Tìm đạo hàm của các hàm số sau y = x 5 – 4 x 3 + 2 x – 3
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


\(a,y'=\left(x^3-4x^2+5\right)'=3x^2-8x\\ b,y''=\left(3x^2-8x\right)'=6x-8\)

1) \(f\left(x\right)=2x-5\)
\(f'\left(x\right)=2\)
\(\Rightarrow f'\left(4\right)=2\)
2) \(y=x^2-3\sqrt[]{x}+\dfrac{1}{x}\)
\(\Rightarrow y'=2x-\dfrac{3}{2\sqrt[]{x}}-\dfrac{1}{x^2}\)
3) \(f\left(x\right)=\dfrac{x+9}{x+3}+4\sqrt[]{x}\)
\(\Rightarrow f'\left(x\right)=\dfrac{1.\left(x+3\right)-1.\left(x+9\right)}{\left(x-3\right)^2}+\dfrac{4}{2\sqrt[]{x}}\)
\(\Rightarrow f'\left(x\right)=\dfrac{x+3-x-9}{\left(x-3\right)^2}+\dfrac{2}{\sqrt[]{x}}\)
\(\Rightarrow f'\left(x\right)=\dfrac{12}{\left(x-3\right)^2}+\dfrac{2}{\sqrt[]{x}}\)
\(\Rightarrow f'\left(x\right)=2\left[\dfrac{6}{\left(x-3\right)^2}+\dfrac{1}{\sqrt[]{x}}\right]\)
\(\Rightarrow f'\left(1\right)=2\left[\dfrac{6}{\left(1-3\right)^2}+\dfrac{1}{\sqrt[]{1}}\right]=2\left(\dfrac{3}{2}+1\right)=2.\dfrac{5}{2}=5\)

Ta có
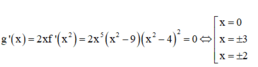
Bảng biến thiên của hàm số y= g( x)
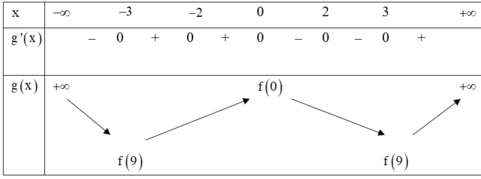
Dựa vào bảng biến thiên ta thấy hàm số đồng biến trên khoảng ( 3: + ∞) hàm số nghịch biến trong khoảng (-∞; -3) .
Hàm số có 3 cực trị, hàm số đạt giá trị nhỏ nhất tại x= ±3
Vậy có 3 khẳng định đúng là khẳng định I, II, IV
Chọn C.

1.
\(y'=\left(\dfrac{x}{lnx}\right)'.3^{\dfrac{x}{lnx}}.ln3=\dfrac{lnx-1}{ln^2x}.3^{\dfrac{x}{lnx}}.ln3\)
2.
\(y'=\left(tanx\right)'.tanx+\left(tanx\right)'.\dfrac{1}{tanx}=\dfrac{tanx}{cos^2x}+\dfrac{1}{tanx.cos^2x}\)
3.
\(y=\left(ln2x\right)^{\dfrac{2}{3}}\Rightarrow y'=\left(ln2x\right)'.\dfrac{2}{3}.\left(ln2x\right)^{-\dfrac{1}{3}}=\dfrac{1}{3x\sqrt[3]{ln2x}}\)

\(a,y'=8x^3-10x\\ \Rightarrow y''=24x^2-10\\ b,y'=e^x+xe^x\\ \Rightarrow y''=e^x+e^x+xe^x=2e^x+xe^x\)

a) Với bất kì \({x_0} \in \mathbb{R}\), ta có:
\(f'\left( {{x_0}} \right) = \mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to {x_0}} \frac{{f\left( x \right) - f\left( {{x_0}} \right)}}{{x - {x_0}}} = \mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to {x_0}} \frac{{x - {x_0}}}{{x - {x_0}}} = \mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to {x_0}} 1 = 1\)
Vậy \(f'\left( x \right) = {\left( x \right)^\prime } = 1\) trên \(\mathbb{R}\).
b) Ta có:
\(\begin{array}{l}{\left( {{x^2}} \right)^\prime } = 2{\rm{x}}\\{\left( {{x^3}} \right)^\prime } = 3{{\rm{x}}^2}\\...\\{\left( {{x^n}} \right)^\prime } = n{{\rm{x}}^{n - 1}}\end{array}\)

1. \(y'=3x^2\sqrt{x}+\dfrac{x^3-5}{2\sqrt{x}}=\dfrac{7x^3-5}{2\sqrt{x}}\)
2. \(y'=3x^5+\dfrac{3}{x^2}+\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{x}}\)
3. \(y'=2-\dfrac{2}{\left(x-2\right)^2}\)

