giải phương trình: (x2 + 1)2 + 3x(x2 + 1) + 2x2 = 0
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Bài 1:
a: \(\Leftrightarrow x^2-5x+6< =0\)
=>(x-2)(x-3)<=0
=>2<=x<=3
b: \(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-6\right)^2< =0\)
=>x=6
c: \(\Leftrightarrow x^2-2x+1>=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)^2>=0\)
hay \(x\in R\)

1) Ta có: \(x^2-4x+4=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-2=0\)
hay x=2
Vậy: S={2}

2:
\(A=\dfrac{x_2-1+x_1-1}{x_1x_2-\left(x_1+x_2\right)+1}\)
\(=\dfrac{3-2}{-7-3+1}=\dfrac{1}{-9}=\dfrac{-1}{9}\)
B=(x1+x2)^2-2x1x2
=3^2-2*(-7)
=9+14=23
C=căn (x1+x2)^2-4x1x2
=căn 3^2-4*(-7)=căn 9+28=căn 27
D=(x1^2+x2^2)^2-2(x1x2)^2
=23^2-2*(-7)^2
=23^2-2*49=431
D=9x1x2+3(x1^2+x2^2)+x1x2
=10x1x2+3*23
=69+10*(-7)=-1

a) Ta có: \(2x^2-3x-2=0\)
nên a=2; b=-3 và c=-2
Vì \(x_1\) và \(x_2\) là nghiệm của phương trình \(2x^2-3x-2=0\) nên Áp dụng hệ thức Viet, ta có:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=\dfrac{-b}{a}=\dfrac{3}{2}\\x_1\cdot x_2=-\dfrac{2}{2}=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Ta có: \(x_1\cdot x_2=-1\)
nên \(2\cdot x_1\cdot x_2=-2\)
Ta có: \(\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2=\left(\dfrac{3}{2}\right)^2=\dfrac{9}{4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x_1^2+x_2^2+2\cdot x_1\cdot x_2=\dfrac{9}{4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x_1^2+x_2^2=\dfrac{9}{4}+2=\dfrac{17}{4}\)

a) Ta có: \(x^2-11x-26=0\)
nên a=1; b=-11; c=-26
Áp dụng hệ thức Viet, ta được:
\(x_1+x_2=\dfrac{-b}{a}=\dfrac{-\left(-11\right)}{1}=11\)
và \(x_1x_2=\dfrac{c}{a}=\dfrac{-26}{1}=-26\)

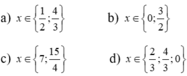
\(\left(x^2+1\right)^2+3x\left(x^2+1\right)+2x^2=0\)
\(\left(x^4+2x^2+1\right)+3x^3+3x+2x^2=0\)
\(x^4+2x^2+1+3x^3+3x+2x^2=0\)
\(x^4+4x^2+1+3x^3+3x=0\)
\(\left(x+1\right)\left(x^3+2x^2+2x+1\right)=0\)
\(\left(x+1\right)\left(x+1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)=0\)
\(\orbr{\begin{cases}x+1=0\Rightarrow x=\left(-1\right)\\x^2+x+1=0\left(vôlí\right)\end{cases}}\)
x= -1
\(\left(x^2+1\right)^2+3x\left(x^2+1\right)+2x^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2+1\right)^2+x\left(x^2+1\right)+2x\left(x^2+1\right)+2x^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2+1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)+2x\left(x^2+x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2+2x+1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)^2\left(x^2+x+1\right)=0\Rightarrow x=-1\)