4x2 + 8x + 12 = 8
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

x3-4x2+8x-8
=(x3-4x2+8x-4)-4
giải tiếp hộ mik vs

\(x^3-4x^2+8x-8\)
\(=x^3-2x^2+4x-2x^2+4x-8\)
\(=\left(x^3-2x^2+4x\right)-\left(2x^2-4x+8\right)\)
\(=x\left(x^2-2x+4\right)-2\left(x^2-2x+4\right)\)
\(=\left(x^2-2x+4\right)\left(x-2\right)\)

\(\left(8x+12-4x^2\right):\left(x-3\right)=\left[4x\left(x-3\right)+20\left(x-3\right)+72\right]:\left(x-3\right)=\left[\left(x-3\right)\left(4x+20\right)+72\right]:\left(x-3\right)=4x+20R72\)

\(x^3-4x^2+8x-8\\ =x^3-2x^2+4x-2x^2+4x-8\\ =x\left(x^2-2x+4\right)-2\left(x^2-2x+4\right)\\ =\left(x-2\right)\left(x^2-2x+4\right)\)
Để giải phương trình đa thức x^3 - 4x^2 + 8x - 8, ta có thể sử dụng phương pháp nhân thức tìm nghiệm.
Đầu tiên, ta kiểm tra x = 1 có phải là nghiệm của phương trình hay không bằng cách thay x = 1 vào phương trình:
(1)^3 - 4(1)^2 + 8(1) - 8 = 1 - 4 + 8 - 8 = -3
Vì kết quả không bằng 0, nên x = 1 không phải là nghiệm của phương trình.
Tiếp theo, ta sử dụng phương pháp chia đa thức để tìm nghiệm. Ta chia đa thức x^3 - 4x^2 + 8x - 8 cho (x - 2) bằng cách sử dụng phép chia đa thức.
x^2 - 2x + 4x - 2 | x^3 - 4x^2 + 8x - 8 - (x^3 - 2x^2) --------------- -2x^2 + 8x + ( -2x^2 + 4x) --------------- 4x - 8 - (4x - 8) ------------ 0
Khi chia x^3 - 4x^2 + 8x - 8 cho (x - 2), ta thu được kết quả là x^2 - 2x + 4.
Vậy phương trình có thể viết lại dưới dạng:
(x - 2)(x^2 - 2x + 4) = 0
Để tìm các nghiệm của phương trình, ta giải các đa thức nhỏ hơn.
Từ x^2 - 2x + 4 = 0, ta có thể sử dụng công thức giải phương trình bậc hai:
x = (2 ± √(2^2 - 4(1)(4))) / (2(1)) = (2 ± √(-12)) / 2 = (2 ± 2i√3) / 2 = 1 ± i√3
Vậy phương trình có 3 nghiệm là x = 2, x = 1 + i√3 và x = 1 - i√3.

\(x^6+2x^3+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^3\right)^2+2x^3+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^3+1\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3=\left(-1\right)^3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-1\)
___________
\(x\left(x-5\right)=4x-20\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x-5\right)-4\left(x-5\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-5\right)\left(x-4\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=4\\x=5\end{matrix}\right.\)
_____________
\(x^4-2x^2=8-4x^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2\left(x^2-2\right)+\left(4x^2-8\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2\left(x^2-2\right)+4\left(x^2-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-2\right)\left(x^2+4\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\pm\sqrt{2}\)
_______________
\(\left(x^3-x^2\right)-4x^2+8x-4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2\left(x-1\right)-4\left(x^2-2x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2\left(x-1\right)-4\left(x-1\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2-4x+4\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x-2\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=2\end{matrix}\right.\)

a) \(4x^2-16+\left(3x+12\right)\left(4-2x\right)\)
\(=\left(2x-4\right)\left(2x+4\right)-3\left(x+4\right)\left(2x-4\right)\)
\(=\left(2x-4\right)\left(2x+4-3x-12\right)\)
\(=-\left(2x-4\right)\left(x+8\right)\)
b) \(x^3+x^2y-15x-15y\)
\(=x^2\left(x+y\right)-15\left(x+y\right)\)
\(=\left(x+y\right)\left(x^2-15\right)\)
c) \(3\left(x+8\right)-x^2-8x\)
\(=3\left(x+8\right)-x\left(x+8\right)\)
\(=\left(x+8\right)\left(3-x\right)\)
d) \(x^3-3x^2+1-3x\)
\(=x^3+1-3x^2-3x\)
\(=\left(x+1\right)\left(x^2-x+1\right)-3x\left(x+1\right)\)
\(=\left(x+1\right)\left(x^2-x+1-3x\right)\)
\(=\left(x+1\right)\left(x^2-4x+1\right)\)
d) \(5x^2-5y^2-20x+20y\)
\(=5\left(x^2-y^2\right)-20\left(x-y\right)\)
\(=5\left(x-y\right)\left(x+y\right)-20\left(x-y\right)\)
\(=5\left(x-y\right)\left(x+y-4\right)\)

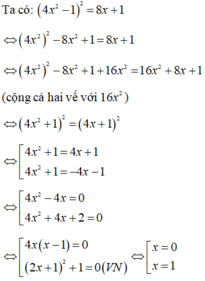
Tập nghiệm của phương trình là S = {0; 1}
Suy ra nghiệm lớn nhất của phương trình là x 0 = 1 < 2
Đáp án cần chọn là B

a) Ta có: 8 > 4 nên để 8x > 4x thì x > 0
Do đó, chỉ đúng khi x > 0 (hay nói cách khác nếu x < 0 thì a sai)
b) Ta có: 4 < 8 nên để 4x > 8x thì x < 0 .
Do đó, khẳng định chỉ đúng khi x < 0
c) chỉ đúng khi x ≠ 0
d) Ta có: 8 > 4 nên với mọi x thì 8+ x > 4+ x ( tính chất cộng hai vế của BĐT với 1 số)
Do đó, khẳng định đúng với mọi x.
Vậy khẳng định d là đúng với mọi giá trị của x.
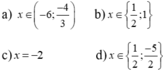
\(4x^2+8x+12-8=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x^2+8x+4=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x+2\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x+2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x=-2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-1\)
\(\left(\left(2^2x^2-8x\right)+12\right)-8=0\)
\(4x^2-8x+4=4\cdot\left(x^2-2x+1\right)\)
\(4\cdot\left(x-1\right)^2=0\)
\(\left(x-1\right)^2=0\)
\(x=1\)