Cho đường thẳng d 1 : y = 4 − x 3 v à d 2 : y = 8 – 2 x . Gọi A, B lần lượt là giao điểm của d 1 v ớ i d 2 v à d 1 với trục tung. Tổng tung độ giao điểm của A và B là:
A. 4 3
B. 2 3
C. 9
D. 8
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

a/ Bạn tự vẽ
b/ Phương trình hoành độ A:
\(-x+1=x+1\Rightarrow x=0\Rightarrow y=1\Rightarrow A\left(0;1\right)\)
Phương trình tọa độ B:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=-1\\y=-x+1\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\y=-1\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow B\left(2;-1\right)\)
Phương trình tọa độ C:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=-1\\y=x+1\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=-2\\y=-1\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow C\left(-2;-1\right)\)

1: Để (d)//(d') thì \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m-3=1\\2\ne-5\left(đúng\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>m-3=1
=>m=4
Thay m=4 vào (d), ta được:
\(y=\left(4-3\right)x+2=x+2\)
Vẽ đồ thị:
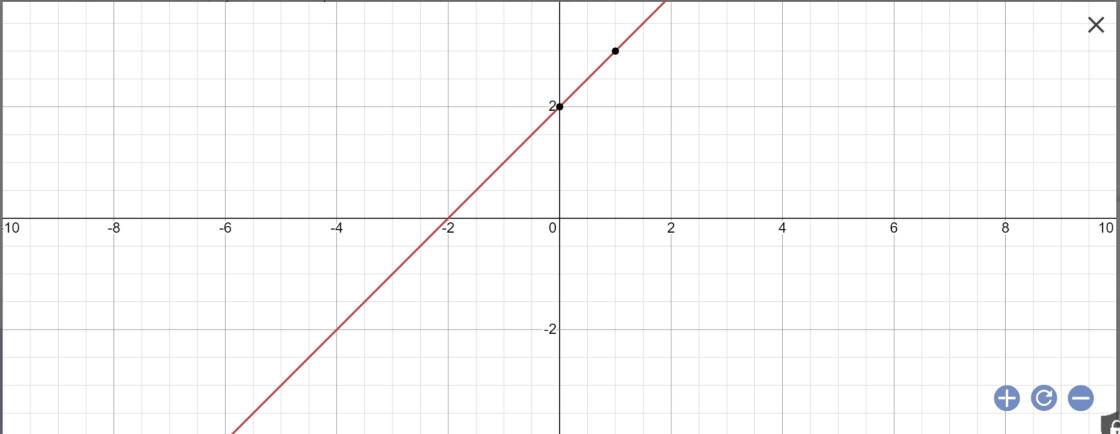
2: Tọa độ A là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\\left(m-3\right)x+2=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\x\left(m-3\right)=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=-\dfrac{2}{m-3}\\y=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: \(A\left(-\dfrac{2}{m-3};0\right)\)
Tọa độ B là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\y=\left(m-3\right)\cdot x+2=0\left(m-3\right)+2=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
vậy: B(0;2)
\(OA=\sqrt{\left(-\dfrac{2}{m-3}-0\right)^2+\left(0-0\right)^2}\)
\(=\sqrt{\left(-\dfrac{2}{m-3}\right)^2+0^2}=\dfrac{2}{\left|m-3\right|}\)
\(OB=\sqrt{\left(0-0\right)^2+\left(2-0\right)^2}=2\)
Vì Ox\(\perp\)Oy
nên OA\(\perp\)OB
=>ΔOAB vuông tại O
=>\(S_{OBA}=\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot OA\cdot OB=\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot2\cdot\dfrac{2}{\left|m-3\right|}=\dfrac{2}{\left|m-3\right|}\)
Để \(S_{OAB}=2\) thì \(\dfrac{2}{\left|m-3\right|}=2\)
=>|m-3|=1
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}m-3=1\\m-3=-1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}m=4\\m=2\end{matrix}\right.\)

b: Tọa độ điểm A là:
-x+1=x+1 và y=x+1
=>x=0 và y=1
Tọa độ điểm B là:
-x+1=-1 và y=-1
=>-x=-2 và y=-1
=>B(2;-1)
Tọa độ điểm C là:
x+1=-1 và y=-1
=>x=-2 và y=-1
=>C(-2;-1)
A(0;1); B(2;-1); C(-2;-1)
\(AB=\sqrt{\left(2-0\right)^2+\left(-1-1\right)^2}=2\sqrt{2}\)
\(AC=\sqrt{\left(-2-0\right)^2+\left(-1-1\right)^2}=2\sqrt{2}\)
=>AB=AC
=>ΔABC cân tại A

