`
`<=>[(x=1/5),(x=3),(x=-3):}`
`12)x(x-3)+3(x-3)=0`
`<=>(x-3)(x+3)=0`
`<=>[(x=3),(x=-3):}`
`13)x(x-5)-4x+20=0`
`<=>x(x-5)-4(x-5)=0`
`<=>(x-5)(x-4)=0`
`<=>[(x=5),(x=4):}`
`14)x^2+4x-5=0`
`<=>x^2+5x-x-5=0`
`<=>(x+5)(x-1)=0`
`<=>[(x=-5),(x=1):}`

a) \(\left(2x-1\right)^6=\left(2x-1\right)^8\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x-1\right)^6-\left(2x-1\right)^8=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x-1\right)^6\left[1-\left(2x-1\right)^2\right]=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}\left(2x-1\right)^6=0\\2x-1=1\\2x-1=-1\end{cases}}\)
\(\Rightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x=\frac{1}{2}\\x=1\\x=0\end{cases}}\)
phần b chuyển vế, đạt nhân tử chung....... làm tương tự phần a
a, Ta có :
\(\left(2x-1\right)^6=\left(2x-1\right)^8\) \(=\left(2x-1\right)^8-\left(2x-1\right)^6\) \(=\left(2x-1\right)^6\left[\left(2x-1\right)^2-1\right]\) = 0
\(\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}\left(2x-1\right)^2-1=0\\\left(2x-1\right)^6=0\end{cases}}\) \(\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}\left(2x-1\right)^2=0\\2x-1=0\end{cases}\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}\orbr{\begin{cases}2x-1=1\\2x-1=-1\end{cases}}\\2x=1\end{cases}}}\)=> \(2x-1=0\) hoặc \(2x-1=-1\) hoặc \(2x-1=1\)
=> \(x=\frac{1}{2};x=0\) hoặc \(x=1\)
Vậy \(x=\frac{1}{2};x=0\) hoặc x = 1

Bạn xem lại đề nhé.
a) \(A=x^2+5y^2+2xy-4x-8y+2015\)
\(A=x^2-4x+4-2y\left(x-2\right)+y^2+2011+4y^2\)
\(A=\left(x-2\right)^2-2y\left(x-2\right)+y^2+2011+4y^2\)
\(A=\left(x-2-y\right)^2+4y^2+2011\)
Vì \(\left(x-y-2\right)^2\ge0;4y^2\ge0\)
\(\Rightarrow A_{min}=2011\)
Dấu bằng xảy ra : \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-y-2=0\\4y^2=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow}\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\y=0\end{matrix}\right.\)

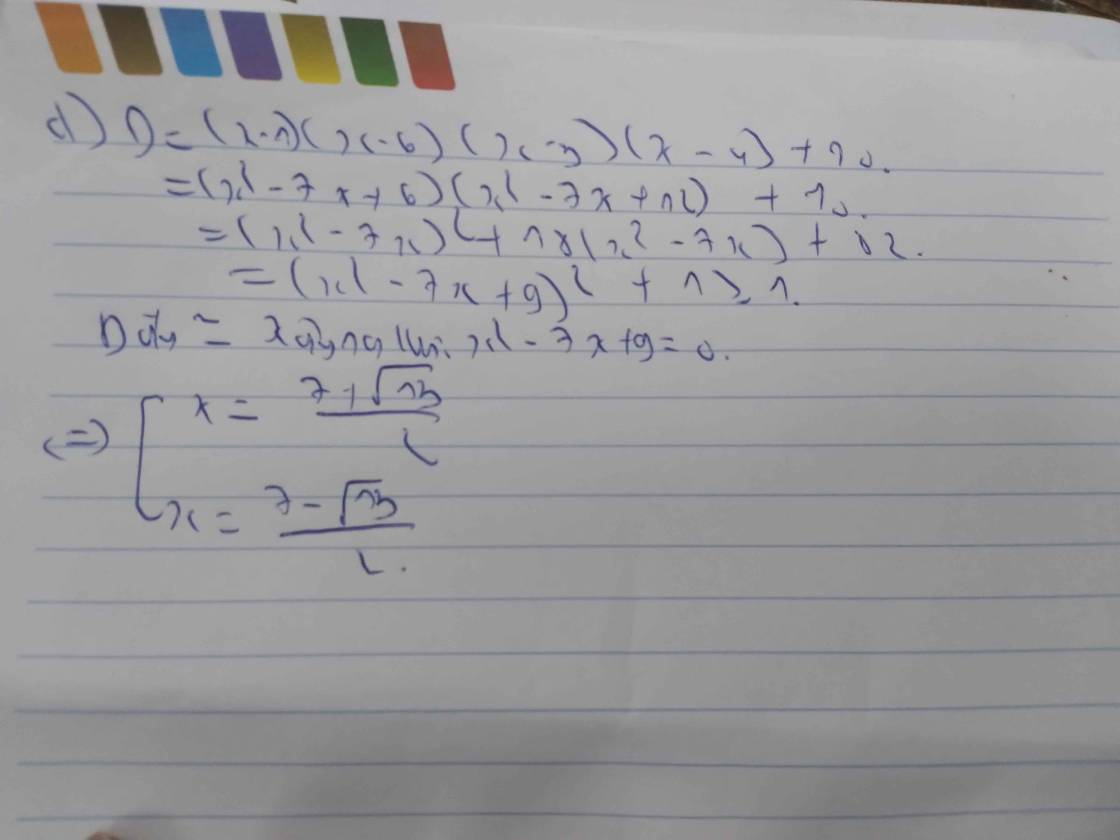
(2x - 1)⁸ = (2x - 1)¹⁰
(2x - 1)¹⁰ - (2x - 1)⁸ = 0
(2x - 1)⁸.[(2x - 1)² - 1] = 0
(2x - 1)⁸ = 0 hoặc (2x - 1)² - 1 = 0
*) (2x - 1)⁸ = 0
2x - 1 = 0
2x = 1
x = 1/2
*) (2x - 1)² - 1 = 0
(2x - 1)² = 1
2x - 1 = 1 hoặc 2x - 1 = -1
**) 2x - 1 = 1
2x = 2
x = 1
**) 2x - 1 = -1
2x = 0
x = 0
Vậy x = 0; x = 1/2; x = 1
(2x - 1)8 = (2x - 1)10
=) (2x - 1)10 : (2x - 1)8 = 1
(2x - 1)2 = 1 =) = 12
=) 2x - 1 = 1
2x = 2
x = 1.