
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Đặt `y=f(x)=x-sinx`
Có: `f(-x)=-x-sin(-x)=-x+sinx=-(x-sinx)=-f(x)`
`=>` Hàm lẻ.

1) Đặt `y=f(x) =-2cosx`
Có: `f(-x) = -2cos(-x) = -2cosx=f(x)`
`=>` Hàm chẵn.
4) `y=f(x) = 1/2 tan^2 x`
`f(-x) = 1/2 [tan (-x)]^2 = 1/2 tan^2x=f(x)`
`=>` Hàm chẵn.
7) `y=f(x)=sin2x`
`f(-x)=sin(-2x)=-sin2x=-f(x)`
`=>` Hàm lẻ.
10) `y=f(x)=tanx.sinx`
`f(-x) = tan (-x) .sin(-x) =tanx.sinx=f(x)`
`=>` Hàm chẵn.

2) TXĐ: \(D=R\Rightarrow\forall x\in R\) thì \(-x\in R\)
\(y=f\left(x\right)=sinx+x\)
\(\Rightarrow f\left(-x\right)=sin\left(-x\right)+\left(-x\right)=-sinx-x=-\left(sinx+x\right)=-f\left(x\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow\)\(y=sinx+x\) là hàm lẻ
5) TXĐ: \(D=R\Rightarrow\forall x\in R\) thì \(-x\in R\)
\(y=f\left(x\right)=sin\left|x\right|+x^2\)
\(\Rightarrow f\left(-x\right)=sin\left|-x\right|+\left(-x\right)^2=sin\left|x\right|+x^2=f\left(x\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow y=sin\left|x\right|+x^2\) là hàm chẵn
8) TXĐ: \(D=R\Rightarrow\forall x\in R\) thì \(-x\in R\)
\(y=f\left(x\right)=-2+3cosx\)
\(\Rightarrow f\left(-x\right)=-2+3cos\left(-x\right)=-2+3cosx=f\left(x\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow y=-2+3cosx\) là hàm chẵn
11) TXĐ:\(D=R\Rightarrow\forall x\in R\) thì \(-x\in R\)
\(y=f\left(x\right)=cosx-sin\left|x\right|\)
\(\Rightarrow f\left(-x\right)=cos\left(-x\right)-sin\left|-x\right|=cosx-sin\left|x\right|=\)\(f\left(x\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow y=cosx-sin\left|x\right|\) là hàm chẵn

`y=f(x)=1/(x.cos3x)`
`f(-x)=1/(-x.cos(-3x))=-1/(x.cos3x)=-f(x)`
`=>` Lẻ.
.
`y=f(x)=(cos^3x+1)/(sin^3x)`
`f(-x)=((cos(-x))^3+1)/((sin(-x))^3)=(-cos^3x-1)/(sin^3x)=-f(x)`
`=>` Lẻ.

Miền xác định của hàm là miền đối xứng
\(y\left(-x\right)=cot\left(-x\right)-sin\left(-x-1\right)=-cotx+sin\left(x+1\right)\)
\(y\left(-x\right)\ne y\left(x\right)\) mà cũng khác \(-y\left(x\right)\) nên hàm không chẵn không lẻ

Tập xác định của hàm số là \(D = \mathbb{R}\;\backslash \left\{ 0 \right\}\)
Do đó, nếu x thuộc tập xác định D thì –x cũng thuộc tập xác định D
Ta có: \(g\left( { - x} \right) = \frac{1}{{ - x}} = - \frac{1}{x} = - g\left( x \right),\;\forall x\; \in \;D\).
Vậy \(g\left( x \right) = \frac{1}{x}\) là hàm số lẻ

TXĐ:R
\(\forall x\in R\Rightarrow\begin{cases}-x\in R\\f\left(-x\right)=3sin\left(-x\right)-2=-3sinx-2\end{cases}\)
Gỉa sử:x=\(\frac{\pi}{2}\Rightarrow\)\(f\left(\frac{\pi}{2}\right)=1\)\(\ne f\left(-\frac{\pi}{2}\right)=-5\)\(\ne-f\left(\frac{\pi}{2}\right)\)=-1
Vậy hàm số không có tính chẵn-lẻ
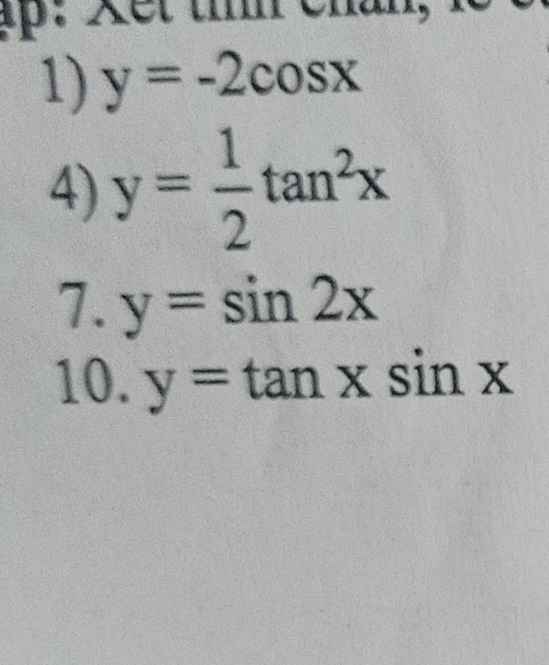

Hàm số nào vậy em?