
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


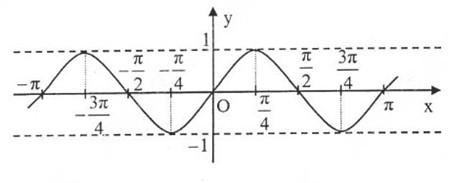
a) Tập xác định của hàm số là \(D = \mathbb{R}\)
Do đó, nếu x thuộc tập xác định D thì –x cũng thuộc tập xác định D
Ta có: \(f\left( { - x} \right) = \sin \left( { - x} \right) = - \sin x = - f\left( x \right),\;\forall x\; \in \;D\)
Vậy \(y = \sin x\) là hàm số lẻ.
b)
\(x\) | \( - \pi \) | \( - \frac{{3\pi }}{4}\) | \( - \frac{\pi }{2}\) | \( - \frac{\pi }{4}\) | 0 | \(\frac{\pi }{4}\) | \(\frac{\pi }{2}\) | \(\frac{{3\pi }}{4}\) | \(\pi \) |
\(\sin x\) | \(0\) | \( - \frac{{\sqrt 2 }}{2}\) | \( - 1\) | \( - \frac{{\sqrt 2 }}{2}\) | 0 | \(\frac{{\sqrt 2 }}{2}\) | 1 | \(\frac{{\sqrt 2 }}{2}\) | 0 |
c) Từ đồ thị trên, ta thấy hàm số \(y = \sin x\) có tập xác định là \(\mathbb{R}\), tập giá trị là [-1;1] và đồng biến trên mỗi khoảng \(\left( { - \frac{\pi }{2} + k2\pi ;\frac{\pi }{2} + k2\pi } \right)\) và nghịch biến trên mỗi khoảng \(\left( {\frac{\pi }{2} + k2\pi ;\frac{{3\pi }}{2} + k2\pi } \right),\;k\; \in \;\mathbb{Z}.\)

2, sin4x+cos5=0 <=> cos5x=cos\(\left(\frac{\pi}{2}+4x\right)\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=\frac{\pi}{2}+k2\pi\\x=-\frac{\pi}{18}+\frac{k2\pi}{9}\end{cases}\left(k\inℤ\right)}\)
ta có \(2\pi>0\Leftrightarrow k< >\frac{1}{4}\)do k nguyên nên nghiệm dương nhỏ nhất trong họ nghiệm \(\frac{\pi}{2}\)khi k=0
\(-\frac{\pi}{18}+\frac{k2\pi}{9}>0\Leftrightarrow k>\frac{1}{4}\)do k nguyên nên nghiệm dương nhỏ nhất trong họ nghiệm \(-\frac{\pi}{18}-\frac{k2\pi}{9}\)là \(\frac{\pi}{6}\)khi k=1
vậy nghiệm dương nhỏ nhất của phương trình là \(\frac{\pi}{6}\)
\(\frac{\pi}{2}+k2\pi< 0\Leftrightarrow k< -\frac{1}{4}\)do k nguyên nên nghiệm âm lớn nhất trong họ nghiệm \(\frac{\pi}{2}+k2\pi\)là \(-\frac{3\pi}{2}\)khi k=-1
\(-\frac{\pi}{18}+\frac{k2\pi}{9}< 0\Leftrightarrow k< \frac{1}{4}\)do k nguyên nên nghiệm âm lớn nhất trong họ nghiệm \(-\frac{\pi}{18}+\frac{k2\pi}{9}\)là \(-\frac{\pi}{18}\)khi k=0
vậy nghiệm âm lớn nhất của phương trình là \(-\frac{\pi}{18}\)

a) Tập giá trị của hàm số\(y = \sin x\) là \(\left[ { - 1;1} \right]\)
b) Đồ thị hàm số \(y = \sin x\) nhận O là tâm đối xứng.
Như vậy hàm số \(y = \sin x\) là hàm số lẻ.
c) Bằng cách dịch chuyển đồ thị hàm số \(y = \sin x\) trên đoạn \(\left[ { - \pi ;\pi } \right]\) song song với trục hoành sang phải theo đoạn có độ dài \(2\pi \), ta nhận được đồ thị hàm số \(y = \sin x\) trên đoạn \(\left[ {\pi ;3\pi } \right]\)
Như vậy, hàm số \(y = \sin x\) có tuần hoàn .
d) Hàm số \(y = \sin x\) đồng biến trên mỗi khoảng \(\left( { - \frac{\pi }{2} + k2\pi ;\frac{\pi }{2} + k2\pi } \right)\), nghịch biến trên mỗi khoảng \(\left( {\frac{\pi }{2} + k2\pi ;\frac{{3\pi }}{2} + k2\pi } \right)\) với \(k \in Z\)

