Mọi người giải giúp em bài 7 ạ! hình ở phía dưới ạ
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Gọi số sản phẩm àm 2 ng công nhân được giao là x (x∈N*, sản phẩm)
Thời gian hoàn thành công việc của người thứ nhất là: \(\dfrac{x}{40}\left(h\right)\)
Thời gian hoàn thành công việc của ngươi thứ hai là: \(\dfrac{x}{50}\left(h\right)\)
Vì ng thứ nhất hoàn thành công việc chậm hơn người thứ hai 2 giờ nên ta có PT:
\(\dfrac{x}{40}-\dfrac{x}{50}=2\)
⇔\(50x-40x=4000\)
⇔\(10x=4000\)
⇔\(x=400\)
Vậy số sản phẩm mỗi công nhân được giao là 400 (sản phẩm)

Mình không nhìn thấy câu hỏi, giờ mới thấy bạn ạ
Do mở rộng cạnh của thửa đất về cả bốn phía nên thửa đất mới sau khi mở rộng cũng là hình vuông. mỗi cạnh của thửa đất lúc sau đã tăng :
0,5 x 2 = 1 (m)
Gọi cạnh hình vuông lúc đầu là x đk x > 0
Thì cạnh hình vuông lúc sau là : x + 1
theo bài ra ta có : (x + 1)( x + 1) - x2 = 20
x2 + x + x + 1 - x2 = 20
2x = 20 -1
2x = 19
x = 19: 2
x = 9,5
Kết luận cạnh hình vuông lúc đầu là 9,5 m

a: Xét ΔABD và ΔHBD có
BA=BH
\(\widehat{ABD}=\widehat{HBD}\)
BD chung
Do đó: ΔABD=ΔHBD
b: Ta có: ΔABD=ΔHBD
nên \(\widehat{BAD}=\widehat{BHD}\)
mà \(\widehat{BAD}=90^0\)
nên \(\widehat{BHD}=90^0\)
hay DH\(\perp\)BC

2\(\sqrt{\dfrac{16}{3}}\) - 3\(\sqrt{\dfrac{1}{27}}\) - \(\dfrac{3}{2\sqrt{3}}\)
= \(\dfrac{8}{\sqrt{3}}\) - \(\dfrac{3}{3\sqrt{3}}\) - \(\dfrac{3}{2\sqrt{3}}\)
= \(\dfrac{8}{\sqrt{3}}\) - \(\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}}\) - \(\dfrac{3}{2\sqrt{3}}\)
= \(\dfrac{16}{2\sqrt{3}}\) - \(\dfrac{2}{2\sqrt{3}}\) - \(\dfrac{3}{2\sqrt{3}}\)
= \(\dfrac{11}{2\sqrt{3}}\)
= \(\dfrac{11\sqrt{3}}{6}\)
f, 2\(\sqrt{\dfrac{1}{2}}\)- \(\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{2}}\) + \(\dfrac{5}{2\sqrt{2}}\)
= \(\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{2}}\) - \(\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{2}}\) + \(\dfrac{5}{2\sqrt{2}}\)
= \(\dfrac{5}{2\sqrt{2}}\)
= \(\dfrac{5\sqrt{2}}{4}\)
(1 + \(\dfrac{3-\sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{3}-1}\)).(1- \(\dfrac{3+\sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{3}+1}\))
= \(\dfrac{\sqrt{3}-1+3-\sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{3}-1}\).\(\dfrac{\sqrt{3}+1-3+\sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{3}+1}\)
= \(\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{3}-1}\).\(\dfrac{-2}{\sqrt{3}+1}\)
= \(\dfrac{-4}{3-1}\)
= \(\dfrac{-4}{2}\)
= -2

vẽ lại mạch ta có RAM//RMN//RNB
đặt theo thứ tự 3 R là a,b,c
ta có a+b+c=1 (1)
điện trở tương đương \(\dfrac{1}{R_{td}}=\dfrac{1}{a}+\dfrac{1}{b}+\dfrac{1}{c}\) \(\Rightarrow I=\dfrac{U}{R_{td}}=9.\left(\dfrac{1}{a}+\dfrac{1}{b}+\dfrac{1}{c}\right)\) với a,b,c>0
áp dụng bất đẳng thức cô si cho \(\dfrac{1}{a},\dfrac{1}{b},\dfrac{1}{c}\) \(\Rightarrow\dfrac{1}{a}+\dfrac{1}{b}+\dfrac{1}{c}\ge\dfrac{3}{\sqrt[3]{abc}}\ge\dfrac{3}{\left(\dfrac{a+b+c}{3}\right)}=\dfrac{9}{a+b+c}=9\)
\(\Leftrightarrow9\left(\dfrac{1}{a}+\dfrac{1}{b}+\dfrac{1}{c}\right)\ge81\Leftrightarrow I\ge81\) I min =81 ( úi dồi ôi O_o hơi to mà vẫn đúng đá nhỉ)
dấu ''='' xảy ra \(\Leftrightarrow a=b=c\left(2\right)\)
từ (1) (2) \(\Rightarrow a=b=c=\dfrac{1}{3}\left(\Omega\right)\)
vậy ... (V LUN MẤT CẢ BUỔI TỐI R BÀI KHÓ QUÁ EM ĐANG ÔN HSG À )


