Cho x, y thỏa mãn x+y=3 và x≥4. Tìm giá trị nhỏ nhất của M biết
M=2x^2-y^2-2x-2y+
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Ta sẽ chứng minh \(P_{min}=1\)
TH1: \(xyz=0\)
\(\Rightarrow x^2y^2z^2=0\Rightarrow x^4+y^4+z^4=1\)
\(P=x^2+y^2+z^2\ge\sqrt{x^4+y^4+z^4}=1\)
TH2: \(xyz\ne0\) , từ điều kiện, tồn tại 1 tam giác nhọn ABC sao cho \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x^2=cosA\\y^2=cosB\\z^2=cosC\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(P=cosA+cosB+cosC-\sqrt{2cosA.cosB.cosC}\)
Ta sẽ chứng minh \(cosA+cosB+cosC-\sqrt{2cosA.cosB.cosC}\ge1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4sin\dfrac{A}{2}sin\dfrac{B}{2}sin\dfrac{C}{2}\ge\sqrt{2cosA.cosB.cosC}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow8sin^2\dfrac{A}{2}sin^2\dfrac{B}{2}sin^2\dfrac{C}{2}\ge cosA.cosB.cosC\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{8sin^2\dfrac{A}{2}sin^2\dfrac{B}{2}sin^2\dfrac{C}{2}}{8sin\dfrac{A}{2}sin\dfrac{B}{2}sin\dfrac{C}{2}cos\dfrac{A}{2}cos\dfrac{B}{2}cos\dfrac{C}{2}}\ge cotA.cotB.cotC\)
\(\Leftrightarrow tan\dfrac{A}{2}tan\dfrac{B}{2}tan\dfrac{C}{2}\ge cotA.cotB.cotC\)
\(\Leftrightarrow tanA.tanB.tanC\ge cot\dfrac{A}{2}cot\dfrac{B}{2}cot\dfrac{C}{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow tanA+tanB+tanC\ge cot\dfrac{A}{2}+cot\dfrac{B}{2}+cot\dfrac{C}{2}\)
Ta có:
\(tanA+tanB=\dfrac{sin\left(A+B\right)}{cosA.cosB}=\dfrac{2sinC}{cos\left(A-B\right)-cosC}\ge\dfrac{2sinC}{1-cosC}=\dfrac{2sin\dfrac{C}{2}cos\dfrac{C}{2}}{2sin^2\dfrac{C}{2}}=cot\dfrac{C}{2}\)
Tương tự: \(tanA+tanC\ge cot\dfrac{B}{2}\) ; \(tanB+tanC\ge cot\dfrac{A}{2}\)
Cộng vế với vế ta có đpcm
Vậy \(P_{min}=1\) khi \(\left(x^2;y^2;z^2\right)=\left(1;0;0\right)\) và các hoán vị hoặc \(\left(x^2;y^2;z^2\right)=\left(\dfrac{1}{2};\dfrac{1}{2};\dfrac{1}{2}\right)\)

vì x+y=4 nền (x+y)^2=4^2 =x^2+ 2xy+y^2=16 ma xy=5 nên 2xy=10 ta có x^2+y^2+10=16 ; x^2+y^2= 16-10 x^2+y^2=6 kết quả mik là z đó nhưng k biết có đúng k bn ak

Đáp án C
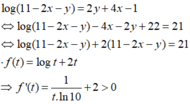
Suy ra f(t) đồng biến trên TXĐ và pt f(t) = 21 chỉ có 1 nghiệm duy nhất
Ta thấy t = 10 là 1 nghiệm của pt nên t = 10 là nghiệm duy nhất của pt
⇒ 11 − 2 x − y = 10 ⇒ y = 1 − 2 x ⇒ P = 16 x 2 ( 1 − 2 x ) − 2 x ( 3 − 6 x + 2 ) − 1 + 2 x + 5 = − 32 x 3 + 28 x 2 − 8 x + 4 P ' = − 96 x 2 + 56 x − 8 P ' = 0 ⇔ x = 1 4 x = 1 3 P ( 0 ) = 4 , P ( 1 3 ) = 88 27 , P ( 1 4 ) = 13 4 , P ( 1 2 ) = 3 ⇒ m = 13 4 , M = 4 ⇒ M + 4 m = 17

