Phương trình 2 x - 2 + m - 3 x 3 + x 3 - 6 x + 9 x + m = 2 x + 1 + 1 có 3 nghiệm phân biệt khi và chỉ khi m ∈ ( a ; b ) . Đặt T = b 2 - a 2 thì
A. T=36
B. T=48
C. T=64
D. T=72
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.



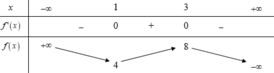


a, ĐK: \(x\le-1,x\ge3\)
\(pt\Leftrightarrow2\left(x^2-2x-3\right)+\sqrt{x^2-2x-3}-3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2\sqrt{x^2-2x-3}+3\right).\left(\sqrt{x^2-2x-3}-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{x^2-2x-3}=-\dfrac{3}{2}\left(l\right)\\\sqrt{x^2-2x-3}=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-2x-3=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-2x-4=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=1\pm\sqrt{5}\left(tm\right)\)
b, ĐK: \(-2\le x\le2\)
Đặt \(\sqrt{2+x}-2\sqrt{2-x}=t\Rightarrow t^2=10-3x-4\sqrt{4-x^2}\)
Khi đó phương trình tương đương:
\(3t-t^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}t=0\\t=3\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{2+x}-2\sqrt{2-x}=0\\\sqrt{2+x}-2\sqrt{2-x}=3\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2+x=8-4x\\2+x=17-4x+12\sqrt{2-x}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{6}{5}\left(tm\right)\\5x-15=12\sqrt{2-x}\left(1\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vì \(-2\le x\le2\Rightarrow5x-15< 0\Rightarrow\left(1\right)\) vô nghiệm
Vậy phương trình đã cho có nghiệm \(x=\dfrac{6}{5}\)

Bài 9:
Không, vì $x+2=0$ có nghiệm duy nhất $x=-2$ còn $\frac{x}{x+2}=0$ ngay từ đầu đkxđ đã là $x\neq -2$ (cả 2 pt không có cùng tập nghiệm)
Bài 8:
a. Khi $m=2$ thì pt trở thành:
$(2^2-9)x-3=2$
$\Leftrightarrow -5x-3=2$
$\Leftrightarrow -5x=5$
$\Leftrightarrow x=-1$
b.
Khi $m=3$ thì pt trở thành:
$(3^2-9)x-3=3$
$\Leftrightarrow 0x-3=3$
$\Leftrightarrow 0=6$ (vô lý)
c. Khi $m=3$ thì pt trở thành:
$[(-3)^2-9]x-3=-3$
$\Leftrightarrow 0x-3=-3$ (luôn đúng với mọi $x\in\mathbb{R}$)
Vậy pt vô số nghiệm thực.

\(a,\left(x-6\right)\left(2x-5\right)\left(3x+9\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-6=0\Leftrightarrow x=6\\2x-5=0\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{5}{2}\\3x+9=0\Leftrightarrow x=-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(b,2x\left(x-3\right)+5\left(x-3\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left(2x+5\right)\left(x-3\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-3=0\Leftrightarrow x=3\\2x+5=0\Leftrightarrow x=-\dfrac{5}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(c,x^2-4-\left(x-2\right)\left(3-2x\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)-\left(x-2\right)\left(3-2x\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2-3+2x\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\x=\dfrac{1}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(x=-7\left(2m-5\right)x-2m^2+8\Leftrightarrow x+7\left(2m-5\right)=8-2m^2\Leftrightarrow x\left(14m-34\right)=8-2m^2\)
\(ycđb\Leftrightarrow14m-34\ne0\Leftrightarrow m\ne\dfrac{34}{14}\)\(\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{8-2m^2}{14m-34}\)
\(3.17\Leftrightarrow4x^2-4x+1-2x-1=0\Leftrightarrow4x^2-6x=0\Leftrightarrow x\left(4x-6\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=\dfrac{3}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
3.15:
a, \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-6=0\\2x-5=0\\3x+9=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=6\\x=\dfrac{5}{2}\\x=-\dfrac{9}{3}=-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
b, \(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)\left(2x+5\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-3=0\\2x+5=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=3\\x=-\dfrac{5}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
c, \(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)-\left(x-2\right)\left(3-2x\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2-3+2x\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-2=0\\3x-1=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\x=\dfrac{1}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
3.16
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2m-5\right).-7-2m^2+8=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-14m+35-2m^2+8=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-14m-2m^2+43=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-2\left(7m+m^2\right)=-43\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m\left(7-m\right)=\dfrac{43}{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{m\left(7-m\right)}{1}-\dfrac{43}{2}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{14m-2m^2}{2}-\dfrac{43}{2}=0\)
pt vô nghiệm

câu 1
a)C1:denta
x^2 +5x+4 =0
<=>52-4(1.4)=9
\(\Leftrightarrow x_{1,2}=\frac{-b\pm\sqrt{\Delta}}{2a}=\frac{-5\pm\sqrt{9}}{2}\)
=>x=-4 hoặc -1
C2:vi ét
tổng các nghiệm x1+x2=\(-\frac{b}{a}=-5\)
tích các nghiệm x1*x2=\(\frac{c}{a}=4\)
=>x=-4 hoặc -1

a: Khi m=1 thì pt sẽ là: x+x-3=6x-6
=>6x-6=2x-3
=>4x=3
=>x=3/4
b: m^2x+m(x-3)=6(x-1)
=>x(m^2+m-6)=-6+3m=3m-6
=>x(m+3)(m-2)=3(m-2)
Để (1) có nghiệm duy nhất thì (m+3)(m-2)<>0
=>m<>-3 và m<>2
=>x=3/(m+3)
\(A=\dfrac{\left(\dfrac{3}{m+3}\right)^2+\dfrac{6}{m+3}+3}{\left(\dfrac{3}{m+3}\right)^2+2}\)
\(=\dfrac{9+6m+18+3m^2+18m+27}{\left(m+3\right)^2}:\dfrac{9+2m^2+12m+18}{\left(m+3\right)^2}\)
\(=\dfrac{3m^2+24m+54}{2m^2+12m+27}>=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
Dấu = xảy ra khi 6m^2+48m+108=2m^2+12m+27
=>4m^2+36m+81=0
=>m=-9/2