Câu 8. Tìm số a để đa thức 2x3 –5x+6x−a chia hết cho đa thức 2x −5.
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


b: \(=\dfrac{2x^4-2x^3-2x^2-3x^3+3x^2+3x+x^2-x-1}{x^2-x-1}\)
\(=2x^2-3x+1\)

a: \(\Leftrightarrow2x^4-2x^3+2x^2+3x^3-3x^2+3x-2x^2+2x+2+a-2⋮x^2-x+1\)
=>a=2

a: Khi x=-1 thì B=2*(-1)^2+1+1=4
b: Để A chia hết cho B thì
\(2x^3-x^2+x+6x^2-3x+3+a-3⋮2x^2-x+1\)
=>a-3=0
=>a=3
c: Để B=1 thì 2x^2-x=0
=>x=0 hoặc x=1/2

Thực hiện phép chia:
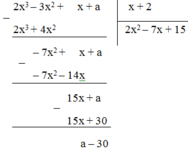
2x3 – 3x2 + x + a chia hết cho x + 2
⇔ số dư = a – 30 = 0
⇔ a = 30.
Cách 2: Phân tích 2x3 – 3x2 + x + a thành nhân tử có chứa x + 2.
2x3 – 3x2 + x + a
= 2x3 + 4x2 – 7x2 – 14x + 15x + 30 + a – 30
(Tách -3x2 = 4x2 – 7x2; x = -14x + 15x)
= 2x2(x + 2) – 7x(x + 2) + 15(x + 2) + a – 30
= (2x2 – 7x + 15)(x + 2) + a – 30
2x3 – 3x2 + x + a chia hết cho x + 2 ⇔ a – 30 = 0 ⇔ a = 30.

Số dư của phép chia đa thức \(\text{f( x ) = 2x^3 - 3x^2 + x + a}\) cho \(\text{x + 2}\) là
\(\text{f ( -2 ) = 2(-2) ^3 - 3 (-2 )^2 + ( - 2 ) + a = -30 + a}\)
Để phép chia là chia hết thì số dư bằng \(\text{0}\)
Hay \(\text{-30 + a = 0}\) \(\Rightarrow\) \(\text{a = 30}\)

1) \(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-4\right)\left(x+4\right)-x\left(x-4\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-4\right)\left(x+4-x\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-4\right)4=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=4\)
2) \(\left(x+3\right)^2-\left(x-3\right)\left(x+5\right)=x^2+6x+9-x^2-2x+15=4x+24\)
3) \(2x^3+3x^2-2x+a=2x^2\left(x-2\right)+7x\left(x-2\right)+16\left(x-2\right)+32+a\)
Để \(2x^3+3x^2-2x+a⋮x-2\) thì \(32+a=0\Leftrightarrow a=-32\)
1.
x2 - 16 - x(x - 4) = 0
<=> (x2 - 42) - x(x - 4) = 0
<=> (x - 4)(x + 4) - x(x - 4) = 0
<=> (x + 4 - x)(x + 4) = 0
<=> 4(x + 4) = 0
<=> x + 4 = 0
<=> x = -4
2.
(x + 3)2 - (x - 3)(x + 5)
= x2 + 6x + 9 - (x2 + 5x - 3x - 15)
= x2 + 6x + 9 - x2 + 5x - 3x - 15
= x2 - x2 + 6x + 5x - 3x + 9 - 15
= 8x - 6

a: \(=\dfrac{2x^4-2x^3-2x^2-3x^3+3x^2+3x+x^2-x-1}{x^2-x-1}\)
\(=2x^2-3x+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^3+x-a=\left(2x-5\right)\cdot a\left(x\right)\)
Thay \(x=\dfrac{5}{2}\Leftrightarrow2\cdot\dfrac{125}{8}+\dfrac{5}{2}-a=0\Leftrightarrow a=\dfrac{135}{4}\)