
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


a) 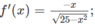
f′(x) > 0 trên khoảng (-4; 0) và f’(x) < 0 trên khoảng (0; 4).
Hàm số đạt cực đại tại x = 0 và f C Đ = 5
Mặt khác, ta có f(-4) = f(4) = 3
Vậy 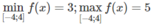
d) f(x) = | x 2 − 3x + 2| trên đoạn [-10; 10]
Khảo sát sự biến thiên và vẽ đồ thị của hàm số g(x) = x 2 – 3x + 2.
Ta có:
g′(x) = 2x − 3; g′(x) = 0 ⇔ x = 3/2
Bảng biến thiên:
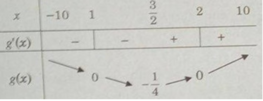
Vì
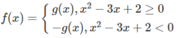
nên ta có đồ thị f(x) như sau:
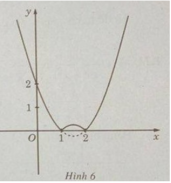
Từ đồ thị suy ra: min f(x) = f(1) = f(2) = 0; max = f(x) = f(−10) = 132
e) 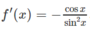
f′(x) < 0 nên và f’(x) > 0 trên (π/2; 5π/6] nên hàm số đạt cực tiểu tại x = π/2 và f C T = f(π/2) = 1
Mặt khác, f(π/3) = 2√3, f(5π/6) = 2
Vậy min f(x) = 1; max f(x) = 2
g) f(x) = 2sinx + sin2x trên đoạn [0; 3π/2]
f′(x) = 2cosx + 2cos2x = 4cos(x/2).cos3(x/2)
f′(x) = 0
⇔ 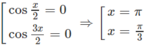
Ta có: f(0) = 0,
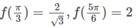
Từ đó ta có: min f(x) = −2 ; max f(x) = 3√3/2

\(f'\left(x\right)=3x^2-6x=0\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(f\left(-1\right)=-2;f\left(0\right)=2;f\left(2\right)=-2\)
\(\Rightarrow M=2;m=-2\Rightarrow P=6\)
Cả 4 đáp án đều sai (kiểm tra lại đề bài, có đúng là \(f\left(x\right)=x^3-3x^2+2\) hay không?)

\(g\left(x\right)=x^4-4x^3+4x^2+a\)
\(g'\left(x\right)=4x^3-12x^2+8x=0\Leftrightarrow4x\left(x^2-3x+2\right)\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=1\\x=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(f\left(0\right)=f\left(2\right)=\left|a\right|\) ; \(f\left(1\right)=\left|a+1\right|\)
TH1: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}M=\left|a\right|\\m=\left|a+1\right|\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left|a\right|\ge\left|a+1\right|\\\left|a\right|\le2\left|a+1\right|\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}-\dfrac{2}{3}\le a\le-\dfrac{1}{2}\\a\le-2\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow a=\left\{-3;-2\right\}\)
TH2: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}M=\left|a+1\right|\\m=\left|a\right|\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left|a+1\right|\ge\left|a\right|\\\left|a+1\right|\le2\left|a\right|\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-\dfrac{1}{2}\le a\le-\dfrac{1}{3}\\a\ge1\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow a=\left\{1;2;3\right\}\)

bn ơi câu a t chưa làm chưa biết nhưng câu b chắc chắn có Max tại x=-3 nhé ! Nếu bn chỉ tìm ra Min là chưa đủ

5.
\(y'=4x^3-8x=0\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=\sqrt{2}\\x=-\sqrt{2}\left(l\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(y\left(0\right)=-2\) ; \(y\left(\sqrt{2}\right)=-6\) ; \(y\left(\sqrt{3}\right)=-5\)
\(\Rightarrow M=-2\)

