
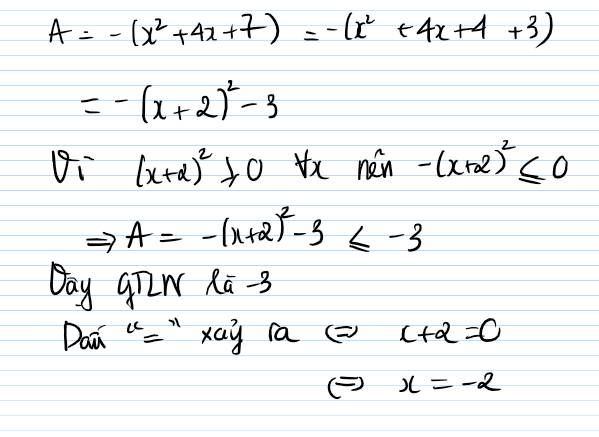
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

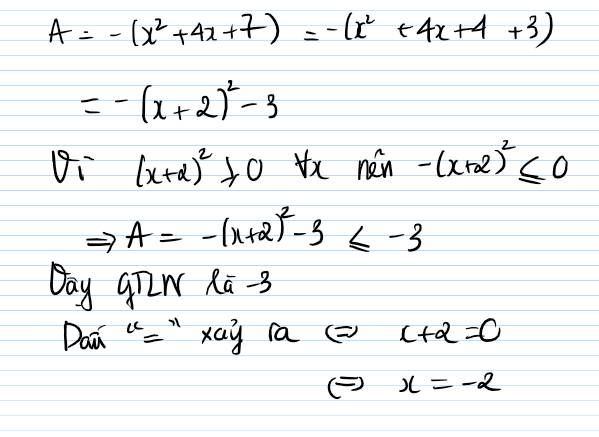

Ta có: -x2+4x-7 = -(x2-4x+7)
= - (x2-2.x.2+22)+3
= -(x-2)2+3
= 3-(x-2)2
Vì (x-2)2 >= 0 => 3-(x-2)2 >= 3
Dấu "=" xảy ra khi x-2 = 0 => x = 2
Vậy Max của biểu thức = 3 khi x = 2
= -(x^2-4x+4)-3
= -(x-2)^2-3
Vì -(x-2)^2\(\le0\forall x\)
-> -(x-2)^2-3 \(\le-3\forall x\)
Dấu = xảy ra <=> x-2=0<=>x=2
Vậy GTLN là -3 <=> x=2

Bài 2:
a: Ta có: \(x^2+4x+7\)
\(=x^2+4x+4+3\)
\(=\left(x+2\right)^2+3\ge3\forall x\)
Dấu '=' xảy ra khi x=-2

a ) \(A=x^2-4x-7\)
\(A=\left(x^2+2.x.2+2^2\right)-11\)
\(A=\left(x+2\right)^2-11\)
Ta có : \(\left(x+2\right)^2\ge0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x+2\right)^2-11\ge-11\)
Vậy GTNN của \(A=-11\)
Khi : \(x+2=0\)
\(x=-2\)
b ) \(B=-x^2+4x-7\)
\(B=-\left(x^2+2.x.2-2^2\right)-3\)
\(B=-\left(x-2\right)^2-3\)
Ta có : \(-\left(x-2\right)^2\le0\)
\(\Rightarrow-\left(x-2\right)^2-3\le-3\)
Vậy GTLN của \(B=-3\)
Khi \(x-2=0\)
\(x=2\)
a)
\(A=\left(x^2-4x+4\right)-11\)
\(=\left(x-2\right)^2-11\)
Ta có
\(\left(x-2\right)^2-11\ge-11\)
Dấu " = " xảy ra khi x = 2
Vậy MINA= - 11 khi x=2
b)
\(B=-\left(x^2-4x+4\right)-3\)
\(B=-\left(x-2\right)^2-3\)
Ta có
\(-\left(x-2\right)^2-3\le-3\) với mọi x
Dấu " = " xảy ra khi = 2
Vậy MAXB= - 3 khi x = 2

