Cho hàm số f(x)= l n 2 ( x 2 - 2 x + 4 ) . Tìm các giá trị của x để f'(x)>0
A. x ≠ 0
B. x> 0
C. x> 1
D. ∀ x
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

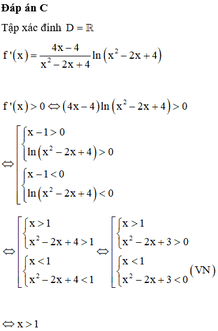

a: f(-3)=10
f(0)=-8
f(1)=-6
f(2)=0
b: f(x)=0
=>(x-2)(x+2)=0
=>x=2 hoặc x=-2

Câu 1:
a)
| \(y=f\left(x\right)=2x^2\) | -5 | -3 | 0 | 3 | 5 |
| f(x) | 50 | 18 | 0 | 18 | 50 |
b) Ta có: f(x)=8
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2=8\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2=4\)
hay \(x\in\left\{2;-2\right\}\)
Vậy: Để f(x)=8 thì \(x\in\left\{2;-2\right\}\)
Ta có: \(f\left(x\right)=6-4\sqrt{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2=6-4\sqrt{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2=3-2\sqrt{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\sqrt{3-2\sqrt{2}}\)
hay \(x=\sqrt{2}-1\)
Vậy: Để \(f\left(x\right)=6-4\sqrt{2}\) thì \(x=\sqrt{2}-1\)

Để hàm số có đạo hàm tại x=0 phải thỏa mãn 2 điều kiện, đó là hàm số liên tục tại x=0 và có đạo hàm bên trái bằng đạo hàm bên phải
Để hàm số liên tục tại x=0 \(\Leftrightarrow\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow0^+}=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow0^-}=f\left(0\right)\Leftrightarrow2=2\left(tm\right)\)
\(f'\left(0^+\right)=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow0^+}\dfrac{f\left(x\right)-f\left(0\right)}{x-0}=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow0^+}\dfrac{mx^2+2x+2-2}{x}=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow0^+}\dfrac{x\left(mx+2\right)}{x}=2\)
\(f'\left(0^-\right)=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow0^-}\dfrac{f\left(x\right)-f\left(0\right)}{x-0}=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow0^-}\dfrac{nx+2-2}{x}=n\)
\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m\in R\\n=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(f\left(0^+\right)=f\left(0^-\right)\Leftrightarrow n=2\)

a) Cho hàm số y = f(x) = -2x + 3.
Ta có: f(-2)= -2.(-2)+3
= 4+3=7
Ta có: f(0)= -2.0+3
= 0+3=3
Ta có: f(\(\dfrac{-1}{2}\))= -2.(-\(\dfrac{1}{2}\))+3
=\(\dfrac{-2.\left(-1\right)}{2}\)+3
=\(\dfrac{2}{2}\)+3
= 1+3= 4
Vậy f(-2)=7;f(0)=3;f( \(\dfrac{-1}{2}\))=4
b) Cho hàm số y = f(x) = -2x + 3
mà f(x)=5
Suy ra: f(x) = -2x + 3=5
hay -2x + 3=5
-2x=5-3
-2x=2
x=2:(-2)
x= -1
Cho hàm số y = f(x) = -2x + 3
mà f(x)=1
Suy ra: f(x) = -2x + 3=1
hay -2x + 3=1
-2x=1-3
-2x= -2
x= -2:(-2)
x=1
Vậy f(x)=5 thì x= -1 và f(x) = 1 thì x=1.
Lời giải:
a.
$f(-2)=(-2)(-2)+3=7$
$f(0)=(-2).0+3=3$
$f(\frac{-1}{2})=(-2).\frac{-1}{2}+3=4$
b.
$f(x)=-2x+3=5$
$\Rightarrow -2x=2$
$\Rightarrow x=-1$
$f(x)=-2x+3=1$
$\Rightarrow -2x=1-3=-2$
$\Rightarrow x=1$