
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


ta có : x^5+2x^4+3x^3+3x^2+2x+1=0
\(\Leftrightarrow\)x^5+x^4+x^4+x^3+2x^3+2x^2+x^2+x+x+1=0
\(\Leftrightarrow\)(x^5+x^4)+(x^4+x^3)+(2x^3+2x^2)+(x^2+x)+(x+1)=0
\(\Leftrightarrow\)x^4(x+1)+x^3(x+1)+2x^2(x+1)+x(x+1)+(x+1)=0
\(\Leftrightarrow\)(x+1)(x^4+x^3+2x^2+x+1)=0
\(\Leftrightarrow\)(x+1)(x^4+x^3+x^2+x^2+x+1)=0
\(\Leftrightarrow\)(x+1)[x^2(x^2+x+1)+(x^2+x+1)]=0
\(\Leftrightarrow\)(x+1)(x^2+x+1)(x^2+1)=0
VÌ x^2+x+1=(x+\(\dfrac{1}{2}\))^2+\(\dfrac{3}{4}\)\(\ne0\) và x^2+1\(\ne0\)
\(\Rightarrow\)x+1=0
\(\Rightarrow\)x=-1
CÒN CÂU B TỰ LÀM (02042006)
b: x^4+3x^3-2x^2+x-3=0
=>x^4-x^3+4x^3-4x^2+2x^2-2x+3x-3=0
=>(x-1)(x^3+4x^2+2x+3)=0
=>x-1=0
=>x=1

Đặt 3-x = a ; 2-x = b
=> 5-2x = a+b
pt <=> a^4+b^4 = (a+b)^4 = a^4+4a^3b+6a^2b^2+4ab^3+b^4
<=> a^4+4a^3b+6a^2b^2+4ab^3+b^4-a^4-b^4 = 0
<=> 4a^3b+6a^2b^2+4ab^3 = 0
<=> 2a^3b+3a^2b^2+2ab^3 = 0
<=> ab.(2a^2+3ab+2b^2) = 0
<=> ab=0 ( vì 2a^2+3ab+2b^2 > 0 )
<=> a=0 hoặc b=0
<=> 3-x=0 hoặc 2-x=0
<=> x=3 hoặc x=2
Vậy .............
Tk mk nha

\(\left(2x+4\right)\left(x-3\right)-\left(x+2\right)\left(x-4\right)=x\left(x+5\right)\)
\(2\left(x+2\right)\left(x-3\right)-\left(x+2\right)\left(x-4\right)=x\left(x+5\right)\)
\(\left(x+2\right)\left(2x-6-x+4\right)=x\left(x+5\right)\)
\(\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)-x^2-5x=0\)
\(x^2-2x+2x-4-x^2-5x=0\)
\(-5x-4=0\)
\(-5x=4\)
\(\Rightarrow\)\(x=\frac{-4}{5}\)
\(\left(x-2\right)^2=\left(2x-4\right)\left(x+5\right)\)
\(\left(x-2\right)^2-2\left(x-2\right)\left(x+5\right)=0\)
\(\left(x-2\right)\left(x-2-2x-10\right)=0\)
\(\left(x-2\right)\left(-x-12\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(\orbr{\begin{cases}x-2=0\\-x-12=0\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=2\\x=-12\end{cases}}}\)
Bạn tự kết luận 2 câu nhé

Giải phương trình:
\(\left(x+3\right)^4+\left(x+5\right)^4=2\) \(\left(\text{1}\right)\)
Đặt \(y=x+4\), khi đó phương trình \(\left(\text{1}\right)\) trở thành:
\(\left(y-1\right)^4+\left(y+1\right)^4=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(y^4-4y^3+6y^2-4y+1+y^4+4y^3+6y^2+4y+1=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(2y^4+12y^2+2=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(y^4+6y^2+1=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(y^4+6y^2+9-9=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(\left(y^2+3\right)^2-3^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(y^2\left(y^2+6\right)=0\) \(\left(\text{1'}\right)\)
Vì \(y^2\ge0\) nên \(y^2+6\ge6>0\) nên từ \(\left(\text{1'}\right)\) suy ra \(y^2=0\), tức là \(\left(x+4\right)^2=0\) \(\Leftrightarrow\) \(x+4=0\) \(\Leftrightarrow\) \(x=-4\)
Vậy, tập nghiệm của pt là \(S=\left\{-4\right\}\)