Bài 2:
a: \(\text{Δ}=\left(-2\right)^2-4\left(m-3\right)=4-4m+12=-4m+16\)
Để pt vô nghiệm thì -4m+16<0
=>m>4
Để phương trình co nghiệmduy nhất thì -4m+16=0
=>m=4
Để phương trình có hai nghiệm phân biệt thì -4m+16>0
=>m<4
b: \(\text{Δ}=\left(2m-2\right)^2-4\left(m^2-m+1\right)\)
\(=4m^2-8m+4-4m^2+4m-4=-4m\)
Để pt vô nghiệm thì -4m<0
=>m>0
Để phương trình co nghiệmduy nhất thì -4m=0
=>m=0
Để phương trình có hai nghiệm phân biệt thì -4m>0
=>m<0
c: \(\Delta=\left(-m\right)^2-4\cdot1\cdot1=m^2-4\)
Để pt vô nghiệm thì m^2-4<0
=>-2<m<2
Để phương trình co nghiệmduy nhất thì m^2-4=0
=>m=2 hoặc m=-2
Để phương trình có hai nghiệm phân biệt thì m^2-4>0
=>m>2 hoặc m<-2

a) \(\dfrac{A}{x-2}=\dfrac{x^2+3x+2}{x^2-4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{A}{x-2}=\dfrac{\left(x+2\right)\left(x+1\right)}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{A}{x-2}=\dfrac{x+1}{x-2}\Leftrightarrow A=x+1\)
b) \(\dfrac{M}{x-1}=\dfrac{x^2+3x+2}{x+1}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{M}{x-1}=\dfrac{\left(x+1\right)\left(x+2\right)}{x+1}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{M}{x-1}=x+2\Leftrightarrow M=\left(x-1\right)\left(x+2\right)=x^2+x-2\)

\(ĐK:x\ne\dfrac{1}{2};x\ne1;x\ne\dfrac{3}{2};x\ne2;x\ne\dfrac{5}{2}\\ PT\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1}{\left(2x-1\right)\left(x-1\right)}+\dfrac{1}{\left(x-1\right)\left(3x-2\right)}+\dfrac{1}{\left(3x-2\right)\left(x-2\right)}+\dfrac{1}{\left(x-2\right)\left(5x-2\right)}=\dfrac{4}{21}\\ \Leftrightarrow2\left[\dfrac{\dfrac{1}{2}}{\left(x-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)\left(x-1\right)}+\dfrac{\dfrac{1}{2}}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x-\dfrac{3}{2}\right)}+\dfrac{\dfrac{1}{2}}{\left(x-\dfrac{3}{2}\right)\left(x-2\right)}+\dfrac{\dfrac{1}{2}}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x-\dfrac{5}{2}\right)}\right]=\dfrac{4}{21}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1}{x-1}-\dfrac{1}{x-\dfrac{1}{2}}+\dfrac{1}{x-\dfrac{3}{2}}-\dfrac{1}{x-1}+\dfrac{1}{x-2}-\dfrac{1}{x-\dfrac{3}{2}}+\dfrac{1}{x-\dfrac{5}{2}}-\dfrac{1}{x-2}=\dfrac{2}{21}\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1}{x-1}-\dfrac{1}{x-\dfrac{5}{2}}=\dfrac{2}{21}\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x-\dfrac{5}{2}-x+1}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x-\dfrac{5}{2}\right)}=\dfrac{2}{21}\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{-\dfrac{3}{2}}{x^2-\dfrac{7}{2}x+\dfrac{5}{2}}=\dfrac{2}{21}\\ \Leftrightarrow x^2-\dfrac{7}{2}x+\dfrac{5}{2}=-\dfrac{63}{4}\\ \Leftrightarrow4x^2-14x+10=-63\\ \Leftrightarrow4x^2-14x+73=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x\in\varnothing\)
 em cần giải gấp bài 3 chi tiết mọi người giúp em với ạ. Làm bài dưới dạng phân số ạ em cần gấp
em cần giải gấp bài 3 chi tiết mọi người giúp em với ạ. Làm bài dưới dạng phân số ạ em cần gấp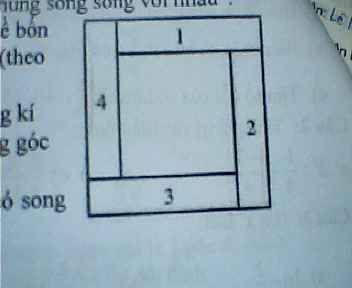


