Tìm x,y thuộc Z thỏa mãn 5xy-2y2-2x2=-2
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Ta có: \(2x^2+xy+2y^2=\dfrac{3}{2}\left(x^2+y^2\right)+\dfrac{1}{2}\left(x^2+2xy+y^2\right)=\dfrac{3}{2}\left(x^2+y^2\right)+\dfrac{1}{2}\left(x+y\right)^2\)
Theo BĐT Bunhacopxky: \(\left(x^2+y^2\right)\left(1+1\right)\ge\left(x+y\right)^2\Rightarrow\dfrac{3}{2}\left(x^2+y^2\right)\ge\dfrac{3}{4}\left(x+y\right)^2\\ \Rightarrow2x^2+xy+2y^2=\dfrac{3}{2}\left(x^2+y^2\right)+\dfrac{1}{2}\left(x+y\right)^2\ge\dfrac{5}{4}\left(x+y\right)^2\\ \Rightarrow\sqrt{2x^2+xy+2y^2}\ge\dfrac{\sqrt{5}}{2}\left(x+y\right)\)
Chứng minh tương tự:
\(\sqrt{2y^2+yz+2z^2}\ge\dfrac{\sqrt{5}}{2}\left(y+z\right)\\ \sqrt{2z^2+xz+2x^2}\ge\dfrac{\sqrt{5}}{2}\left(x+z\right)\)
Cộng vế theo vế, ta được: \(P\ge\sqrt{5}\left(x+y+z\right)=\sqrt{5}\cdot1=\sqrt{5}\)
Dấu "=" \(\Leftrightarrow x=y=z=\dfrac{1}{3}\)
Bạn tham khảo nhé
https://hoc24.vn/cau-hoi/cho-cac-so-duong-xyz-thoa-man-xyz1cmrcan2x2xy2y2can2y2yz2z2can2z2zx2x2can5.182722154737

\(\dfrac{x}{4}=\dfrac{y}{4}=\dfrac{z}{5}=>\dfrac{2x^2}{32}=\dfrac{2y^2}{32}=\dfrac{3z^2}{75}\)
AD t/c của dãy tỉ số bằng nhâu ta có
\(\dfrac{2x^2}{32}=\dfrac{2y^2}{32}=\dfrac{3z^2}{75}=\dfrac{2x^2+2y^2-3z^2}{32+32-75}=\dfrac{-100}{-11}=\dfrac{100}{11}\)
\(=>\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{400}{11}\\y=\dfrac{400}{11}\\z=\dfrac{500}{11}\end{matrix}\right.\)

\(2x^2+2y^2-5xy+x-2y+3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2y\right)\left(2x-y\right)+x-2y+3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2y\right)\left(2x-y+1\right)=-3\)
| x-2y | -3 | -1 | 1 | 3 |
| 2x-y+1 | 1 | 3 | -3 | -1 |
| x | 1 | 5/3 | -3 | -7/3 |
| y | 2 | 4/3 | -2 | -8/3 |
Vậy \(\left(x;y\right)=\left(1;2\right)\) là bộ nghiệm nguyên dương duy nhất

Bạn vui lòng viết đề đầy đủ, và gõ bằng công thức toán để được hỗ trợ tốt hơn.



a/
$x+y=xy$
$\Leftrightarrow xy-x-y=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x(y-1)-(y-1)=1$
$\Leftrightarrow (y-1)(x-1)=1$
Do $x,y$ nguyên nên $x-1,y-1$ cũng nguyên. Mà tích của chúng bằng 1 nên ta xét các TH sau:
TH1: $x-1=1, y-1=1\Rightarrow x=2; y=2$ (tm)
TH2: $x-1=-1, y-1=-1\Rightarrow x=0; y=0$ (tm)
b/
$5xy-2y^2-2x^2=-2$
$\Leftrightarrow 2x^2-5xy+2y^2=2$
$\Leftrightarrow (2x-y)(x-2y)=2$
Do $x,y$ nguyên nên $2x-y, x-2y$ cũng là số nguyên. Mà tích của chúng bằng 2 nên ta xét các TH sau:
TH1: $2x-y=1, x-2y=2$
$\Rightarrow x=0; y=-1$
TH2: $2x-y=-1, x-2y=-2$
$\Rightarrow x=0; y=1$
TH3: $2x-y=2, x-2y=1$
$\Rightarrow x=1; y=0$
TH4: $2x-y=-2, x-2y=-1$
$\Rightarrow x=-1; y=0$


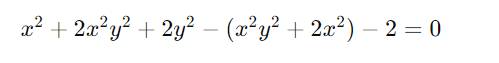
Lời giải:
$5xy-2y^2-2x^2=-2$
$\Rightarrow 2x^2+2y^2-5xy=2$
$\Rightarrow (2x-y)(x-2y)=2$
Với $x,y$ là số nguyên thì $2x-y, x-2y\in\mathbb{Z}$. Mà tích của hai số là 2 nên ta xét các TH sau:
TH1: $2x-y=1, x-2y=2\Rightarrow x=0; y=-1$
TH2: $2x-y=-1, x-2y=-2\Rightarrow x=0; y=1$
TH3: $2x-y=2, x-2y=1\Rightarrow x=1; y=0$
TH4: $2x-y=-2, x-2y=-1\Rightarrow x=-1; y=0$