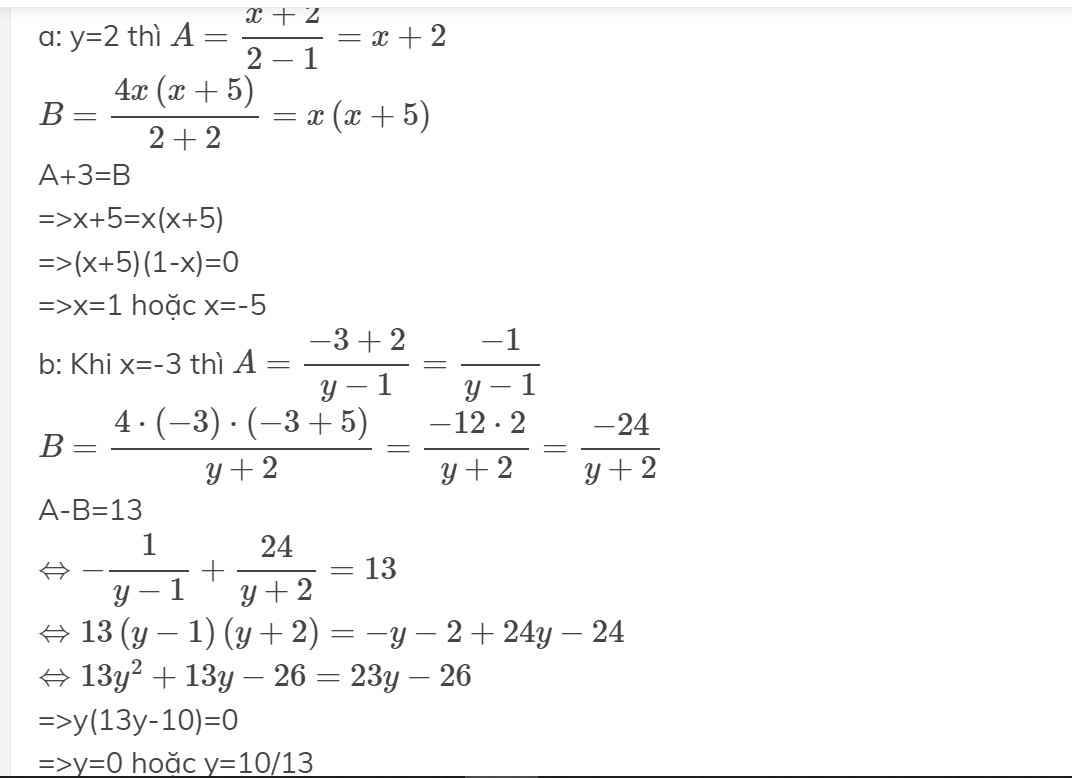
a: y=2 thì \(A=\dfrac{x+2}{2-1}=x+2\)
\(B=\dfrac{4x\left(x+5\right)}{2+2}=x\left(x+5\right)\)
A+3=B
=>x+5=x(x+5)
=>(x+5)(1-x)=0
=>x=1 hoặc x=-5
b: Khi x=-3 thì \(A=\dfrac{-3+2}{y-1}=\dfrac{-1}{y-1}\)
\(B=\dfrac{4\cdot\left(-3\right)\cdot\left(-3+5\right)}{y+2}=\dfrac{-12\cdot2}{y+2}=\dfrac{-24}{y+2}\)
A-B=13
\(\Leftrightarrow-\dfrac{1}{y-1}+\dfrac{24}{y+2}=13\)
\(\Leftrightarrow13\left(y-1\right)\left(y+2\right)=-y-2+24y-24\)
\(\Leftrightarrow13y^2+13y-26=23y-26\)
=>y(13y-10)=0
=>y=0 hoặc y=10/13

a, Ta có : \(3\left(x-1\right)-2\left(x+3\right)=-15\)
=> \(3x-3-2x-6=-15\)
=> \(3x-3-2x-6+15=0\)
=> \(x=-6\)
Vậy phương trình có nghiệm là x = -6 .
b, Ta có : \(3\left(x-1\right)+2=3x-1\)
=> \(3x-3+2=3x-1\)
=> \(3x-3+2-3x+1=0\)
=> \(0=0\)
Vậy phương trình có vô số nghiệm .
c, Ta có : \(7\left(2-5x\right)-5=4\left(4-6x\right)\)
=> \(14-35x-5=16-24x\)
=> \(14-35x-5-16+24x=0\)
=> \(-35x+24x=7\)
=> \(x=\frac{-7}{11}\)
Vậy phương trình có nghiệm là \(x=\frac{-7}{11}\) .
Bài 2 :
a, Ta có : \(\frac{x}{30}+\frac{5x-1}{10}=\frac{x-8}{15}-\frac{2x+3}{6}\)
=> \(\frac{x}{30}+\frac{3\left(5x-1\right)}{30}=\frac{2\left(x-8\right)}{30}-\frac{5\left(2x+3\right)}{30}\)
=> \(x+3\left(5x-1\right)=2\left(x-8\right)-5\left(2x+3\right)\)
=> \(x+15x-3=2x-16-10x-15\)
=> \(x+15x-3-2x+16+10x+15=0\)
=> \(24x+28=0\)
=> \(x=\frac{-28}{24}=\frac{-7}{6}\)
Vậy phương trình có nghiệm là \(x=\frac{-7}{6}\) .
b, Ta có : \(\frac{x+4}{5}-x+4=\frac{x}{3}-\frac{x-2}{2}\)
=> \(\frac{6\left(x+4\right)}{30}-\frac{30x}{30}+\frac{120}{30}=\frac{10x}{30}-\frac{15\left(x-2\right)}{30}\)
=> \(6\left(x+4\right)-30x+120=10x-15\left(x-2\right)\)
=> \(6x+24-30x+120=10x-15x+30\)
=> \(6x+24-30x+120-10x+15x-30=0\)
=> \(-19x+114=0\)
=> \(x=\frac{-114}{-19}=6\)
Vậy phương trình có nghiệm là x = 6 .


Đặt \(a=x+4\).
Ta có: \(\left(a-1\right)^4+\left(a+1\right)^4=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(a^4-4a^3+6a^2-4a+1\right)+\left(a^4+4a^3+6a^2+4a+1\right)=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2a^4+12a^2+2=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow a^4+6a^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow a^2\left(a^2+6\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow a^2=0\)
\(\Rightarrow x+4=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-4\).
Đặt \(x+4=a\)
Khi đó ,PT tương đương với :
\(\left(a-1\right)^4+\left(a+1\right)^4=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow a^4-4a^3+6a^2-4a+1+a^4+4a^3+6a^2+4a+1=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2a^4+12a^2+2=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow a^4+6a^2+1=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow a^4+6a^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow a^2\left(a^2+6\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow a^2=0\)( do \(a^2+6>0\forall a\))
\(\Leftrightarrow a=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x+4=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-4\)
Vậy PT có 1 nghiệm duy nhất là : \(x=-4\)