\(P=\left(x+y\right)^3-3xy\left(x+y\right)+2x^2y^2\)
\(=2x^2y^2-3xy+1=2t^2-3t+\frac{5}{8}+\frac{3}{8}\) (đặt t = xy \(\Rightarrow t\le\frac{\left(x+y\right)^2}{4}=\frac{1}{4}\))
\(=\frac{1}{8}\left(4t-1\right)\left(4t-5\right)+\frac{3}{8}\ge\frac{3}{8}\)
Do đó \(P\ge\frac{3}{8}\)
Đẳng thức xảy ra khi \(\hept{\begin{cases}x+y=1\\t=\frac{1}{4}\\x=y\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow x=y=\frac{1}{2}\)
True?

https://diendantoanhoc.net/topic/182493-%C4%91%E1%BB%81-thi-tuy%E1%BB%83n-sinh-v%C3%A0o-l%E1%BB%9Bp-10-%C4%91hsp-h%C3%A0-n%E1%BB%99i-n%C4%83m-2018-v%C3%B2ng-2/
bài này năm trrong đề thi tuyển sinh vào lớp 10 ĐHSP Hà Nội Năm 2018 (vòng 2) bn có thể tìm đáp án trên mạng để tham khảo

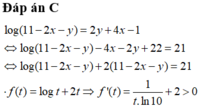
Suy ra f(t) đồng biến trên TXĐ và pt f ( t ) = 21 chỉ có 1 nghiệm duy nhất
Ta thấy t = 10 là 1 nghiệm của pt nên t = 10 là nghiệm duy nhất của pt
⇒ 11 - 2 x - y = 10 ⇒ y = 1 - 2 x ⇒ P = 16 x 2 1 - 2 x - 2 x 3 - 6 x + 2 - 1 + 2 x + 5 = - 32 x 3 + 28 x 2 - 8 x + 4 P ' = - 96 x 2 + 56 x - 8 P ' = 0 ⇔ [ x = 1 4 x = 1 3 P 0 = 4 , P 1 3 = 88 27 , P 1 4 = 13 4 , P 1 2 = 3 ⇒ m = 13 4 , M = 4 ⇒ M + 4 m = 17

a) \(6xy+4x-9y-7=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x.\left(3y+2\right)-9y-6-1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x.\left(3y+x\right)-3.\left(3y+2\right)=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x-3\right).\left(3y+2\right)=1\)
Mà \(x,y\in Z\Rightarrow2x-3;3y+2\in Z\)
Tự làm típ
\(A=x^3+y^3+xy\)
\(A=\left(x+y\right)\left(x^2-xy+y^2\right)+xy\)
\(A=x^2-xy+y^2+xy\)( vì \(x+y=1\))
\(A=x^2+y^2\)
Áp dụng bất đẳng thức Bunhiakovxky ta có :
\(\left(1^2+1^2\right)\left(x^2+y^2\right)\ge\left(x\cdot1+y\cdot1\right)^2=\left(x+y\right)^2=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2\left(x^2+y^2\right)\ge1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+y^2\ge\frac{1}{2}\)
Hay \(x^3+y^3+xy\ge\frac{1}{2}\)
Dấu "=" xảy ra \(\Leftrightarrow x=y=\frac{1}{2}\)
bạn có thể viết lại đề ko?
cứ theo đề của bạn nhé:
\(x+y=3\Leftrightarrow x=3-y\)
\(M=2x^2-y^2-2x-2y\)
\(=2x^2-\left(3-x\right)^2-2.\left(x+y\right)\)
\(=2x^2-x^2+6x-9-2.3\)
\(=\left(x+3\right)^2-24\)
mà \(x\ge4\Rightarrow\left(x+3\right)^2\ge49\)
\(\Rightarrow M\ge49-24=25\)
\(DBXR\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=4\\y=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)