Câu 6. Giá trị nhỏ nhất của biểu thức P = 3x2 – 4x + 10 là:
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Tìm giá trị nhỏ nhất của biểu thức:
a) Ta có:
\(M=2x^2+4x+7\)
\(M=2\cdot\left(x^2+2x+\dfrac{7}{2}\right)\)
\(M=2\cdot\left(x^2+2x+1+\dfrac{5}{2}\right)\)
\(M=2\cdot\left[\left(x+1\right)^2+2,5\right]\)
\(M=2\left(x+1\right)^2+5\)
Mà: \(2\left(x+1\right)^2\ge0\forall x\) nên:
\(M=2\left(x+1\right)^2+5\ge5\forall x\)
Dấu "=" xảy ra:
\(2\left(x+1\right)^2+5=5\Leftrightarrow2\left(x+1\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)^2=0\Leftrightarrow x+1=0\Leftrightarrow x=-1\)
Vậy: \(M_{min}=5\) khi \(x=-1\)
b) Ta có:
\(N=x^2-x+1\)
\(N=x^2-2\cdot\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot x+\dfrac{1}{4}+\dfrac{3}{4}\)
\(N=\left(x-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{3}{4}\)
Mà: \(\left(x+\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2\ge0\forall x\) nên \(N=\left(x-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{3}{4}\ge\dfrac{3}{4}\forall x\)
Dấu '=" xảy ra:
\(\left(x-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{3}{4}=\dfrac{3}{4}\Leftrightarrow\left(x-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-\dfrac{1}{2}=0\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
Vậy: \(N_{min}=\dfrac{3}{4}\) khi \(x=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
Tìm giá trị lớn nhất của biểu thức
a) Ta có:
\(E=-4x^2+x-1\)
\(E=-\left(4x^2-x+1\right)\)
\(E=-\left[\left(2x\right)^2-2\cdot2x\cdot\dfrac{1}{4}+\dfrac{1}{16}+\dfrac{15}{16}\right]\)
\(E=-\left[\left(2x-\dfrac{1}{4}\right)^2+\dfrac{15}{16}\right]\)
Mà: \(\left(2x+\dfrac{1}{4}\right)^2+\dfrac{15}{16}\ge\dfrac{15}{16}\forall x\) nên
\(\Rightarrow E=-\left[\left(2x+\dfrac{1}{4}\right)^2+\dfrac{15}{16}\right]\le-\dfrac{15}{16}\forall x\)
Dấu "=" xảy ra:
\(-\left[\left(2x+\dfrac{1}{4}\right)^2+\dfrac{15}{16}\right]=-\dfrac{15}{16}\Leftrightarrow-\left(2x+\dfrac{1}{4}\right)^2-\dfrac{15}{16}=-\dfrac{15}{16}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-\left(2x+\dfrac{1}{4}\right)^2=0\Leftrightarrow2x-\dfrac{1}{4}=0\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{1}{16}\)
Vậy: \(E_{max}=-\dfrac{15}{16}\) khi \(x=\dfrac{1}{16}\)
b) Ta có:
\(F=5x-3x^2+6\)
\(F=-3x^2+5x-6\)
\(F=-\left(3x^2-5x-6\right)\)
\(F=-3\left(x^2-\dfrac{5}{3}x-2\right)\)
\(F=-3\left[\left(x-\dfrac{5}{6}\right)^2-\dfrac{97}{36}\right]\)
\(F=-3\left(x-\dfrac{5}{6}\right)^2+\dfrac{97}{36}\)
Mà: \(-3\left(x-\dfrac{5}{6}\right)^2\le0\forall x\) nên:
\(F=-3\left(x-\dfrac{5}{6}\right)^2+\dfrac{97}{36}\le\dfrac{97}{36}\forall x\)
Dấu "=" xảy ra:
\(-3\left(x-\dfrac{5}{6}\right)^2+\dfrac{97}{36}=\dfrac{97}{36}\Leftrightarrow-3\left(x-\dfrac{5}{6}\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-\dfrac{5}{6}=0\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{5}{6}\)
Vậy: \(F_{max}=\dfrac{97}{36}\) khi \(x=\dfrac{5}{6}\)