a) f(x) = 2x3 – 3x2 – 12x + 1 ⇒ f’(x) = 6x2 – 6x – 12
f’(x) = 0 ⇔ x ∈ {-1, 2}
So sánh các giá trị:
f(x) = -3; f(-1) = 8;
f(2) = -19, f(52)=−332f(52)=−332
Suy ra:
maxx∈[−2,52]f(x)=f(−1)=8minx∈[−2,52]f(x)=f(2)=−19maxx∈[−2,52]f(x)=f(−1)=8minx∈[−2,52]f(x)=f(2)=−19
b) f(x) = x2 lnx ⇒ f’(x)= 2xlnx + x > 0, ∀ x ∈ [1, e] nên f(x) đồng biến.
Do đó:
maxx∈[1,e]f(x)=f(e)=e2minx∈[1,e]f(x)=f(1)=0maxx∈[1,e]f(x)=f(e)=e2minx∈[1,e]f(x)=f(1)=0
c) f(x) = f(x) = xe-x ⇒ f’(x)= e-x – xe-x = (1 – x)e-x nên:
f’(x) = 0 ⇔ x = 1, f’(x) > 0, ∀x ∈ (0, 1) và f’(x) < 0, ∀x ∈ (1, +∞)
nên:
maxx∈[0,+∞)f(x)=f(1)=1emaxx∈[0,+∞)f(x)=f(1)=1e
Ngoài ra f(x) = xe-x > 0, ∀ x ∈ (0, +∞) và f(0) = 0 suy ra
maxx∈[0,+∞)f(x)=f(0)=0maxx∈[0,+∞)f(x)=f(0)=0
d) f(x) = 2sinx + sin2x ⇒ f’(x)= 2cosx + 2cos2x
f’(x) = 0 ⇔ cos 2x = -cosx ⇔ 2x = ± (π – x) + k2π
⇔ x∈{−π+k2π;π3+k2π3}x∈{−π+k2π;π3+k2π3}
Trong khoảng [0,3π2][0,3π2] , phương trình f’(x) = 0 chỉ có hai nghiệm là x1=π3;x2=πx1=π3;x2=π
So sánh bốn giá trị : f(0) = 0; f(π3)=3√32;f(π)=0;f(3π2)=−2f(π3)=332;f(π)=0;f(3π2)=−2
Suy ra:
maxx∈[0,3π2]f(x)=f(π3)=3√32minx∈[0,3π2]f(x)=f(3π2)=−2
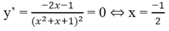
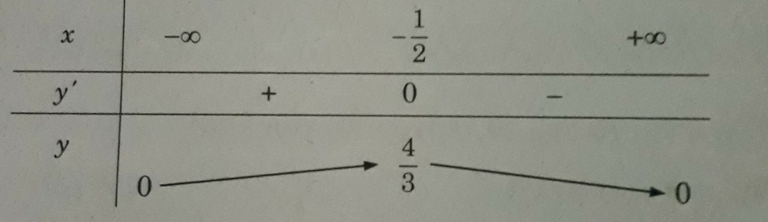

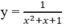
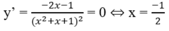
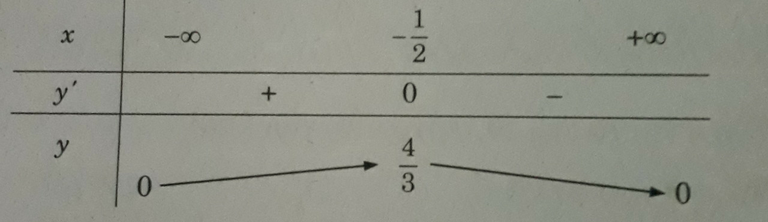
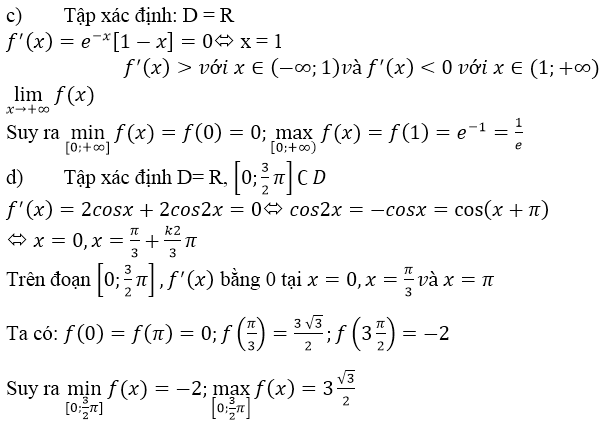
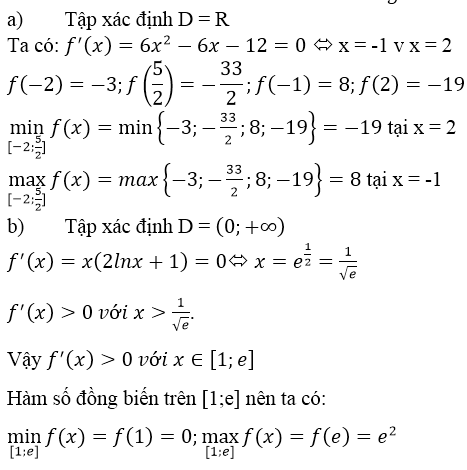
Ta có: y(0) = y(8) = 0, y(2) = 6 2 3
Chọn C