
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

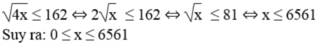

a) \(\sqrt{25x}\) = 35
b) \(\sqrt{4x}\)<= 162
c) \(3\sqrt{x}\) = √12
d) \(2\sqrt{x}\) >=10

\(x^4+y^4=162\)
<=> \(\left(x^2+y^2\right)^2-2x^2y^2=162\)
<=> \(\left(9+xy\right)^2-2\left(xy\right)^2=162\)
<=> \(-\left(xy\right)^2+18xy-81=0\)
<=> \(xy=9\)
khi đó: \(x^2+y^2=9+xy=9+9=18\)
<=> \(\left(x+y\right)^2-2xy=18\)
<=> \(\left(x+y\right)^2=36\)
<=> x + y = 6 hoặc x + y = -6
+) TH1: x + y = 6 và xy = 9
x, y là nghiệm của hệ: \(X^2-6X+9=0\Leftrightarrow X=3\)
khi đó: x = y = 3
+) TH2: x + y = -6 và xy = 9
x, y là nghiệm của hệ: \(X^2+6X+9=0\Leftrightarrow X=-3\)
khi đó: x = y = - 3
Vậy hệ có 2 ngiệm: ( 3; 3) và ( -3; -3)

Lời giải:
Đặt $x^2+y^2=a; xy=b$. Khi đó:
HPT \(\Leftrightarrow \left\{\begin{matrix}
(x^2+y^2)-xy=9\\
(x^2+y^2)^2-2(xy)^2=162\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow \left\{\begin{matrix}
a-b=9\\
a^2-2b^2=162\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow (b+9)^2-2b^2=162\)
\(\Leftrightarrow -b^2+18b-81=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow -(b-9)^2=0\Rightarrow b=9\)
\(\Rightarrow a=b+9=18\)
Vậy $x^2+y^2=18$ và $xy=9$
\(\Rightarrow (x+y)^2=x^2+y^2+2xy=36\Rightarrow x+y=\pm 6\)
Nếu $x+y=6; xy=9$. Áp dụng định lý Vi-et đảo, $x,y$ là nghiệm của PT $X^2-6X+9=0$
$\Rightarrow x=y=3$
Nếu $x+y=-6; xy=9$. Áp dụng định lý Vi-et đảo, $x,y$ là nghiệm của PT $X^2+6X+9=0$
$\Rightarrow x=y=-3$
Vậy $(x,y)=(\pm 3; \pm 3)$


