Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

\(\text{Câu 1: }\\ \text{Theo bài ra ta có : }x+y-z=10\\ \dfrac{x}{2}=\dfrac{y}{3}\Rightarrow\dfrac{x}{2}=\dfrac{4y}{12}\Rightarrow\dfrac{x}{8}=\dfrac{y}{12}\left(1\right)\\ \dfrac{y}{4}=\dfrac{z}{5}\Rightarrow\dfrac{3y}{12}=\dfrac{z}{5}\Rightarrow\dfrac{y}{12}=\dfrac{z}{15}\left(2\right)\\ \text{Từ }\left(1\right)\text{ và }\left(2\right)\text{ suy ra : }\dfrac{x}{8}=\dfrac{y}{12}=\dfrac{z}{15}\\ \text{ Áp dụng tính chất dãy tỉ số bằng nhau ta được : }\\ \dfrac{x}{8}=\dfrac{y}{12}=\dfrac{z}{15}=\dfrac{x+y-z}{8+12-15}=\dfrac{10}{5}=2\\ \Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{x}{8}=2\Rightarrow x=16\\\dfrac{y}{12}=2\Rightarrow y=24\\\dfrac{z}{15}=2\Rightarrow z=30\end{matrix}\right.\\ \text{Vậy }x=16\\ y=24\\ z=30\)
\(\text{Câu 2 : }\\ \text{Ta có : }\dfrac{x}{2}=\dfrac{y}{5}\\ \Rightarrow\left(\dfrac{x}{2}\right)^2=\left(\dfrac{y}{5}\right)^2=\dfrac{x}{2}\cdot\dfrac{y}{5}=\dfrac{xy}{2\cdot5}=\dfrac{7+3}{10}=\dfrac{10}{10}=1\\ \Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left(\dfrac{x}{2}\right)^2=1\Rightarrow\dfrac{x}{2}=1\Rightarrow x=2\\\left(\dfrac{y}{5}\right)^2=1\Rightarrow\dfrac{y}{5}=1\Rightarrow y=5\end{matrix}\right.\\ \text{Vậy }x=2\\ y=5\)
Câu 3 : \(\dfrac{\text{Giải}}{ }\)
Gọi số học sinh 4 khối \(6,7,8,9\) lần lượt là \(a;b;c;d\) \(\left(a;b;c;d\in N\text{*}\right)\) \(\left(em\right)\)
Theo bài ra ta có : \(b-d=70\)
\(a;b;c;d\) tỉ lệ với \(9;8;7;6\) \(\Rightarrow\dfrac{a}{9}=\dfrac{b}{8}=\dfrac{c}{7}=\dfrac{d}{6}\)
Áp dụng tính chất dãy tỉ số bằng nhau ta được :
\(\dfrac{a}{9}=\dfrac{b}{8}=\dfrac{c}{7}=\dfrac{d}{6}=\dfrac{b-d}{8-6}=\dfrac{70}{2}=35\)
\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{a}{9}=35\Rightarrow a=315\\\dfrac{b}{8}=35\Rightarrow b=280\\\dfrac{c}{7}=35\Rightarrow c=245\\\dfrac{d}{6}=35\Rightarrow d=210\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\text{Vậy }a=315\\ b=280\\ c=245\\ d=210\)

Đặt k = 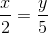 . Ta có x = 2k, y = 5k
. Ta có x = 2k, y = 5k
Từ xy=10. suy ra 2k.5k = 10 => 10 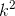 = 10 =>
= 10 => 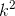 = 1 => k = ± 1
= 1 => k = ± 1
Với k = 1 ta được 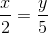 = 1 suy ra x = 2, y = 5
= 1 suy ra x = 2, y = 5
Với k = -1 ta được 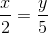 = -1 suy ra x = -2, y = -5
= -1 suy ra x = -2, y = -5
Gọi \(\dfrac{x}{2}=\dfrac{y}{5}=k\)
Với \(\dfrac{x}{2}=k\Rightarrow x=2k\); \(\dfrac{y}{5}=k\Rightarrow y=5k\)
Theo đề bài,ta còn có:
\(xy=10\)
hay 2k.5k=10
10k2 =10
\(\Rightarrow k=\pm1\)
Với k=1 \(\Rightarrow\dfrac{x}{2}=\dfrac{y}{5}=1\Rightarrow x=2;y=5\)
Với k=-1 \(\Rightarrow\dfrac{x}{2}=\dfrac{y}{5}=-1\Rightarrow x=-2;y=-5\)