A=x2-4x+7
= x2-4x+4+3
= (x-2)2+3
Vì (x+2)2>/ 0
Nên (x-2)2+3>/3
Vậy MAX của A=3 khi x-2=0 => x=2

a)A=4(x+11/8)^2 -153/16
Min A=-153/16 khi x=-11/8
b)B=3(x-1/3)^2 -4/3
Min B=-4/3 khi x=1/3
Bài 1:
a) \(A=4x^2+11x-2=\left(4x^2+11x+\dfrac{121}{16}\right)-\dfrac{153}{16}=\left(2x+\dfrac{11}{4}\right)^2-\dfrac{153}{16}\ge-\dfrac{153}{16}\)
\(minA=-\dfrac{153}{16}\Leftrightarrow x=-\dfrac{11}{8}\)
b) \(B=3x^2-2x-1=3\left(x^2-\dfrac{2}{3}x+\dfrac{1}{9}\right)-\dfrac{4}{3}=3\left(x-\dfrac{1}{3}\right)^2-\dfrac{4}{3}\ge-\dfrac{4}{3}\)
\(minB=-\dfrac{4}{3}\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{1}{3}\)
Bài 2:
a) \(A=-x^2+3x-1=-\left(x^2-3x+\dfrac{9}{4}\right)+\dfrac{5}{4}=-\left(x-\dfrac{3}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{5}{4}\le\dfrac{5}{4}\)
\(maxA=\dfrac{5}{4}\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{3}{2}\)
b) \(B=-x^2-4x+7=-\left(x^2+4x+4\right)+11=-\left(x+2\right)^2+11\le11\)
\(maxB=11\Leftrightarrow x=-2\)

a) Ta có: \(Q=-x^2-y^2+4x-4y+2=-\left(x^2+y^2-4x+4y-2\right)\)
\(=-\left(x^2-4x+4+y^2+4y+4\right)+10\)
\(=-\left[\left(x-2\right)^2+\left(y+2\right)^2\right]+10\le10\forall x,y\)
Vậy MaxQ=10 khi x=2, y=-2
b) +Ta có: \(A=-x^2-6x+5=-\left(x^2+6x-5\right)=-\left(x^2+6x+9-14\right)\)
\(=-\left(x^2+6x+9\right)+14=-\left(x+3\right)^2+14\le14\forall x\)
Vậy MaxA=14 khi x=-3
+Ta có: \(B=-4x^2-9y^2-4x+6y+3=-\left(4x^2+9y^2+4x-6y-3\right)\)
\(=-\left(4x^2+4x+1+9y^2-6y+1-5\right)\)
\(=-\left[\left(2x+1\right)^2+\left(3y-1\right)^2\right]+5\le5\forall x,y\)
Vậy MaxB=5 khi x=-1/2, y=1/3
c) Ta có: \(P=x^2+y^2-2x+6y+12=x^2-2x+1+y^2+6y+9+2\)
\(=\left(x-1\right)^2+\left(y+3\right)^2+2\ge2\forall x,y\)
Vậy MinP=2 khi x=1, y=-3

1: A=(x-1)^2>=0
Dấu = xảy ra khi x=1
5: B=-(x^2+6x+10)
=-(x^2+6x+9+1)
=-(x+3)^2-1<=-1
Dấu = xảy ra khi x=-3
2: B=x^2+4x+4-9
=(x+2)^2-9>=-9
Dấu = xảy ra khi x=-2
6: =-(x^2-5x-3)
=-(x^2-5x+25/4-37/4)
=-(x-5/2)^2+37/4<=37/4
Dấu = xảy ra khi x=5/2
3: =x^2+x+1/4-1/4
=(x+1/2)^2-1/4>=-1/4
Dấu = xảy ra khi x=-1/2
7: =4x^2+4x+1-2
=(2x+1)^2-2>=-2
Dấu = xảy ra khi x=-1/2

\(A=x^2-4x+7=\left(x^2-4x+4\right)+3=\left(x-2\right)^2+3\)
Vì: \(\left(x-2\right)^2\ge0\)
=> \(\left(x-2\right)^2+3\ge3\)
Vậy GTNN của A là 3 khi x=2
\(B=2x^2+12x-1=2\left(x^2+6x+9\right)-19=2\left(x+3\right)^2-19\)
Vì: \(2\left(x+3\right)^2\ge0\)
=> \(2\left(x+3\right)^2-19\ge-19\)
Vậy GTNN của B là -19 khi x=-3
\(C=5x-x^2=-\left(x^2-5x+\frac{25}{4}\right)+\frac{25}{4}=-\left(x-\frac{5}{2}\right)^2+\frac{25}{4}\)
Vì: \(-\left(x-\frac{5}{2}\right)^2\le0\)
=> \(-\left(x-\frac{5}{2}\right)^2+\frac{25}{4}\le\frac{25}{4}\)
Vậy GTLN của C là \(\frac{25}{4}\) khi \(x=\frac{5}{2}\)
Căm ơn bạn nhiều nhé ! Nếu được thì bạn làm giúp tớ bài hình bên trên nhé.