Tìm giá trị của x để A < 0
A = x2+ 3x / (x - 3 ) .3x2
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Bài 1:
a) Ta có: \(P=1+\dfrac{3}{x^2+5x+6}:\left(\dfrac{8x^2}{4x^3-8x^2}-\dfrac{3x}{3x^2-12}-\dfrac{1}{x+2}\right)\)
\(=1+\dfrac{3}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x+3\right)}:\left(\dfrac{8x^2}{4x^2\left(x-2\right)}-\dfrac{3x}{3\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}-\dfrac{1}{x+2}\right)\)
\(=1+\dfrac{3}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x+3\right)}:\left(\dfrac{4}{x-2}-\dfrac{x}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}-\dfrac{1}{x+2}\right)\)
\(=1+\dfrac{3}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x+3\right)}:\dfrac{4\left(x+2\right)-x-\left(x-2\right)}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}\)
\(=1+\dfrac{3}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x+3\right)}\cdot\dfrac{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}{4x+8-x-x+2}\)
\(=1+3\cdot\dfrac{\left(x-2\right)}{\left(x+3\right)\left(2x+10\right)}\)
\(=1+\dfrac{3\left(x-2\right)}{\left(x+3\right)\left(2x+10\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{\left(x+3\right)\left(2x+10\right)+3\left(x-2\right)}{\left(x+3\right)\left(2x+10\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{2x^2+10x+6x+30+3x-6}{\left(x+3\right)\left(2x+10\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{2x^2+19x-6}{\left(x+3\right)\left(2x+10\right)}\)

\(1,\\ a,\dfrac{x^2}{x+1}+\dfrac{x}{x+1}=\dfrac{x^2+x}{x+1}=\dfrac{x\left(x+1\right)}{x+1}=x\)
\(b,\left(\dfrac{2xy}{x^2-y^2}+\dfrac{x-y}{2x+2y}\right):\dfrac{x+y}{2x}=\left(\dfrac{4xy}{2\left(x-y\right)\left(x+y\right)}+\dfrac{\left(x-y\right)^2}{2\left(x-y\right)\left(x+y\right)}\right).\dfrac{2x}{x+y}=\dfrac{4xy+x^2-2xy+y^2}{2\left(x-y\right)\left(x+y\right)}.\dfrac{2x}{x+y}=\dfrac{2x\left(x^2+2xy+y^2\right)}{2\left(x-y\right)\left(x+y\right)^2}=\dfrac{2x\left(x+y\right)^2}{2\left(x-y\right)\left(x+y\right)^2}=\dfrac{x}{x-y}\)

\(f\left(x\right)⋮g\left(x\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^4-3x^3+4x^2-x^2+3x-4+\left(a-3\right)x+\left(b+4\right)⋮x^2-3x+4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(a,b\right)=\left(3;-4\right)\)

c) Để A nhận giá trị nguyên khi và chỉ khi:
![]()
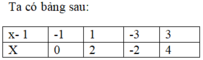
Kết hợp với điều kiện, tập hợp các giá trị của x nguyên để A nguyên là: {0; 2; -2; 4}.

a) Thay \(a=0\) vào phương trình, ta được:
\(x^2-2x-3=0\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=3\\x=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy ...
b) Ta có: \(\Delta'=4-3a\)
Để phương trình có 2 nghiệm x1 và x2 \(\Leftrightarrow\Delta'\ge0\) \(\Leftrightarrow a\le\dfrac{4}{3}\)
Vậy ...
c) Phương trình có nghiệm bằng -1
\(\Rightarrow1+2\left(1-a\right)+a^2+a-3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow a^2-a=0\) \(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}a=1\\a=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy ...
pt: \(x^2+2\left(a-1\right)x+a^2+a-3=0\) (1)
a) khi a=0 pt(1) \(\Leftrightarrow x^2-2x-3=0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-1\\x=3\end{matrix}\right.\)
b) \(\Delta'=b'^2-ac=\left(a-1\right)^2-\left(a^2+a-3\right)=-3a+4\)
phương trình có 2 nghiệm phân biệt khi \(\Delta'>0\Leftrightarrow-3a+4>0\Leftrightarrow a< \dfrac{4}{3}\)
c) pt(1) có nghiệm x=-1 \(\Leftrightarrow\left(-1\right)^2+2\left(a-1\right).\left(-1\right)+a^2+a-3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow a^2-a=0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}a=0\\a=1\end{matrix}\right.\)

a, ĐKXĐ:\(x-1\ne0\Rightarrow x\ne1\)
b, \(\dfrac{3x^2+3x}{x-1}=0\\ \Rightarrow3x^2+3x=0\\ \Rightarrow3x\left(x+1\right)=0\\ \Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)