a:
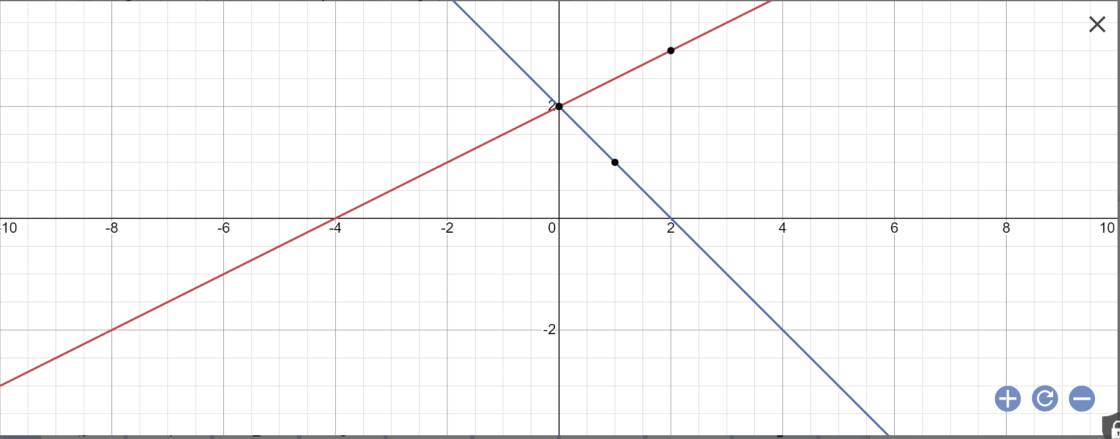
b: Gọi \(\alpha\) là góc tạo bởi (d1) với trục Ox
(d1): \(y=\dfrac{1}{2}x+2\)
=>\(a=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
=>\(tan\alpha=a=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
=>\(\alpha\simeq26^034'\)
c: Tọa độ A là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\\dfrac{1}{2}x+2=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{1}{2}x=-2\\y=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=-4\\y=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
Tọa độ B là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\-x+2=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\-x=-2\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\y=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
Tọa độ C là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{1}{2}x+2=-x+2\\y=-x+2\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{3}{2}x=0\\y=-x+2\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\y=-0+2=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: A(-4;0); B(2;0); C(0;2)
\(AB=\sqrt{\left(2+4\right)^2+\left(0-0\right)^2}=6\)
\(AC=\sqrt{\left(0+4\right)^2+\left(2-0\right)^2}=\sqrt{4^2+2^2}=2\sqrt{5}\)
\(BC=\sqrt{\left(0-2\right)^2+\left(2-0\right)^2}=\sqrt{2^2+2^2}=2\sqrt{2}\)
Chu vi tam giác ABC là:
\(C_{ABC}=AB+AC+BC=6+2\sqrt{5}+2\sqrt{2}\)(cm)
Xét ΔABC có \(cosBAC=\dfrac{AB^2+AC^2-BC^2}{2\cdot AB\cdot AC}=\dfrac{36+20-8}{2\cdot6\cdot2\sqrt{5}}=\dfrac{48}{24\sqrt{5}}=\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{5}}\)
=>\(sinBAC=\sqrt{1-cos^2BAC}=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{5}}\)
Diện tích tam giác ABC là:
\(S_{ABC}=\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot AB\cdot AC\cdot sinBAC\)
\(=\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot6\cdot2\sqrt{5}\cdot\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{5}}=6\)

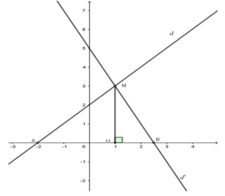
Xét phương trình hoành độ giao điểm của d 1 v à d 2
x + 2 = − 2 x + 5 ⇔ x = 1 ⇒ y = 3 ⇒ d 1 ∩ d 2 t ạ i M ( 1 ; 3 )
Gọi H là chân đường vuông góc kẻ từ M tới Ox. Suy ra MH = 3
d ∩ Ox tại A (−2; 0) ⇒ OA = 2
d’ ∩ Ox tại B 5 2 ; 0 ⇒ O B = 5 2
A B = O A + O B = 2 + 5 2 = 9 2
SMAB = 1 2 AB.MH = . 1 2 . 3 9 2 = 27 4 (đvdt)
Đáp án cần chọn là: D

b: Tọa độ A là:
-x+1=x+1 và y=x+1
=>x=0 và y=1
Tọa độ B là:
-x+1=-1 và y=-1
=>x=2 và y=-1
Toa độ C là:
x+1=-1 và y=-1
=>x=-2 và y=-1
A(0;1); B(2;-1); C(-2;-1)
\(AB=\sqrt{\left(2-0\right)^2+\left(-1-1\right)^2}=2\sqrt{2}\)
\(AC=\sqrt{\left(-2-0\right)^2+\left(-1-1\right)^2}=2\sqrt{2}\)
=>AB=AC
=>ΔABC cân tại A

Để d cắt Ox, Oy tại 2 điểm pb thì \(\left(m-1\right)\left(m^2-4\right)\ne0\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}m\ne1\\m\ne\pm2\\\end{matrix}\right.\)
Tọa độ A là nghiệm: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\\left(m-1\right)x+m^2-4=0\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\x=\frac{4-m^2}{m-1}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow OA=\left|\frac{4-m^2}{m-1}\right|=\left|\frac{m^2-4}{m-1}\right|\)
Tọa độ B là nghiệm: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\y=m^2-4\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow OB=\left|m^2-4\right|\)
\(3OA=OB\Leftrightarrow3\left|\frac{m^2-4}{m-1}\right|=\left|m^2-4\right|\Leftrightarrow\left|m-1\right|=3\) \(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}m=4\\m=-2\left(l\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Phương trình hoành độ giao điểm của d 1 v à d 2 là:
4 − x 3 = 8 − 2 x ⇔ 24 – 6 x = 4 – x ⇔ 5 x = 20 ⇒ x = 4 ⇒ y = 0 nên A (4; 0)
+) B (0; yB) là giao điểm của đường thẳng d1 và trục tung. Khi đó y B = 4 − 0 3
y B = 4 3
Suy ra tổng tung độ y A + y B = 0 + 4 3 = 4 3
Đáp án cần chọn là: A