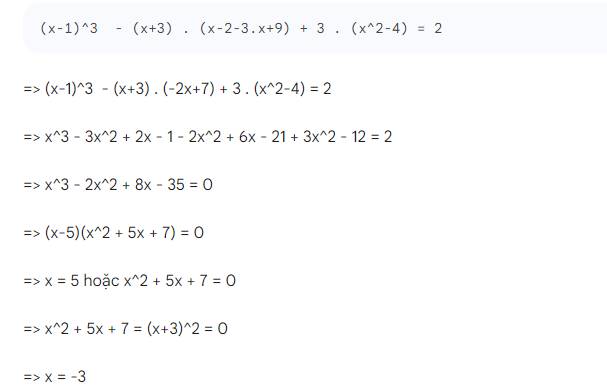Tìm x biết \(^{^{\left(x-2\right)^2}}\)(x+1)(x-4)<0
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


1: Ta có: \(4x^2-36=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=3\\x=-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
2: Ta có: \(\left(x-1\right)^2+x\left(4-x\right)=11\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-2x+1+4x-x^2=11\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x=10\)
hay x=5

Đặt \(t=\left(x+\frac{1}{x}\right)^2\)\(\Rightarrow\)\(x^2+\frac{1}{x^2}=t-2\)điều kiện t>=0,x # 0
Phương trình trở thành
8t +4(t-2)2 - 4(t-2)2t =(x+4)2
8t + 4t2 - 16t + 16 -4t3 + 16t2 - 16t=(x+4)2
-4t3 + 20t2 -24t=x2 +8x
-4t(t2 -5t +6)=x(x+8)
-4t(t-2)(t-3)=x(x+8)
Mình chỉ giúp dược tới đó

a/ \(x=\dfrac{-5}{12}\)
b/ \(x\approx-1,9526\)
c/ \(x=\dfrac{21-i\sqrt{199}}{10}\)
d/ \(x=\dfrac{-20}{13}\)

\(\left|x-1\right|+2\left|x-2\right|+3\left|x-3\right|+4\left|x-4\right|+5\left|x-5\right|+20x=0\left(1\right)\)
TH1: x<1
(1) trở thành 1-x+2(2-x)+3(3-x)+4(4-x)+5(5-x)+20x=0
=>\(1-x+4-2x+9-3x+16-4x+25-5x+20x=0\)
=>\(5x+55=0\)
=>x=-11(nhận)
TH2: 1<=x<2
Phương trình (1) sẽ trở thành:
\(x-1+2\left(2-x\right)+3\left(3-x\right)+4\left(4-x\right)+5\left(5-x\right)+20x=0\)
=>\(x-1+4-2x+9-3x+16-4x+25-5x+20x=0\)
=>\(7x+53=0\)
=>\(x=-\dfrac{53}{7}\left(loại\right)\)
TH3: 2<=x<3
Phương trình (1) sẽ trở thành:
\(x-1+2\left(x-2\right)+3\left(3-x\right)+4\left(4-x\right)+5\left(5-x\right)+20x=0\)
=>\(x-1+2x-4+9-3x+16-4x+25-5x+20x=0\)
=>\(11x+45=0\)
=>\(x=-\dfrac{45}{11}\left(loại\right)\)
TH4: 3<=x<4
Phương trình (1) sẽ trở thành:
\(x-1+2\left(x-2\right)+3\left(x-3\right)+4\left(4-x\right)+5\left(5-x\right)+20x=0\)
=>\(x-1+2x-4+3x-9+16-4x+25-5x+20x=0\)
=>\(-3x+27=0\)
=>x=9(loại)
TH5: 4<=x<5
Phương trình (1) sẽ trở thành:
\(\left(x-1\right)+2\left(x-2\right)+3\left(x-3\right)+4\left(x-4\right)+5\left(5-x\right)+20x=0\)
=>\(x-1+2x-4+3x-9+4x-16+25-5x+20x=0\)
=>\(25x-5=0\)
=>x=1/5(loại)
TH6: x>=5
Phương trình (1) sẽ trở thành:
\(\left(x-1\right)+2\left(x-2\right)+3\left(x-3\right)+4\left(x-4\right)+5\left(x-5\right)+20x=0\)
=>\(x-1+2x-4+3x-9+4x-16+5x-25+20x=0\)
=>35x-55=0
=>x=55/35(loại)

a: \(A=\dfrac{x-2-2x-4+x}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}\cdot\dfrac{-\left(x-2\right)\left(x+1\right)}{6\left(x+2\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{-6}{\left(x+2\right)}\cdot\dfrac{-\left(x+1\right)}{6\left(x+2\right)}=\dfrac{\left(x+1\right)}{\left(x+2\right)^2}\)
b: A>0
=>x+1>0
=>x>-1
c: x^2+3x+2=0
=>(x+1)(x+2)=0
=>x=-2(loại) hoặc x=-1(loại)
Do đó: Khi x^2+3x+2=0 thì A ko có giá trị

(x-1)^3-(x+3)(x^2-3x+9)+3(x^2-4)=2
=>x^3-3x^2+3x-1-x^3-27+3x^2-12=2
=>3x-40=2
=>x=42/3=14

rút 4 ra ngoài nhan bạn 4(2(x+1/x)^2+(x^2+1/x^2)^2-(x^2+1/x^2)(x+1/x)^2=(x+4)^2
mik xét cái này cho dễ nhìn nhan
2(x+1/x)^2-(x^2+1/x^2)(x+1/x)^2
= (x+1/x)^2(2-x^2-1/x^2)
= -(x+1/x)^2(x^2-2+1/x^2)
= -(x+1/x)^2(x-1/x)^2=-(x^2-1/x^2)^2
thế ở trên ta có
4(-(x^2-1/x^2)^2+(x^2+1/x^2)^2)=(x+4)^2
4(-x^4+2-1/x^4+x^4+2+1/x^4)=x^2+8x+16
4.4=x^2+8x+16
suy ra x^2+8x=0
x(x+8)=0
suy ra x=0 hoặc x=-8
mak nhìn để bài thì x=0 ko được nên x=-8

B1: ĐXXĐ: \(x\ne\pm2;x\ne-1\)
\(=\left(\dfrac{x-2}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)}-\dfrac{2\left(x+2\right)}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)}+\dfrac{x}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)}\right):\dfrac{-6\left(x+2\right)}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+1\right)}\)
\(=\left(\dfrac{x-2-2x-2+x}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)}\right):\dfrac{-6\left(x+2\right)}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+1\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{-4}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)}:\dfrac{-6\left(x+2\right)}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+1\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{-4}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)}.\dfrac{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+1\right)}{-6\left(x+2\right)}=\dfrac{2\left(x+1\right)}{3\left(x+2\right)^2}\)
b, \(A=\dfrac{2\left(x+1\right)}{3\left(x+2\right)^2}>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x+2>0\) (vì \(3\left(x+2\right)^2\ge0\forall x\))
\(\Leftrightarrow x>-1\).
-Vậy \(x\in\left\{x\in Rlx>-1;x\ne2\right\}\) thì \(A>0\).