
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Ta có A= x^3 + 2x^2 + 5x + 10/ x^2 + 4x+4
A= x^2(x+2)+5(x+2)/ (x+2)^2
A= (x^2)(x^2+5)/ (x+2)(x+2)
A= x^2+5/ x+2
Để A= x^2+5/ x+2 bé nhất thì x^2+5 phải bé nhất
MÀ x^2 lớn hơn hoặc = 0 vs mọi x => x^2=0 => x^2 + 5 = 5 vs x=0
Thay x=0 vào A có 0^2 + 5/ 0+2 = 5/2
Vậy MinA=5/2 vs x=0

\(b,Q=-5x^2-4x+1\)
\(=-5\left(x^2+\dfrac{4}{5}x+\dfrac{4}{25}\right)+\dfrac{9}{5}\)
\(=-5\left(x+\dfrac{2}{5}\right)^2+\dfrac{9}{5}\)
Với mọi giá trị của x ta có:
\(-5\left(x+\dfrac{2}{5}\right)^2\le0\)
\(\Rightarrow-5\left(x+\dfrac{2}{5}\right)^2+\dfrac{9}{5}\le\dfrac{9}{5}\)
Vậy MaxQ = \(\dfrac{9}{5}\)
Để Q = \(\dfrac{9}{5}\) thì \(x+\dfrac{2}{5}=0\Rightarrow x=-\dfrac{2}{5}\)
\(c,K=x\left(x-3\right)\left(x-4\right)\left(x-7\right)\)
\(=x\left(x-7\right)\left(x-3\right)\left(x-4\right)\)
\(=\left(x^2-7x\right)\left(x^2-7x+12\right)\)
Đặt \(x^2-7x+6=t\) , ta có:
\(K=\left(t-6\right)\left(t+6\right)\)
\(=t^2-36\)
\(=\left(x^2-7x+6\right)^2-36\)
Với mọi giá trị của x ta có:
\(\left(x^2-7x+6\right)^2\ge0\Rightarrow\left(x^2-7x+6\right)^2-36\ge-36\)
Vậy Min K = -36
Để K = - 36 thì \(x^2-7x+6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-x-6x+6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x-1\right)-6\left(x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-6\right)\left(x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-6=0\\x-1=0\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=6\\x=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
a)\(P=2x^2-8x+1\)
=\(2\left(x^2-4x+4\right)-7\)
=\(2\left(x-2\right)^2-7\)
Với mọi x thì \(2\left(x-2\right)^2>=0\)
=>\(2\left(x-2\right)^2-7>=-7\)
Hay \(P>=-7\) với mọi x
Để \(P=-7\) thì
\(\left(x-2\right)^2=0\)
=>\(x-2=0\)
=>\(x=2\)
Vậy...
Các câu sau tương tự

a) \(\dfrac{5x+10}{4x-8}.\dfrac{4-2x}{x+2}\\ =\dfrac{-5x-10}{8-4x}.\dfrac{4-2x}{x+2}\\ =\dfrac{-5\left(x+2\right)}{4\left(2-x\right)}.\dfrac{2\left(2-x\right)}{x+2}=\dfrac{-5}{2}\)
b)\(\dfrac{x^2-36}{2x+10}.\dfrac{3}{6-x}\\ =\dfrac{\left(x-6\right).\left(x+6\right)}{2\left(x+5\right)}.\dfrac{-3}{x-6}\\ =\dfrac{-3x-18}{2x+10}\)

a)
\(A=\dfrac{2x^2-16x+41}{x^2-8x+22}=\dfrac{2\left(x^2-8x+22\right)-3}{x^2-8x+22}\)
\(A-2=-\dfrac{3}{x^2-8x+22}=-\dfrac{3}{\left(x-4\right)^2+6}\ge-\dfrac{3}{6}=-\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(A\ge\dfrac{3}{2}\) khi x =4

Giải:
a) \(\dfrac{12x^3}{y^4}.\dfrac{2y^5}{x^2}\)
\(=\dfrac{12.2.x^3.y^5}{x^2.y^4}\)
\(=\dfrac{24.x^2.x.y^4.y}{x^2.y^4}\)
\(=24xy\)
Vậy ...
b) \(\dfrac{5x-10}{4x-8}:\dfrac{2x+4}{4-2x}\)
\(=\dfrac{5\left(x-2\right)}{4\left(x-2\right)}:\dfrac{2\left(x+2\right)}{2\left(2-x\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{5}{4}:\dfrac{x+2}{2-x}\)
\(=\dfrac{5}{4}.\dfrac{2-x}{x+2}\)
\(=\dfrac{5\left(2-x\right)}{4\left(x+2\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{10-5x}{4x+8}\)
Vậy ...
c) \(\dfrac{3x+10}{x+3}.\dfrac{2x+4}{x+3}\)
\(=\dfrac{3x+10}{x+3}.\dfrac{2\left(x+2\right)}{x+3}\)
\(=\dfrac{\left(3x+10\right).2.\left(x+2\right)}{\left(x+3\right)^2}\)
Vậy ...