Đáp án: B.
Xét f(x) = x 3 + m x 2 + x - 5
Vì 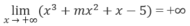
và f(0) = -5 với mọi m ∈ R cho nên phương trình f(x) = 0 luôn có nghiệm dương.
Tính đạo hàm của các hàm số sau:
a) \(y = {x^3} - 3{x^2} + 2x + 1;\)
b) \(y = {x^2} - 4\sqrt x + 3.\)

tham khảo:
a)\(y'=\dfrac{d}{dx}\left(x^3\right)-\dfrac{d}{dx}\left(3x^2\right)+\dfrac{d}{dx}\left(2x\right)+\dfrac{d}{dx}\left(1\right)\)
\(y'=3x^2-6x+2\)
b)\(\dfrac{d}{dx}\left(x^n\right)=nx^{n-1}\)
\(\dfrac{d}{dx}\left(\sqrt{x}\right)=\dfrac{1}{2\sqrt{x}}\)
\(\dfrac{d}{dx}\left(f\left(x\right)+g\left(x\right)\right)=f'\left(x\right)+g'\left(x\right)\)
\(\dfrac{d}{dx}\left(cf\left(x\right)\right)=cf'\left(x\right)\)
\(y'=\dfrac{d}{dx}\left(x^2\right)-\dfrac{d}{dx}\left(4\sqrt{x}\right)+\dfrac{d}{dx}\left(3\right)\)
\(y'=2x-2\sqrt{x}\)
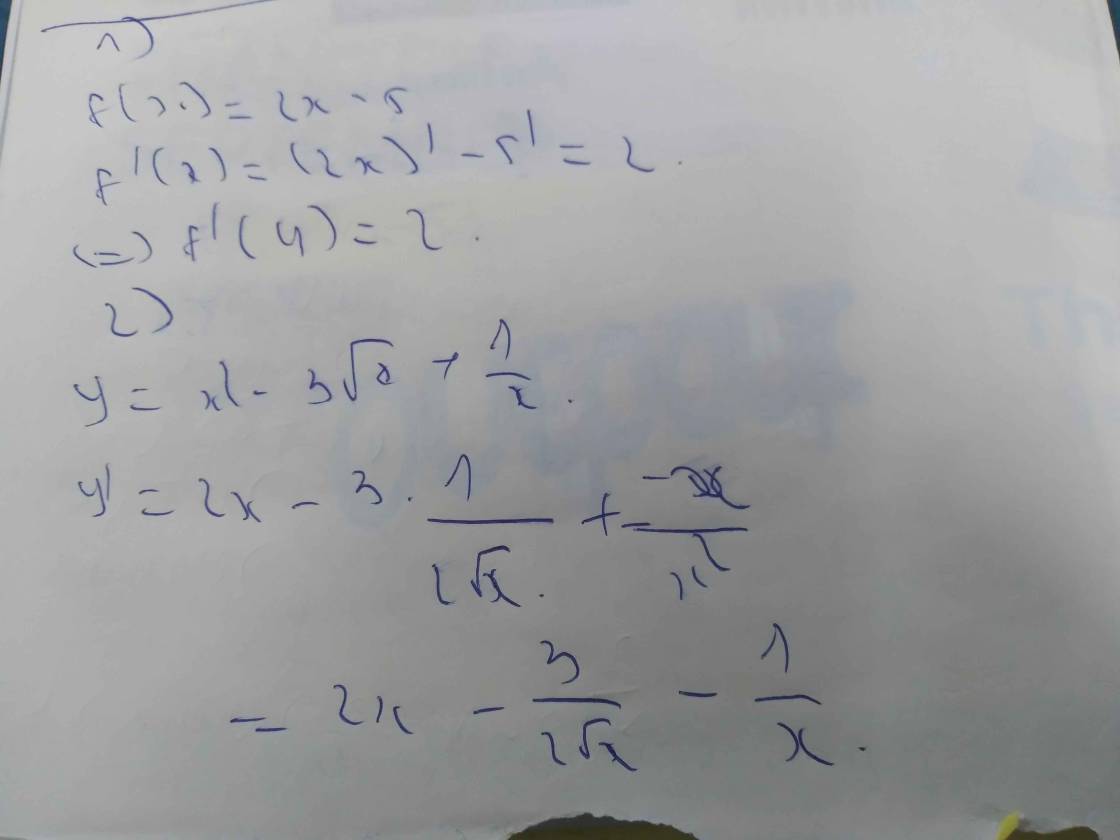

y’ = (x5 – 4x3 + 2x – 3)’
= (x5)’ – (4x3)’ + (2x)’ – (3)’
= 5x4 – 4.3x2 + 2
= 5x4 – 12x2 + 2.