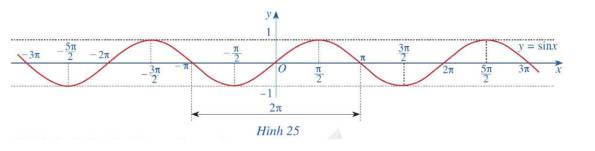
Đồ thị hàm số y = sin x trên đoạn [-2π, 2π]
Dựa vào đồ thị hàm số y = sinx
a) Những giá trị của x ∈ [−3π2,2π][−3π2,2π] để hàm số y = sin x nhận giá trị bằng -1 là:
x=−π2;x=3π2x=−π2;x=3π2
b) Những giá trị của x ∈ [−3π2,2π][−3π2,2π] để hàm số y = sin x nhận giá trị âm là:
x ∈ (-π, 0) ∪ (π, 2 π)

a. \(sin\left(4x+\pi\right)=sin35^o\)
\(\Leftrightarrow sin\left(4x+180^o\right)=sin35^o\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}4x+180^o=35^o+k.360^o,k\in Z\\4x+180^o=180^o-35^o+k.360^o,k\in Z\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}4x=-145^o+k.360^o,k\in Z\\4x=-35^o+k.360^o,k\in Z\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-\frac{145^o}{4}+k.90,k\in Z\\x=-\frac{35^o}{4}+k.90^o,k\in Z\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy.....
b.\(sin4x=\frac{1}{5}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}4x=arcsin\left(\frac{1}{5}\right)+k2\pi,k\in Z\\4x=\pi-arcsin\left(\frac{1}{5}\right)+k2\pi,k\in Z\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\frac{arcsin\left(\frac{1}{5}\right)}{4}+\frac{k\pi}{2},k\in Z\\x=\frac{\pi}{4}-\frac{arcsin\left(\frac{1}{5}\right)}{4}+\frac{k\pi}{2},k\in Z\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy....
c. \(sin\left(x+\frac{8\pi}{7}\right)=3\)
Ta có: \(-1\le sinx\le1\)
\(\Rightarrow-1\le sin\left(3x+\frac{8\pi}{7}\right)\le1\)
Do đó phương trình trên vô nghiệm
d. \(sinx=-7\)
Ta có: \(-1\le sinx\le1\)
Do đó phương trình trên vô nghiệm
e. \(sin\left(3x+\pi\right)=sin\left(2x-3\pi\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}3x+\pi=2x-3\pi+k2\pi,k\in Z\\3x+\pi=\pi-2x+3\pi+k2\pi,k\in Z\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-4\pi+k2\pi,k\in Z\\5x=3\pi+k2\pi,k\in Z\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-4\pi+k2\pi,k\in Z\\x=\frac{3}{5}\pi+\frac{k2\pi}{5},k\in Z\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy......
f. \(sin\left(4x-\frac{\pi}{2}\right)=sin\left(\pi-2x\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}4x-\frac{\pi}{2}=\pi-2x+k2\pi,k\in Z\\4x-\frac{\pi}{2}=\pi-\pi+2x+k2\pi,k\in Z\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}6x=\frac{3}{2}\pi+k2\pi,k\in Z\\2x=\frac{\pi}{2}+k2\pi,k\in Z\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\frac{\pi}{4}+\frac{k\pi}{3},k\in Z\\x=\frac{\pi}{4}+k\pi,k\in Z\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy......



\(sin\left(-555^o\right)\)
\(=sin\left(720^o-555^o\right)\)
\(=sin165^o\)
\(=sin\left(180^o-165^o\right)\)
\(=sin\left(15^o\right)\)
\(=sin\left(45^o-30^o\right)\)
\(=sin\left(45^o\right)\cdot cos\left(30^o\right)-sin\left(30^o\right)\cdot cos\left(45\right)^o\)
\(=\dfrac{\sqrt{2}}{2}\cdot\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}-\dfrac{\sqrt{2}}{2}\cdot\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(=\dfrac{\sqrt{6}}{4}-\dfrac{\sqrt{2}}{4}\)
\(=\dfrac{\sqrt{6}-\sqrt{2}}{4}\)
-0.2588.