Giải các phương trình sau bằng cách đưa về phương trình tích 3 +6 -4x =0
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Tham khảo bài này :
(3x+1)(7x+3)=(5x-7)(3x+1)
<=> (3x+1)(7x+3)-(5x-7)(3x+1)=0
<=> (3x+1)(7x+3-5x+7)=0
<=> (3x+1)(2x+10)=0
<=> 2(3x+1)(x+5)=0
=> 3x+1=0 hoặc x+5=0
=> x= -1/3 hoặc x=-5
Vậy x = -1/3 hoặc x = -5
\(a,x^2+10x+25-4x\left(x+5\right)=0.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+5\right)^2-4x\left(x+5\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+5\right)\left(5-3x\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x+5=0\\5-3x=0\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=-5\\x=\frac{5}{3}\end{cases}}}\)
\(b,\left(4x-5\right)^2-2\left(16x^2-25\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(4x-5\right)^2-2\left(4x+5\right)\left(4x-5\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-\left(4x-5\right)\left(4x+15\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}4x-5=0\\4x+15=0\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=\frac{5}{4}\\x=-\frac{15}{4}\end{cases}}}\)

(x - 2 ) + 3( x 2 – 2) = 0 ⇔ (x - 2 )+ 3(x + 2 )(x - 2 ) = 0
⇔ (x - 2 )[1 + 3(x + 2 )] = 0 ⇔ (x - 2 )(1 + 3x + 3 2 ) = 0
⇔ x - 2 = 0 hoặc 1 + 3x + 3 2 = 0
x - 2 = 0 ⇔ x = 2
1 + 3x + 3
2
= 0 ⇔ x = 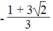
Vậy phương trình có nghiệm x =
2
hoặc x = 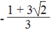

Ta có: x 2 + x + 1 2 = 4 x - 1 2
⇔ [( x 2 +x +1) + (4x -1 )] [( x 2 +x +1) - (4x -1 )]=0
⇔ ( x 2 +5x)( x 2 -3x +2) =0 ⇔ x(x+5) ( x 2 -3x +2) =0
⇔ x =0 hoặc x+5 =0 hoặc x2 -3x +2 =0
x+5 =0 ⇔ x=-5
x 2 -3x +2 =0
∆ = - 3 2 -4.2.1 = 9 -8 =1 > 0
∆ = 1 =1
![]()
Vậy phương trình đã cho có 4 nghiệm:
x 1 =0 ; x 2 =-5 ; x 3 =2 ; x 4 =1

