Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

LEARN THIS! Past perfect (Thì quá khứ hoàn thành)
a. We form the past perfect with (1) had or (2) hadn’t and the past participle.
(Chúng ta tạo thì quá khứ hoàn thành với had hoặc hadn’t với động từ ở thể quá khứ phân từ.)
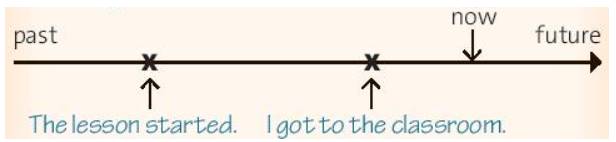
b. We use the past perfect when we are already talking about past events and we want to talk about an even earlier event.
(Chúng ta dùng thì quá khứ hoàn thành khi ai đó đang nói về những sự kiện xảy ra trong quá khứ và chúng ta muốn nói đến những sự kiện trước đó nữa.)
When I got to the classroom, the lesson had started.
(Khi mình đến lớp thì bài học đã bắt đầu.)
c. We often use the past perfect with after, before or when.
(Chúng ta thường dùng thì quá khứ hoàn thành với after, before hoặc when.)
Before I got to the bus station, the bus had already left.
(Trước khi mình đến trạm xe buýt, thì xe buýt đã đi mất.)
After I’d called Maggie, I watched a film on TV.
(Sau khi mình gọi cho Maggie, mình xem một bộ phim trên TV.)
had thrown … away; had risen; had increased; had spilled; had kept; had sold; had thrown; had … forgotten; hadn’t saved

E. In pairs, make sentences about a past vacation. Change the verbs into the simple past.
(Thực hành theo cặp, hãy viết câu về một kỳ nghỉ trong quá khứ. Thay đổi các động từ dùng thì quá khứ đơn.)
1. Last summer, / my family / go on / vacation. Last summer, my family went on vacation.
2. We / drive / all day. ____We drove all day___________________________________
3. In the evening, / we / arrive / at the campsite. ___________________In the evening, we arrived at the campsite____________________
4. Every day, / I / swim / in a lake / and / walk / in the forest. ________________Every day, I swam in a lake and walked in the forest_______________________
5. One day, / we / take / a tour of an old city. _________________One day, we took a tour of an old city______________________
6. We / be / very happy. ______We were very happy_________________________________
7. It / be / an amazing trip. ______It was an amazing trip_________________________________

a. was listening / started
b. fell / realised / jumped
c. swam / came / climbed / were arguing
d. began / was deciding / heard

Prepositions – Place (Position and Direction)
Location prepositions are used to her gender from the position of an object or an action is happening in a certain place (location)
Adv of place
inroom, building, street, town, country
book, paper etc.
car, taxi
picture, worldin the kitchen, in London
in the book
in the car, in a taxi
in the picture, in the world
atmeaning next to, by an object
for table
for events
place where you are to do something typical (watch a film, study, work)at the door, at the station
at the table
at a concert, at the party
at the cinema, at school, at work
onattached
for a place with a river
being on a surface
for a certain side (left, right)
for a floor in a house
for public transport
for television, radiothe picture on the wall
London lies on the Thames.
on the table
on the left
on the first floor
on the bus, on a plane
on TV, on the radio
by, next to, besideleft or right of somebody or somethingJane is standing by / next to / beside the car.
underon the ground, lower than (or covered by) something elsethe bag is under the table
belowlower than something else but above groundthe fish are below the surface
overcovered by something else
meaning more than
getting to the other side (also across)
overcoming an obstacleput a jacket over your shirt
over 16 years of age
walk over the bridge
climb over the wall
abovehigher than something else, but not directly over ita path above the lake
acrossgetting to the other side (also over)
getting to the other sidewalk across the bridge
swim across the lake
throughsomething with limits on top, bottom and the sidesdrive through the tunnel
tomovement to person or building
movement to a place or country
for bedgo to the cinema
go to London / Ireland
go to bed
intoenter a room / a buildinggo into the kitchen / the house
towardsmovement in the direction of something (but not directly to it)go 5 steps towards the house
ontomovement to the top of somethingjump onto the table
fromin the sense of where froma flower from the garden


1.After I had had dinner,I watched TV
2.After we had bought a newspaper,we had a coffee
3.After we had played tennis,we went home
4.When my cousin phoned,I had gone to sleep
5.When we arrived at the match,Mesi had scored two goals
6.When their mother got home,the children had done the housework

Thì quá khứ đơn và quá khú hoàn thành: ( Chú ý: hành động trước và đã hoàn thành ta chia thì QKHT, còn hành xảy ra sau mình chia QKĐ)
1. Before she moved to San Diego, she _______had worked_________ as a tourist guide. (WORK)
2. By the time the police arrived, the burglar ________had broken_____ into my neighbour’s house. (BREAK)
3. They __________hadn't used_________ Google Classroom before, so I showed them how to use it. (NOT/ USE)
4. The lights ________went off_____ because we hadn’t paid the electricity bill. (GO OFF)
5. We watched TV after our daughter ______had gone____ to bed. (GO)
6. She ______visited_______ Victoria once in 1993 before she moved there in 1996. (VISIT)
7. By the time my wife ________came_____ home, I had done the laundry. (COME)
8. I was sure that I ____had seen___ the woman before. (SEE)


Cách dùng
Diễn đạt một hành động đã xảy ra và chấm dứt hoàn toàn trong quá khứ, không còn liên quan đến hiện tại.
Dấu hiệu nhận biết thì quá khứ đơn
Trong câu có các từ như: yesterday, ago, last (night, week, month, year), in the past, the day before, in the (1990s, 2000s ...), với những khoảng thời gian đã qua trong ngày (today, this morning, this afternoon).
When (khi): trong câu kể
Ví dụ 1: Yesterday morning, Tom got up early; then he ate breakfast and went to school. (Sáng hôm qua, Tom dậy trễ, sau đó cậu ấy ăn sáng và đến trường.)
Ví dụ 2: Tom lived in VietNam six years ago, now he lives in Paris. (6 năm trước Tom sống ở Việt Nam, còn giờ cậu ấy sống ở Paris.)
Cách dùng:
- Diễn đạt một hành động xảy ra một, một vài lần hoặc chưa bao giờ xảy ra trong quá khứ
- Diễn đạt các hành động xảy ra liên tiếp trong quá khứ
- Diễn đạt một hành động xen vào một hành động đang diễn ra trong quá khứ
- Dùng trong câu điều kiện loại II