Áp dụng tính chất của dãy tỉ số bằng nhau ta có:
\(\dfrac{x}{2}\)=\(\dfrac{y}{5}\)=\(\dfrac{x+y}{2+5}\)=\(\dfrac{-21}{7}\)=-3
=>\(\dfrac{x}{2}\)=\(\dfrac{y}{5}\)=5x=2y
=>x=5.-3=-15
=>y=2.-3=-6
Vậy x=-15;y=6

\(\dfrac{x}{5}=\dfrac{y}{6}\Rightarrow\dfrac{x}{20}=\dfrac{y}{24}\) và \(\dfrac{y}{8}=\dfrac{z}{7}\Rightarrow\dfrac{y}{24}=\dfrac{z}{21}\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{x}{20}=\dfrac{y}{24}=\dfrac{z}{21}\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{x+y-z}{20+24-21}=\dfrac{138}{23}\)=6
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{x}{20}=6\Rightarrow x=120\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{y}{24}=6\Rightarrow y=144\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{z}{21}=6\Rightarrow z=126\)
Vậy : x = 120
y = 144
z = 126

a)
Ta có: \(9x=5y=15z\Rightarrow\dfrac{9x}{45}=\dfrac{5y}{45}=\dfrac{15z}{45}\Rightarrow\dfrac{x}{5}=\dfrac{y}{9}=\dfrac{z}{3}\Rightarrow\dfrac{-x}{-5}=\dfrac{y}{9}=\dfrac{z}{3}_{\left(1\right)}\)
và \(-x+y-z=11_{\left(2\right)}.\)
Từ \(_{\left(1\right)}\) và \(_{\left(2\right)}\), kết hợp tính chất dãy tỉ só bằng nhau có:
\(\dfrac{-x}{-5}=\dfrac{y}{9}=\dfrac{z}{3}=\dfrac{-x+y-z}{-5+9-3}=\dfrac{11}{1}=11.\)
Từ đó: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{-x}{-5}=11\Rightarrow-x=-55\Rightarrow x=55.\\\dfrac{y}{9}=11\Rightarrow y=99.\\\dfrac{z}{3}=11\Rightarrow z=33.\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy.....
b); c); d); e) làm tương tự.

\(\dfrac{6}{2x+1}=\dfrac{2}{7}\)
=> 2(2x+1) = 6.7
4x+2=42
4x=40
x=10
Vậy x=10
a)\(\dfrac{6}{2x+1}=\dfrac{2}{7}\\ =>6.7=2.\left(2x+1\right)\\ =>2x+1=\dfrac{6.7}{2}=\dfrac{42}{2}=21\\ =>2x=21-1=20\\ =>x=\dfrac{20}{2}=10\)
b) \(\dfrac{24}{7x-3}=-\dfrac{4}{25}\\ =>24.25=-4.\left(7x-3\right)\\ =>7x-3=\dfrac{24.25}{-4}=-150\\ =>7x=-150+3=-147\\ =>x=\dfrac{-147}{7}=-21\)
c) \(\dfrac{4}{x-6}=\dfrac{y}{24}=-\dfrac{12}{18}\\ =>x-6=\dfrac{4.18}{-12}=-6\\ =>x=-6+6=0\\ y=\dfrac{-12.24}{18}=-16\)
d) \(-\dfrac{1}{5}\le\dfrac{x}{8}\le\dfrac{1}{4}\\ < =>-\dfrac{8}{40}\le-\dfrac{5x}{40}\le\dfrac{10}{40}\\ =>-8\le-5x\le10\\ Mà:-8< -5.1< -5.0< -5.\left(-1\right)< -5.\left(-2\right)=10\\ =>x\in\left\{-2;-1;0;1\right\}\)
e) \(\dfrac{x+46}{20}=x\dfrac{2}{5}\\ < =>\dfrac{x+46}{20}=\dfrac{5x+2}{5}\\ =>5\left(x+46\right)=20\left(5x+2\right)\\ < =>5x+230=100x+40\\ < =>230-40=100x-5x\\ < =>190=95x\\ =>x=\dfrac{190}{95}=2\)
f) \(y\dfrac{5}{y}=\dfrac{56}{y}\\ < =>\dfrac{y^2+5}{y}=\dfrac{56}{y}\\ =>y\left(y^2+5\right)=56y\\ =>y^2+5=\dfrac{56y}{y}=56\\ =>y^2=56-5=51\\ =>y=\sqrt{51}\)