a) ( 3.x + 1 ) . ( 7.x + 3 ) = (5.x-7 ) . ( 3.x + 1 )
<=> ( 3.x + 1 ) . ( 7.x + 3 ) - ( 5.x - 7) . ( 3.x + 1 ) = 0
<=> ( 3.x + 1 ) . ( 7.x + 3 - 5.x + 7 ) = 0
<=> ( 3.x + 1 ) . ( 2.x + 10 ) = 0
<=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}3.x+1=0\\2.x+10=0\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=\frac{-1}{3}\\x=-5\end{cases}}}\)
Vậy x = { \(\frac{-1}{3};-5\)}
b) x2 + 10.x + 25 - 4.x . ( x + 5 ) = 0
<=> ( x + 5 )2 -4.x . (x + 5 ) = 0
<=> ( x+ 5 ) . ( x + 5 - 4.x ) = 0
<=> ( x + 5 ) . ( 5 - 3.x ) = 0
<=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x+5=0\\5-3.x\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=-5\\x=\frac{5}{3}\end{cases}}}\)
Vậy x = \(\left\{\frac{5}{3};-5\right\}\)
c) (4.x - 5 )2 - 2. ( 16.x2 -25 ) = 0
<=> ( 4.x-5)2 -2 .( 4.x-5) .( 4.x + 5 ) = 0
<=> ( 4.x -5 )2 - ( 8.x+ 10 ) . ( 4.x -5 ) = 0
<=> ( 4.x -5 ) . ( 4.x-5 - 8.x - 10 ) = 0
<=> ( 4.x - 5 ) . ( -4.x - 15 ) = 0
<=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}4.x-5=0\\-4.x-15=0\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=\frac{5}{4}\\x=\frac{-15}{4}\end{cases}}}\)
Vậy x = \(\left\{\frac{5}{4};\frac{-15}{4}\right\}\)
d) ( 4.x + 3 )2 = 4. ( x2 - 2.x + 1 )
<=> 16.x2 + 24.x + 9 - 4.x2 + 8.x - 4 = 0
<=> 12.x2 + 32.x + 5 =0
<=> 12. ( x +\(\frac{1}{8}\) ) . ( x + \(\frac{5}{2}\)) = 0
<=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x+\frac{1}{6}=0\\x+\frac{5}{2}=0\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=\frac{-1}{6}\\x=\frac{-5}{2}\end{cases}}}\)
Vậy x = \(\left\{\frac{-1}{6};\frac{-5}{2}\right\}\)
e) x2 -11.x + 28 = 0
<=> x2 -4.x - 7.x + 28 = 0
<=> ( x - 7 ) . ( x - 4 ) = 0
<=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x-7=0\\x-4=0\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=7\\x=4\end{cases}}}\)
Vậy x = { 4 ; 7 }
f ) 3.x.3 - 3.x2 - 6.x = 0
<=> 3.x. ( x2 -x - 2 ) = 0
<=> 3.x. ( x - 2 ) . ( x + 1 ) = 0
<=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x-2=0\\x+1=0\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=2\\x=-1\end{cases}}}\)
\([x=0\) \([x=0\)
( Lưu ý :Lưu ý này không cần ghi vào vở : Chị nối 2 ý đó làm 1 nha cj ! )
Vậy x = { 2 ; -1 ; 0 }

Ta có: x 3 – 5 x 2 –x +5 = 0 ⇔ x 2 ( x -5) – ( x -5) =0
⇔ (x -5)(x2 -1) =0 ⇔ (x -5)(x -1)(x +1) =0
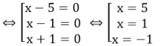
Vậy phương trình đã cho có 3 nghiệm :x1 = 5;x2 =1;x3=-1

`a,(x+3)(x^2+2021)=0`
`x^2+2021>=2021>0`
`=>x+3=0`
`=>x=-3`
`2,x(x-3)+3(x-3)=0`
`=>(x-3)(x+3)=0`
`=>x=+-3`
`b,x^2-9+(x+3)(3-2x)=0`
`=>(x-3)(x+3)+(x+3)(3-2x)=0`
`=>(x+3)(-x)=0`
`=>` $\left[ \begin{array}{l}x=0\\x=-3\end{array} \right.$
`d,3x^2+3x=0`
`=>3x(x+1)=0`
`=>` $\left[ \begin{array}{l}x=0\\x=-1\end{array} \right.$
`e,x^2-4x+4=4`
`=>x^2-4x=0`
`=>x(x-4)=0`
`=>` $\left[ \begin{array}{l}x=0\\x=4\end{array} \right.$
1) a) \(\left(x+3\right).\left(x^2+2021\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+3=0\\x^2+2021=0\end{matrix}\right.\\\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-3\left(nhận\right)\\x^2=-2021\left(loại\right)\end{matrix}\right. \)
=> S={-3}

2 x 2 + 5x + 3 = 0 ⇔ 2 x 2 + 2x + 3x + 3 = 0
⇔ 2x(x + 1) + 3(x + 1) = 0 ⇔ (2x + 3)(x + 1) = 0
⇔ 2x + 3 = 0 hoặc x + 1 = 0
2x + 3 = 0 ⇔ x = -1,5
x + 1 = 0 ⇔ x = -1
Vậy phương trình có nghiệm x = -1,5 hoặc x = -1

Ta có: 3 x 3 +6 x 2 -4x =0 ⇔ x(3 x 2 +6x -4) =0
⇔ x = 0 hoặc 3 x 2 +6x -4 =0
Giải phương trình 3 x 2 +6x -4 =0
∆ ’ = 3 2 - 3(-4) = 9 + 12 = 21 > 0
∆ ' = 21
Vậy phương trình đã cho có 3 nghiệm