Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

Bài 1:
a) \(\frac{8^2.4^5}{2^{20}}=\frac{\left(2^3\right)^2.\left(2^2\right)^5}{2^{20}}=\frac{2^{16}}{2^{20}}=\frac{1}{2^4}=\frac{1}{16}\)
...
đăng nhìu bài z con định giết ta đó ak :(
bài 1
b,81^1*3^17/27^10*9^15 c.(0,25)^3*8 d,cô giáo chữa rồi
=(3^4)^11*3^17/(3^3)^10*(3^2)15 =(0,25)^3*2^3
=3^44*3^17/3^30*3^30 =(0,25*2)^3
=3^61/3^60 =(1/2)^3
=3 =1/8
bài 2
a,(x-1)^3=27 b,x^2+x
(x-1)^3=3^3 x*(x+1)=0
x-1=3 x=0 hoặc x+1=0
x=4 vậy x=0 hoặc -1
c,(2x+1)^2=25
(2x+1)^2=(+-5)^2
TH1 2x+1=5 TH2: 2x+1=-5 d,e đến lp làm
2x=5-1 2x=-5-1
2x=4 2x=-6
x=4/2 x=-6/2
x=2 x=-3

1.
\(f\left(x\right)=2x^4+6x^3+8x^2+12x+1\)
2.
\(h\left(x\right)=\left(2x^4+6x^3+8x^2+12x+1\right)-\left(2x^4+6x^3+17x^2+12x-26\right)\)
\(=-9x^2+27\)
3.
\(h\left(x\right)=0\Leftrightarrow-9x^2+27=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2=3\Rightarrow x=\pm\sqrt{3}\)

a: \(P\left(x\right)=6x^3+4x^2+2x-4\)
\(Q\left(x\right)=-x^4+6x^3-4x^2+3x-8\)
b: \(P\left(x\right)-Q\left(x\right)=x^4+8x^2-x+4\)
\(P\left(x\right)+Q\left(x\right)=-x^4+12x^3+5x-12\)

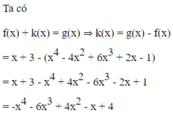
Nhận thấy số hạng có lũy thừa cao nhất của biến là - x 4 nên hệ số cao nhất là -1
Chọn đáp án A