Ta có :
\(x-y+z=8\)
\(\dfrac{x}{2}=\dfrac{y}{4}=\dfrac{z}{6}\)
Áp dụng t/c dãy tỉ số bằng nhau ta có :
\(\dfrac{x}{2}=\dfrac{y}{4}=\dfrac{z}{6}=\dfrac{x-y+z}{2-4+6}=\dfrac{8}{4}=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{x}{2}=2\Leftrightarrow x=4\\\dfrac{y}{4}=2\Leftrightarrow y=8\\\dfrac{z}{6}=2\Leftrightarrow z=12\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy ..

a) \(\dfrac{x}{3}=\dfrac{y}{7}\) và x + y = 20
Áp dụng tính chất dãy tỉ số bằng nhau ta có:
\(\dfrac{x}{3}=\dfrac{y}{7}=\dfrac{x+y}{3+7}=\dfrac{20}{10}=2\)
\(\dfrac{x}{3}=2\Rightarrow x=6\)
\(\dfrac{y}{7}=2\Rightarrow y=14\)
Vậy x và y lần lượt là 6 và 14
b) \(\dfrac{x}{5}=\dfrac{y}{2}\) và x - y = 6
Áp dụng tính chất dãy tỉ số bằng nhau ta có:
\(\dfrac{x}{5}=\dfrac{y}{2}=\dfrac{x-y}{5-2}=\dfrac{6}{3}=2\)
\(\dfrac{x}{5}=2\Rightarrow x=10\)
\(\dfrac{y}{2}=2\Rightarrow y=4\)
Vậy x và y lần lượt là 10 và 4
a) \(\dfrac{x}{3}=\dfrac{y}{4}\) và \(x+y=20\)
Đặt \(\dfrac{x}{3}=\dfrac{y}{4}=k\)
\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=3k\\y=4k\end{matrix}\right.\)
Ta có: \(3k+4k=20\)
\(\Rightarrow7k=20\)
\(\Rightarrow k=\dfrac{20}{7}\) (1)
Thay (1) vào, ta có:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=3.\dfrac{20}{7}\\y=4.\dfrac{20}{7}\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{60}{7}\\y=\dfrac{80}{7}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy...
b) \(\dfrac{x}{5}=\dfrac{y}{2}\) và x - y = 6
Đặt \(\dfrac{x}{5}=\dfrac{y}{2}=k\)
\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=5k\\y=2k\end{matrix}\right.\)
Ta có: 5k - 2k = 6
3k = 6
k = 2 (1)
Thay (1) vào, ta có:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=5.2\\y=2.2\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=10\\y=4\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy ....

Ta có \(\frac{x+5}{2}=\frac{y-2}{3}\)và \(x-y=-10\)
Áp dụng tính chất dãy tỉ số bằng nhau, ta có:
\(\frac{x+5}{2}=\frac{y-2}{3}=\frac{x+5-y-2}{2-3}=\frac{x-y+5-2}{2-3}=\frac{-10+5-2}{2-3}=\frac{-7}{-1}=7\)
=> \(\frac{x+5}{2}=7\)=> x + 5 = 14 => x = 9
và \(\frac{y-2}{3}=7\)=> y - 2 = 21 => y = 23

a)\(\dfrac{x}{3}=\dfrac{y}{7}=\dfrac{x+y}{3+7}=\dfrac{20}{10}=2\)
\(\dfrac{x}{3}=2\Rightarrow x=6\)
\(\dfrac{y}{7}=2\Rightarrow y=14\)
b)\(\dfrac{x}{5}=\dfrac{y}{2}=\dfrac{x-y}{5-2}=\dfrac{6}{3}=2\)
\(\dfrac{x}{5}=2\Rightarrow x=10\)
\(\dfrac{y}{2}=2\Rightarrow y=4\)
Áp dụng tính chất dãy tỉ số bằng nhau ta có :
\(\dfrac{x}{6}\)=\(\dfrac{y}{10}\)=\(\dfrac{x+y}{6+10}\)=\(\dfrac{8}{16}\)=\(\dfrac{1}{2}\)Do đó :\(\dfrac{x}{6}\)=\(\dfrac{1}{2}\)=> x = 3\(^{\dfrac{y}{10}}\)=\(\dfrac{1}{2}\)=>y=5Vậy x=3 ; y=5