\(\dfrac{x}{x-1}-\dfrac{2x}{x^2-1}=0\left(ĐKXĐ:x\ne\pm1\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x\left(x+1\right)}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}-\dfrac{2x}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}=0\\ \Rightarrow x^2+x-2x=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x^2-x=0\Leftrightarrow x\left(x-1\right)=0\\ \Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x-1=0\Rightarrow x=1\left(loại\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm là S={0}.
b)
\(\dfrac{\left(x+2\right)^2}{2x-3}-1=\dfrac{x^2+10}{2x-3}\left(ĐKXĐ:x\ne\dfrac{3}{2}\right)\)
quy đồng và khử mẫu phương trình trên, ta được:
\(\left(x+2\right)^2+3-2x=x^2+10\\ \Leftrightarrow x^2+4x+4-2x-x^2=10-3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x+4=7\Leftrightarrow2x=7-4=3\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{3}{2}\left(loại\right)\)
vậy phương trình đã cho vô nghiệm.
c)\(\dfrac{x+5}{x-5}-\dfrac{x-5}{x+5}=\dfrac{20}{x^2-25}\left(ĐKXĐ:x\ne\pm5\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\left(x+5\right)^2}{\left(x-5\right)\left(x+5\right)}-\dfrac{\left(x-5\right)^2}{\left(x+5\right)\left(x-5\right)}=\dfrac{20}{\left(x+5\right)\left(x-5\right)}\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x+5\right)^2-\left(x-5\right)^2=20\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+25x+25-x^2+25x-25=20\\ \Leftrightarrow50x=20\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{2}{5}\)
vậy tập nghiệm của phương trình là \(S=\left\{\dfrac{2}{5}\right\}\)
d)\(\dfrac{3x+2}{3x-2}-\dfrac{6}{2+3x}=\dfrac{9x^2}{9x^2-4}\left(ĐKXĐ:x\ne\pm\dfrac{2}{3}\right)\)
quy đồng và khử mẫu phương trình trên, ta được:
\(\left(3x+2\right)^2-6\left(3x-2\right)=9x^2\\ \Leftrightarrow9x^2+12x+4-18x+12-9x^2=0\\ \Leftrightarrow16-6x=0\Leftrightarrow6x=16\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{16}{6}\)
vậy tập nghiệm của phương trình là \(S=\left\{\dfrac{16}{6}\right\}\)
e)\(\dfrac{3}{5x-1}+\dfrac{2}{3-5x}=\dfrac{4}{\left(1-5x\right)\left(5x-3\right)}\left(ĐKXĐ:x\ne\dfrac{1}{5};\dfrac{3}{5}\right)\)
quy đồng và khử mẫu phương trình trên, ta được:
\(3\left(3-5x\right)+2\left(5x-1\right)=4\\ \Leftrightarrow9-15x+10x-2=4\\ \Leftrightarrow-5x=-3\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{3}{5}\left(loại\right)\)
vậy phương trình đã cho vô nghiệm.
f)
\(\dfrac{3}{1-4x}=\dfrac{2}{4x+1}-\dfrac{8+6x}{16x^2-1}\left(ĐKXĐ:x\ne\pm\dfrac{1}{4}\right)\)
quy đồng và khử mẫu phương trình trên, ta được:
\(-3\left(4x+1\right)=2\left(4x-1\right)-8-6x\\ \Leftrightarrow-12x-3=8x-2-8-6x\\ \Leftrightarrow-14x=-7\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm là \(S=\left\{\dfrac{1}{2}\right\}\)
g)
\(\dfrac{y-1}{y-2}-\dfrac{5}{y+2}=\dfrac{12}{y^2-4}+1\left(ĐKXĐ:y\ne\pm2\right)\)
quy đồng và khử mẫu phương trình trên, ta được:
\(\left(y-1\right)\left(y+2\right)-5\left(y-2\right)=12+y^2-4\\ \Leftrightarrow y^2+y-2-5y+10=12+y^2-4\\ \Leftrightarrow-4y+8=8\Leftrightarrow-4y=0\Rightarrow y=0\)
vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm là S={0}
h)
\(\dfrac{x+1}{x-1}-\dfrac{x-1}{x+1}=\dfrac{4}{x^2-1}\left(ĐKXĐ:x\ne\pm1\right)\)
quy đồng và khử mẫu phương trình trên, ta được:
\(\left(x+1\right)^2-\left(x-1\right)^2=4\\ \Leftrightarrow x^2+2x+1-x^2+2x-1=4\\ \Leftrightarrow4x=4\Rightarrow x=1\)
vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm là S={1}.
i)
\(\dfrac{2x-3}{x+2}-\dfrac{x+2}{x-2}=\dfrac{2}{x^2-4}\left(ĐKXĐ:x\ne\pm2\right)\)
quy đồng và khử mẫu phương trình trên, ta được:
\(\left(2x-3\right)\left(x-2\right)-\left(x+2\right)=2\\ \Leftrightarrow2x^2-7x+6-x^2-4x-4=2\\ \Leftrightarrow x^2-11x=0\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x-11=0\Rightarrow x=11\end{matrix}\right.\)
vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm là S={0;11}
j)
\(\dfrac{x-1}{x^2-4}=\dfrac{3}{2-x}\left(ĐKXĐ:x\ne\pm2\right)\)
quy đồng và khử mẫu phương trình trên, ta được:
\(x-1=-3\left(x+2\right)\Leftrightarrow x-1=-3x-6\\ \Leftrightarrow4x=5\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{5}{4}\)
vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm là \(S=\left\{\dfrac{5}{4}\right\}\)

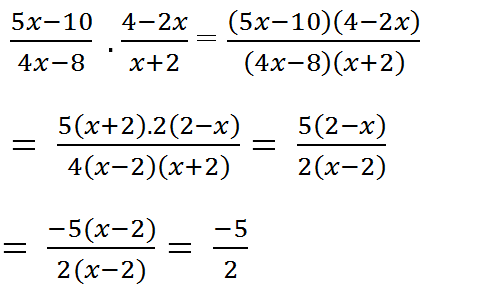


Bạn ơi giờ x càng bé thì A càng bé mà bạn?
Cái éo nào??? Thử x=-1 với x=2 thử coi