tìm TXĐ của hàm số y= \(\dfrac{x^2+x+1}{x^2-9}\)
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


ĐKXĐ:
a. \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-1\ge0\\x-3\ne0\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\ge1\\x\ne3\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow D=[1;+\infty)\backslash\left\{3\right\}\)
b. \(D=R\)
c. \(x+3>0\Rightarrow x>-3\Rightarrow D=\left(-3;+\infty\right)\)
d. \(\left|x-2\right|\ge0\Rightarrow x\in R\Rightarrow D=R\)

1.
Hàm số xác định khi \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{1+x}{1-x}\ge0\\1-x\ne0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-1\le x< 1\\x\ne1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow-1\le x< 1\)
2.
Hàm số xác định khi \(cosx+1\ne0\Leftrightarrow cosx\ne-1\Leftrightarrow x\ne-\pi+k2\pi\)
3.
Hàm số xác định khi \(cosx-cos3x\ne0\Leftrightarrow sin2x.sinx\ne0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x\ne k\pi\\x\ne\dfrac{k\pi}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)

a: ĐKXĐ: x\(\in\)R\{3}
b: ĐKXĐ: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x>1\\x\ne2\end{matrix}\right.\)

1. Hàm số xác định `<=> 1-cosx \ne 0<=>cosx \ne 1<=>x \ne k2π`
Vì: `1+cosx >=0 forallx ; 1-cosx >=0 forall x`
2. Hàm số xác định `<=> sin^2x \ne cos^2x <=> (1-cos2x)/2 \ne (1+cos2x)/2`
`<=>cos2x \ne 0<=> 2x \ne π/2+kπ <=> x \ne π/4+kπ/2`
3. Hàm số xác định `<=> cos2x \ne 0<=> x \ne π/4+kπ/2 (k \in ZZ)`.
Bạn cho mình hỏi tại sao x khác k2\(\pi\) là lý thuyết ở đoạn nào thế ạ?

Xét pt: \(x^2-2mx+m^2-2m+3=0\) (1)
\(\Delta'=m^2-\left(m^2-2m+3\right)=2m-3\)
- Nếu \(2m-3< 0\Leftrightarrow m< \dfrac{3}{2}\Rightarrow\left(1\right)\) vô nghiệm hay hàm xác định trên R
- Nếu \(2m-3=0\Leftrightarrow m=\dfrac{3}{2}\Rightarrow\left(1\right)\) có nghiệm kép \(x=\dfrac{3}{2}\) hay TXĐ của hàm: \(D=R\backslash\left\{\dfrac{3}{2}\right\}\)
- Nếu \(2m-3>0\Leftrightarrow m>\dfrac{3}{2}\Rightarrow\left(1\right)\) có 2 nghiệm pb \(x_{1,2}=m\pm\sqrt{2m-3}\) hay TXĐ của hàm là: \(D=R\backslash\left\{m-\sqrt{2m-3};m+\sqrt{2m-3}\right\}\)

a: ĐKXĐ: 2*sin x+1<>0
=>sin x<>-1/2
=>x<>-pi/6+k2pi và x<>7/6pi+k2pi
b: ĐKXĐ: \(\dfrac{1+cosx}{2-cosx}>=0\)
mà 1+cosx>=0
nên 2-cosx>=0
=>cosx<=2(luôn đúng)
c ĐKXĐ: tan x>0
=>kpi<x<pi/2+kpi
d: ĐKXĐ: \(2\cdot cos\left(x-\dfrac{pi}{4}\right)-1< >0\)
=>cos(x-pi/4)<>1/2
=>x-pi/4<>pi/3+k2pi và x-pi/4<>-pi/3+k2pi
=>x<>7/12pi+k2pi và x<>-pi/12+k2pi
e: ĐKXĐ: x-pi/3<>pi/2+kpi và x+pi/4<>kpi
=>x<>5/6pi+kpi và x<>kpi-pi/4
f: ĐKXĐ: cos^2x-sin^2x<>0
=>cos2x<>0
=>2x<>pi/2+kpi
=>x<>pi/4+kpi/2

`@` H/s xác định `<=>{(x+2 >= 0),(2-x >= 0):}<=>{(x >= -2),(x <= 2):}<=>-2 <= x <= 2`
`=>TXĐ: D=[-2;2]`
`@-2 <= x <= 2`
`<=>{(0 <= x+2 <= 4),(2 >= -x >= -2):}`
`<=>{(0 <= x+2 <= 4),(4 >= 2-x >= 0):}`
`<=>{(0 <= \sqrt{x+2} <= 2),(2 >= \sqrt{2-x} >= 0):}`
`=>TGT` là `[0;2]`

