giải phương trình
![]()
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


ta có :
\(\left|x+1\right|+\left|x-1\right|=1+\left|\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)\right|\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left|x-1\right|\left|x+1\right|-\left|x-1\right|-\left|x+1\right|+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(\left|x-1\right|-1\right)\left(\left|x+1\right|-1\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}\left|x-1\right|=1\\\left|x+1\right|=1\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\in\left\{-2,0,2\right\}\)

Bài 1:
a) Ta có: \(2\left(3-4x\right)=10-\left(2x-5\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6-8x-10+2x-5=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-6x+11=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-6x=-11\)
hay \(x=\dfrac{11}{6}\)
b) Ta có: \(3\left(2-4x\right)=11-\left(3x-1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6-12x-11+3x-1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-9x-6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-9x=6\)
hay \(x=-\dfrac{2}{3}\)


Thay x = 3, y = 5 vào vế trái của phương trình (3) ta được:
VT = 5.3 – 2.5 = 15 – 10 = 5 = VP
Vậy (x; y) = (3; 5) là nghiệm của phương trình (3).
Hệ phương trình đã cho có nghiệm (x; ) = (3; 5)

a: Khi m=2 thì pt sẽ là x^2-6x-3=0
=>\(x=3\pm2\sqrt{3}\)


Thay x = -3, y = 31/5 vào vế trái của phương trình (2), ta được:
VT = -3.(-3) + 2.31/5 = 9 + 62/5 = 107/5 ≠ 22 = VP
Vậy (x; y) = (-3; 31/5 ) không phải là nghiệm của phương trình (2).
Hệ phương trình đã cho vô nghiệm.

a) Cách giải các phương trình lượng giác cơ bản:
+ Phương trình sin x = a.
Nếu |a| > 1 ⇒ phương trình vô nghiệm.
Nếu |a| ≤ 1 ⇒ tìm một cung α sao cho sin α = a.
Khi đó phương trình trở thành sin x = sin α
⇒ Phương trình có nghiệm: 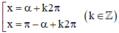
+ Phương trình cos x = a.
Nếu |a| > 1 ⇒ phương trình vô nghiệm.
Nếu |a| ≤ 1 ⇒ tìm một cung α sao cho cos α = a.
Khi đó phương trình trở thành cos x = cos α.
⇒ Phương trình có nghiệm: x = ±α + k2π (k ∈ Z).
+ Phương trình tan x = a.
Tìm một cung α sao cho tan α = a.
Khi đó phương trình trở thành tan x = tan α.
⇒ Phương trình có nghiệm x = α + kπ (k ∈ Z).
+ Phương trình cot x = a
Tìm một cung α sao cho cot α = a.
Khi đó phương trình trở thành cot x = cot α.
⇒ Phương trình có nghiệm x = α + kπ (k ∈ Z).
b) Cách giải phương trình a.sin x + b.cos x = c.
+ Nếu a = 0 hoặc b = 0 ⇒ Phương trình lượng giác cơ bản .
+ a ≠ 0 và b ≠ 0. Chia cả hai vế của phương trình cho  ta được:
ta được:

Ta giải phương trình trên như phương trình lượng giác cơ bản.

\(x^2-\left(2-\sqrt{3}\right)x-2\sqrt{3}=0\)
\(\Delta=\left[-\left(2-\sqrt{3}\right)^2\right]-4\left(-2\sqrt{3}\right)\)
\(=\left(4-4\sqrt{3}+3\right)+8\sqrt{3}=7+4\sqrt{3}=\sqrt{3}^2+2.2.\sqrt{3}+2^2=\left(\sqrt{3}+2\right)^2>0\)
=> pt có 2 nghiệm phân biệt
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1=\dfrac{2-\sqrt{3}-\sqrt{3}-2}{2}=\dfrac{-2\sqrt{3}}{2}=-\sqrt{3}\\x_2=\dfrac{2-\sqrt{3}+\sqrt{3}+2}{2}=\dfrac{4}{2}=2\end{matrix}\right.\)

a) Sai lầm là coi -2 là hạng từ và chuyển vế hạng tử này trong khi -2 là một nhân tử.
Lời giải đúng:
-2x > 23
⇔ x < 23 : (-2) (chia cho số âm nên đổi chiều)
⇔ x < -11,5
Vậy nghiệm của bất phương trình là x < -11,5
b) Sai lầm là nhân hai vế của bất phương trình với 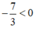 mà không đổi chiều bất phương trình.
mà không đổi chiều bất phương trình.
Lời giải đúng:
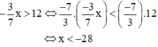
Vậy nghiệm của bất phương trình là x < -28

1. a = 3 thì phương trình trở thành:
\(\frac{x+3}{3-x}-\frac{x-3}{3+x}=\frac{-3\left[3.\left(-3\right)+1\right]}{\left(-3\right)^2}-x^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{\left(x+3\right)^2+\left(3-x\right)^2}{\left(3-x\right)\left(3+x\right)}=\frac{-3\left[-9+1\right]}{9}-x^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{x^2+6x+9+x^2-6x+9}{\left(3-x\right)\left(3+x\right)}=\frac{-3.\left(-8\right)}{9}-x^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{2x^2+18}{9-x^2}=\frac{24}{9}-x^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{2x^2+18}{9-x^2}+x^2=\frac{24}{9}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{2x^2+18+9x^2-x^4}{9-x^2}=\frac{24}{9}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{11x^2+18-x^4}{9-x^2}=\frac{24}{9}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow99x^2+18-9x^4=216-24x^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow9x^4-123x^2+198=0\)
Đặt \(x^2=t\left(t\ge0\right)\)
Phương trình trở thành \(9t^2-123t+198=0\)
Ta có \(\Delta=123^2-4.9.198=8001,\sqrt{\Delta}=3\sqrt{889}\)
\(\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}t=\frac{123+3\sqrt{889}}{18}=\frac{41+\sqrt{889}}{6}\\t=\frac{123-3\sqrt{889}}{18}=\frac{41-\sqrt{889}}{6}\end{cases}}\)
Lúc đó \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x^2=\frac{41+\sqrt{889}}{6}\\x^2=\frac{41-\sqrt{889}}{6}\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=\pm\sqrt{\frac{41+\sqrt{889}}{6}}\\x=\pm\sqrt{\frac{41-\sqrt{889}}{6}}\end{cases}}\)
Vậy pt có 4 nghiệm \(S=\left\{\pm\sqrt{\frac{41+\sqrt{889}}{6}};\pm\sqrt{\frac{41-\sqrt{889}}{6}}\right\}\)

a: x^2-mx+m-1=0
Khi m=5 thì (1) sẽ là x^2-5x+4=0
=>x=1 hoặc x=4
b:Δ=(-m)^2-4(m-1)=m^2-4m+4=(m-2)^2
Để phươg trình có 2 nghiệm phân biệt thì m-2<>0
=>m<>2
x2=2x1
x2+x1=m
=>3x1=m và x2=2x1
=>x1=m/3 và x2=2/3m
x1*x2=m-1
=>2/9m^2-m+1=0
=>2m^2-9m+9=0
=>2m^2-3m-6m+9=0
=>(2m-3)(m-3)=0
=>m=3 hoặc m=3/2
iải phương trình gì
Đề đâu
Dora Nichow
ngu loz