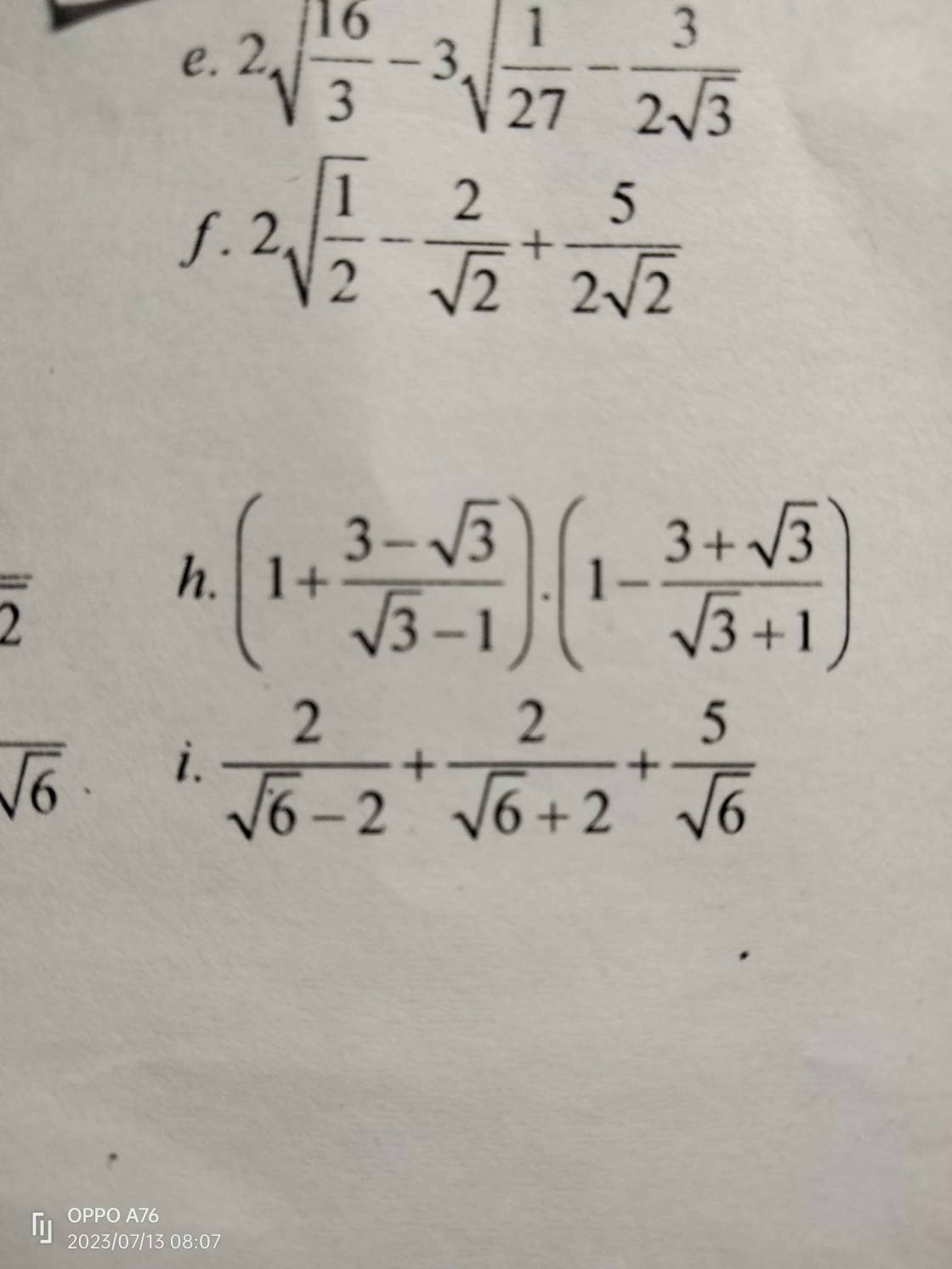


 em cần giải gấp bài 2 ạ, mọi người giúp em với ạ
em cần giải gấp bài 2 ạ, mọi người giúp em với ạ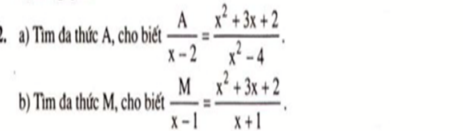 mọi người giải giúp em bài này với ạ em đang cần gấp ạ
mọi người giải giúp em bài này với ạ em đang cần gấp ạ
Kẻ đường cao AH
\(\Rightarrow\widehat{BAH}=\widehat{ACB}\) (cùng phụ góc B) \(\Rightarrow\widehat{BAH}=a\)
\(\left(sina+cosa\right)^2=sin^2a+cos^2a+2sina.cosa\)
\(=1+2sina.cosa=1+2.\frac{BH}{AB}.\frac{AH}{AB}=1+\frac{2AH.BH}{AB^2}=1+\frac{2AH.BH}{BH.BC}=1+\frac{2AH}{BC}\)
\(1+sinb=1+\frac{AH}{AM}=1+\frac{AH}{\frac{BC}{2}}=1+\frac{2AH}{BC}\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(sina+cosa\right)^2=1+sinb\)