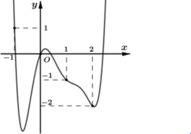
Cho hàm số và hàm số . Tìm m để phương trình có 4 nghiệm phân biệt.
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

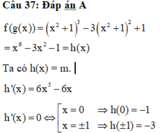

a: \(F\left(3\right)=3\left(3-2\right)=3\cdot1=3\)
\(\left[F\left(\dfrac{2}{3}\right)\right]^2=\left[\dfrac{2}{3}\cdot\left(\dfrac{2}{3}-2\right)\right]^2\)
\(=\left[\dfrac{2}{3}\cdot\dfrac{-4}{3}\right]^2=\left(-\dfrac{8}{9}\right)^2=\dfrac{64}{81}\)
\(G\left(-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)=-\left(-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)+6=6+\dfrac{1}{2}=\dfrac{13}{2}\)
b: F(x)=0
=>x(x-2)=0
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x-2=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
c: F(a)=G(a)
=>\(a\left(a-2\right)=-a+6\)
=>\(a^2-2a+a-6=0\)
=>\(a^2-a-6=0\)
=>(a-3)(a+2)=0
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}a-3=0\\a+2=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}a=3\\a=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)

2: ĐKXĐ: x<>1
\(f'\left(x\right)=\dfrac{\left(x^2-3x+3\right)'\left(x-1\right)-\left(x^2-3x+3\right)\left(x-1\right)'}{\left(x-1\right)^2}\)
\(=\dfrac{\left(2x-3\right)\left(x-1\right)-\left(x^2-3x+3\right)}{\left(x-1\right)^2}\)
\(=\dfrac{2x^2-5x+3-x^2+3x-3}{\left(x-1\right)^2}=\dfrac{x^2-2x}{\left(x-1\right)^2}\)
f'(x)=0
=>x^2-2x=0
=>x(x-2)=0
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
1:
\(f\left(x\right)=\dfrac{1}{3}x^3-2\sqrt{2}\cdot x^2+8x-1\)
=>\(f'\left(x\right)=\dfrac{1}{3}\cdot3x^2-2\sqrt{2}\cdot2x+8=x^2-4\sqrt{2}\cdot x+8=\left(x-2\sqrt{2}\right)^2\)
f'(x)=0
=>\(\left(x-2\sqrt{2}\right)^2=0\)
=>\(x-2\sqrt{2}=0\)
=>\(x=2\sqrt{2}\)

Đáp án B
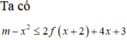
![]()
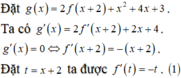
(1) là phương trình hoành độ giao điểm của đồ thị f'(t) và đường thẳng d : y = -t (hình vẽ)
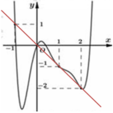
Dựa vào đồ thị của f'(t) và đường thẳng y =-t ta có




Chọn B.
Ta có: f(x + 1) = log2(x + 1) và g(x + 2) = log2(2 - x)
![]()
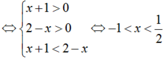

Đáp án C
Với f x > 0 , ∀ x ∈ ℝ . Xét biểu thức f ' x f x = 2 - 2 x *
Lấy nguyên hàm 2 vế (*), ta được ∫ d f x f x = ∫ 2 - 2 x d x
⇔ ∫ d f x f x = - x 2 + 2 x + C ⇔ ln f x = - x 2 + 2 x + C
Mà f(0) =1 suy ra C = lnf(0) = ln1 = 0. Do đó f x = e - x 2 + 2 x
Xét hàm số f x = e - x 2 + 2 x trên - ∞ ; + ∞ , có f ' x = - 2 x + 2 = 0 ⇔ x = 1
Tính giá trị f 1 = e ; lim x → - ∞ f x = 0 ; lim x → - ∞ f x = 0
Suy ra để phương trình f(x) = m có hai nghiệm thực phân biệt ⇔ 0 < m < e .

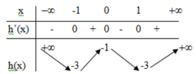
\(g'\left(x\right)=0\Rightarrow x=0\)
Ta thấy \(g\left(x\right)\) đồng biến trên \(\left(0;+\infty\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow g\left(f\left(x\right)\right)\) đồng biến khi \(f\left(x\right)\ge0\)
\(\Rightarrow g\left(f\left(x\right)\right)\) đồng biến trên \(\left(3;+\infty\right)\) khi \(f\left(x\right)\ge0\) ; \(\forall x>3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-4x\ge-m\) ; \(\forall x>3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-m\le\min\limits_{x>3}\left(x^2-4x\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow-m\le-3\Rightarrow m\ge3\)