1
ĐK: \(x\ge1\)
Đặt \(t=\sqrt{x-1}\left(t\ge0\right)\Rightarrow x=t^2+1\)
Khi đó:
\(x-2\sqrt{x-1}=16\)
\(\Leftrightarrow t^2-2t+1=16\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(t-1\right)^2=4^2\\ \Leftrightarrow t-1=4\\ \Leftrightarrow t=4+1=5\left(tm\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x-1}=5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-1=5^2=25\\ \Leftrightarrow x=25+1=26\left(tm\right)\)
Vậy PT có nghiệm duy nhất x = 26.
2 ĐK: \(3\le x\le1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{1-x}=0\\\sqrt{x-3}=0\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=3\end{matrix}\right.\)
Từ điều kiện và bài giải ta kết luận PT vô nghiệm.
3 ĐK: \(x\ge4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x-4}=7-2=5\\ \Leftrightarrow x-4=5^2=25\\ \Leftrightarrow x=25+4=29\left(tm\right)\)
Vậy PT có nghiệm duy nhất x = 29.
4
ĐK: \(x\ge1\)
Đặt \(t=\sqrt{x-1}\left(t\ge0\right)\Rightarrow x=t^2+1\)
Khi đó:
\(x-\sqrt{x-2\sqrt{x-1}}=0\\ \Leftrightarrow t^2+1-\sqrt{t^2-2t+1}=0\\ \Leftrightarrow t^2+1-\sqrt{\left(t-1\right)^2}=0\\ \Leftrightarrow t^2+1-\left|t-1\right|=0\left(1\right)\)
Trường hợp 1:
Với \(0\le t< 1\) thì:
\(\left(1\right)\Leftrightarrow t^2+1-\left(1-t\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow t^2+t=0\\ \Leftrightarrow t\left(t+1\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}t=0\Rightarrow\sqrt{x-1}=0\Rightarrow x=1\left(nhận\right)\\t=-1\left(loại\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Trường hợp 2:
Với \(t\ge1\) thì:
\(\left(1\right)\Leftrightarrow t^2+1-\left(t-1\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow t^2-t+2=0\)
\(\Delta=\left(-1\right)^2-4.2=-7< 0\)
=> Loại trường hợp 2.
Vậy PT có nghiệm duy nhất x = 1.
5
ĐK: \(x\ge2\)
Đặt \(\sqrt{x-2}=t\left(t\ge0\right)\Rightarrow x=t^2+2\)
Khi đó:
\(\sqrt{x-2}-\sqrt{x^2-2x}=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x-2}-\sqrt{x}.\sqrt{x-2}=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\sqrt{t^2+2-2}-\sqrt{t^2+2}.\sqrt{t^2+2-2}=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\sqrt{t^2}-\sqrt{t^2+2}.\sqrt{t^2}=0\\ \Leftrightarrow t-\sqrt{t^2+2}.t=0\\ \Leftrightarrow t\left(1-\sqrt{t^2+2}\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}t=0\Rightarrow\sqrt{x-2}=0\Rightarrow x=2\left(tm\right)\\\sqrt{t^2+2}=1\Rightarrow t^2+2=1\Rightarrow t^2=-1\left(loại\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy phương trình có nghiệm duy nhất x = 2.
6 Không có ĐK vì đưa về tổng bình lên luôn \(\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{\sqrt{2}^2-2.\sqrt{2}.\sqrt{1}+\sqrt{1}^2}-\sqrt{x^2+2x.\sqrt{2}+\sqrt{2}^2}=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\sqrt{\left(\sqrt{2}-\sqrt{1}\right)^2}-\sqrt{\left(x+\sqrt{2}\right)^2}=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left|\sqrt{2}-\sqrt{1}\right|-\left|x+\sqrt{2}\right|=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\sqrt{2}-1-\left|x+\sqrt{2}\right|=0\)
Trường hợp 1:
Với \(x\ge-\sqrt{2}\) thì:
\(\left(1\right)\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{2}-1-\left(x+\sqrt{2}\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\sqrt{2}-1-x-\sqrt{2}=0\\ \Leftrightarrow-1-x=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x=-1\left(tm\right)\)
Với \(x< -\sqrt{2}\) thì:
\(\left(1\right)\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{2}-1--\left(x+\sqrt{2}\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\sqrt{2}-1+x+\sqrt{2}=0\\ \Leftrightarrow2\sqrt{2}+1+x=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x=-1-2\sqrt{2}\left(tm\right)\)
Vậy phương trình có 2 nghiệm \(x=-1\) hoặc \(x=-1-2\sqrt{2}\)


pt đã cho \(\Leftrightarrow\left|x-1\right|+\left|x-3\right|=2+\left|x-4\right|\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)^2+\left(x-3\right)^2+2\left(x-1\right)\left(x-3\right)=4+\left(x-4\right)^2+4\left(x-4\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-2x+1+x^2-6x+9+2x^2-8x+6=4+x^2-8x+16+4x-16\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x^2-16x+16=4+x^2-4x\Leftrightarrow4\left(x-2\right)^2-\left(x-2\right)^2=0\Leftrightarrow3\left(x-2\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=2\)
Kl:x=2
ko hiểu nổi tại sao thử lại vào pt lại ko đúng nữa, sorry!