Ta có
I = ( x 2 + 4 x + 5 ) ( x 2 + 4 x + 6 ) + 3 = ( x 2 + 4 x + 5 ) ( x 2 + 4 x + 5 + 1 ) + 3 = x 2 + 4 x + 5 2 + x 2 + 4 x + 5 + 3 = x 2 + 4 x + 5 2 + x 2 + 4 x + 4 + 1 + 3 = x 2 + 4 x + 5 2 + x + 2 2 + 4
Ta có x 2 + 4 x + 5 = x 2 + 4 x + 4 + 1
= x + 2 2 + 1 ≥ 1; Ɐx nên x 2 + 4 x + 5 2 ≥ 1; Ɐx
Và x + 2 2 ≥ 0; Ɐx x 2 + 4 x + 5 2 + x + 2 2 + 4 ≥ 1 + 4
ó x 2 + 4 x + 5 2 + x + 2 2 + 4 ≥ 5
Dấu “=” xảy ra khi => x = -2
Vậy giá trị nhỏ nhất của I là 5 khi x = -2
Đáp án cần chọn là: B

Bài 1:
a: \(M=x^2-10x+3\)
\(=x^2-10x+25-22\)
\(=\left(x^2-10x+25\right)-22\)
\(=\left(x-5\right)^2-22>=-22\forall x\)
Dấu '=' xảy ra khi x-5=0
=>x=5
b: \(N=x^2-x+2\)
\(=x^2-x+\dfrac{1}{4}+\dfrac{7}{4}\)
\(=\left(x-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{7}{4}>=\dfrac{7}{4}\forall x\)
Dấu '=' xảy ra khi x-1/2=0
=>x=1/2
c: \(P=3x^2-12x\)
\(=3\left(x^2-4x\right)\)
\(=3\left(x^2-4x+4-4\right)\)
\(=3\left(x-2\right)^2-12>=-12\forall x\)
Dấu '=' xảy ra khi x-2=0
=>x=2

5-/3x-4/
ta có: /3x-4/\(\ge0,\forall x\)
\(\Rightarrow\)5-/3x-4/\(\le5\)
Dấu "=" xảy ra khi 3x-4=0 =>3x=4 =>\(x=\frac{3}{4}\)
Vậy GTNL của 5-/3x-4/ là 5 với x=\(\frac{3}{4}\)
\(\left(4x-6\right)^{2008}+8\)
ta có: \(\left(4x-6\right)^{2008}\ge0,\forall x\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(4x-6\right)^{2008}+8\ge8\)
dấu "=" xảy ra khi (4x-6)2008=0
=> 4x-6=0 =>4x=6 =>x=\(\frac{3}{2}\)
vậy GTNN của (4x-6)2008 là 8 với x=\(\frac{3}{2}\)

Chọn B.
Phương pháp:
Biến đổi đẳng thức đã cho để đưa về dạng phương trình đường tròn (C) tâm I bán kính R.
Từ đó ta đưa bài toán về dạng bài tìm M x ; y ∈ C để O M - a lớn nhất hoặc nhỏ nhất.
Xét các trường hợp xảy ra để tìm a.
Cách giải:
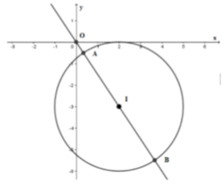
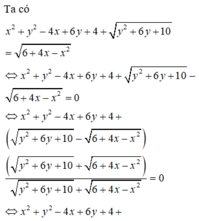
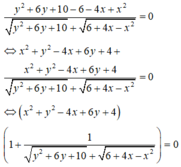


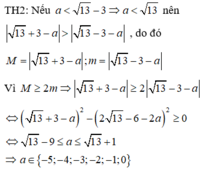

P = 3( \(x^2\)- \(\frac{4}{3}\)x + \(\frac{10}{3}\))
P = 3( \(x^2\)- 2x\(\frac{2}{3}\)+ \(\frac{4}{9}\)+ \(\frac{26}{9}\))
P = 3( \(\left(x-\frac{2}{3}\right)^2\)+ \(\frac{26}{9}\))
P = 3\(\left(x-\frac{2}{3}\right)^2\)+ \(\frac{26}{3}\)
Nhận thấy: 3\(\left(x-\frac{2}{3}\right)^2\)>=0 với mọi x
--> 3\(\left(x-\frac{2}{3}\right)^2\)+ \(\frac{26}{3}\)>=\(\frac{26}{3}\) với mọi x
hay P>=\(\frac{26}{3}\)với mọi x
--> GTNN của P bằng \(\frac{26}{3}\)
Dấu "=" xảy ra <=>\(\left(x-\frac{3}{2}\right)^2\)=0
<=> x - \(\frac{3}{2}\)=0
<=> x = \(\frac{3}{2}\)
Vậy GTNN của biểu thức P là \(\frac{26}{3}\)tại x = \(\frac{3}{2}\).