ĐKXĐ: \(\dfrac{\left|x-1\right|}{x+2}-1\ge0\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\left|x-1\right|}{x+2}>1\)
Với \(x< -2\) ko thỏa mãn
Với \(x>-2\Rightarrow x+2>0\)
BPT tương đương: \(\left|x-1\right|>x+2\Rightarrow\left(x-1\right)^2>\left(x+2\right)^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6x< -3\Rightarrow x< -\dfrac{1}{2}\Rightarrow-2< x< -\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(\Rightarrow x=-1\) là số nguyên duy nhất trong TXĐ của hàm số
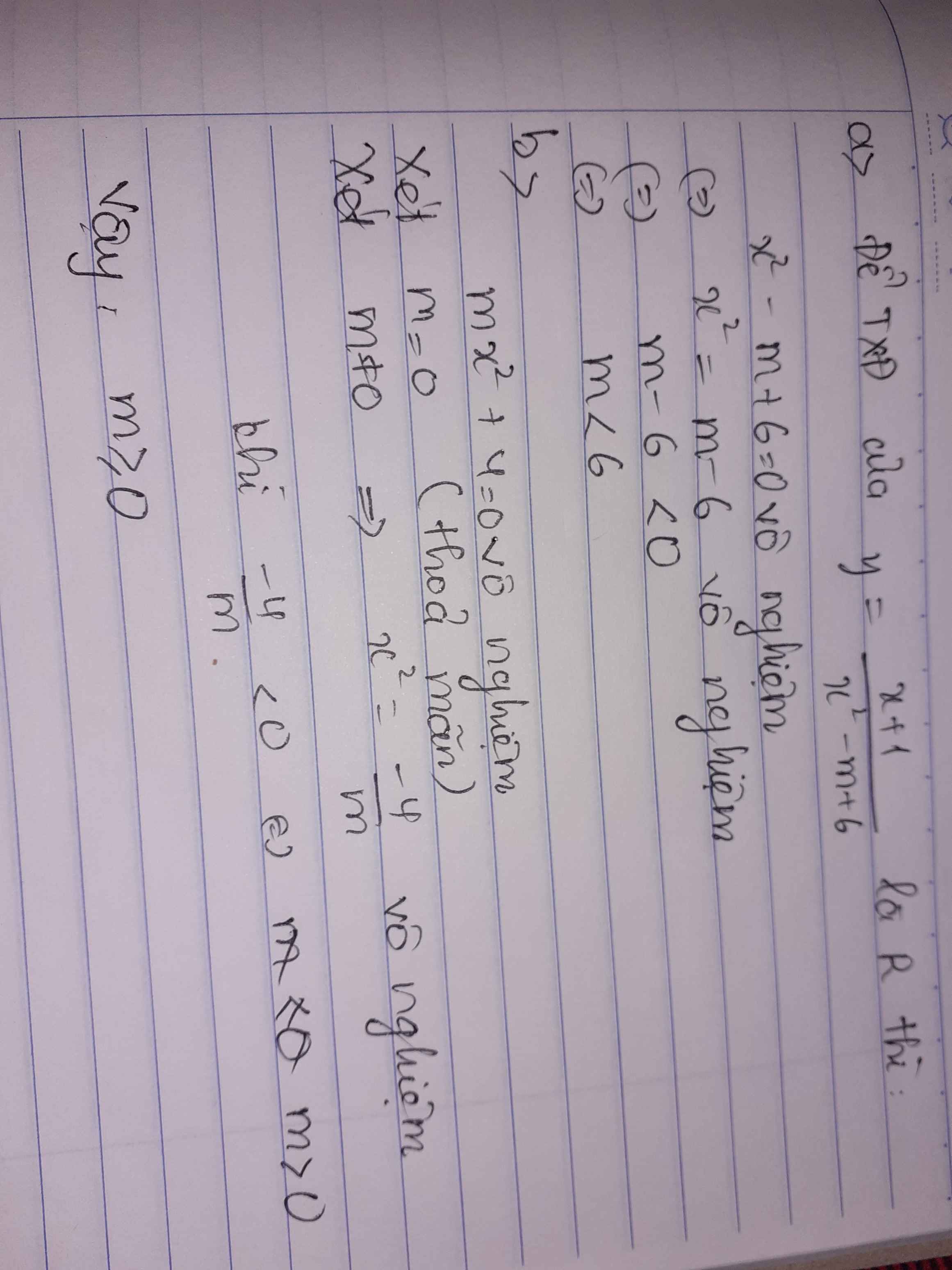
TXĐ: D=R\{3;-3}