Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

a) Ta có:
−1≤cosx≤1,∀x∈R⇔0≤1+cosx≤2⇔0≤2(1+cosx)≤4⇔1≤√2(1+cosx+1≤3−1≤cosx≤1,∀x∈R⇔0≤1+cosx≤2⇔0≤2(1+cosx)≤4⇔1≤2(1+cosx+1≤3
Vậy y ≤ 3, ∀ x ∈ R
Dấu “ = “ xảy ra ⇔ cos x = 1 ⇔ x = k2π (k ∈ Z)
Vậy ymax = 3 khi x = k2π
b) Ta có:
Với mọi x ∈ R, ta có:
sin(x−π6)≤1⇔3sin(x−π6)≤3⇔3sin(x−π6)−2≤1⇔y≤1sin(x−π6)≤1⇔3sin(x−π6)≤3⇔3sin(x−π6)−2≤1⇔y≤1
Vậy ymax = 1 khi sin(x−π6)=1⇔x=2π3+k2π,k∈Z

Đồ thị hàm số y = sin x trên đoạn [-2π, 2π]
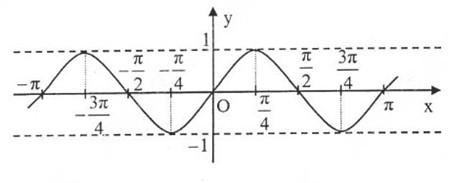
Dựa vào đồ thị hàm số y = sinx
a) Những giá trị của x ∈ [−3π2,2π][−3π2,2π] để hàm số y = sin x nhận giá trị bằng -1 là:
x=−π2;x=3π2x=−π2;x=3π2
b) Những giá trị của x ∈ [−3π2,2π][−3π2,2π] để hàm số y = sin x nhận giá trị âm là:
x ∈ (-π, 0) ∪ (π, 2 π)

ta có : \(sin\left(3x-\dfrac{\pi}{4}\right)=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\Leftrightarrow sin\left(3x-\dfrac{\pi}{4}\right)=sin\dfrac{\pi}{3}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}3x-\dfrac{\pi}{4}=\dfrac{\pi}{3}+k2\pi\\3x-\dfrac{\pi}{4}=\pi-\dfrac{\pi}{3}+k2\pi\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{7\pi}{36}+\dfrac{2k\pi}{3}\\x=\dfrac{11\pi}{36}+\dfrac{2k\pi}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
giả sử \(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{7\pi}{36}+\dfrac{2k\pi}{3}< 0\\\dfrac{11\pi}{36}+\dfrac{2k\pi}{3}< 0\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}k< -\dfrac{7}{24}\\k< -\dfrac{11}{24}\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow k=-1\) là số lớn nhất ở đây
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{-17\pi}{36}\\x=\dfrac{-13\pi}{36}\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow x^-_{max}=\dfrac{-13\pi}{36}\)
giả sử \(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{7\pi}{36}+\dfrac{2k\pi}{3}>0\\\dfrac{11\pi}{36}+\dfrac{2k\pi}{3}>0\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}k>-\dfrac{7}{24}\\k>-\dfrac{11}{24}\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow k=0\) là số nhỏ nhất ở đây
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{7\pi}{36}\\x=\dfrac{11\pi}{36}\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow x^+_{min}=\dfrac{7\pi}{36}\)
\(\Rightarrow\) tổng nghiệm âm lớn nhất và nghiệm dương nhỏ nhất của pt là
\(\dfrac{-13\pi}{36}+\dfrac{7\pi}{36}=\dfrac{-\pi}{6}\)
đổi ra độ ta có : \(\dfrac{-\pi}{6}=-30^o\) \(\Rightarrow\) (B)

\(cos\cdot\left(3x-\dfrac{\pi}{6}\right)=sin\cdot\left(x+\dfrac{\pi}{4}\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow cos\cdot\left(3x-\dfrac{\pi}{6}\right)=cos\cdot\left(\dfrac{\pi}{2}-x-\dfrac{\pi}{4}\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow cos\cdot\left(3x-\dfrac{\pi}{6}\right)=cos\cdot\left(\dfrac{\pi}{4}-x\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}3x-\dfrac{\pi}{6}=\dfrac{\pi}{4}-x+k2\pi\\3x-\dfrac{\pi}{6}=\dfrac{-\pi}{4}+x+k2\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}4x=\dfrac{5\pi}{12}+k2\pi\\2x=\dfrac{-\pi}{12}+k2\pi\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{5\pi}{48}+\dfrac{k\pi}{2}\\x=\dfrac{-\pi}{24}+k\pi\end{matrix}\right.\left(k\in Z\right)\)

Bài 1. a) trục hoành cắt đoạn đồ thị y = tanx (ứng với x ∈ ![]() ) tại ba điểm có hoành độ - π ; 0 ; π. Do đó trên đoạn
) tại ba điểm có hoành độ - π ; 0 ; π. Do đó trên đoạn ![]() chỉ có ba giá trị của x để hàm số y = tanx nhận giá trị bằng 0, đó là x = - π; x = 0 ; x = π.
chỉ có ba giá trị của x để hàm số y = tanx nhận giá trị bằng 0, đó là x = - π; x = 0 ; x = π.
b) Đường thẳng y = 1 cắt đoạn đồ thị y = tanx (ứng với x ∈ ![]() ) tại ba điểm có hoành độ
) tại ba điểm có hoành độ ![]() . Do đó trên đoạn
. Do đó trên đoạn ![]() chỉ có ba giá trị của x để hàm số y = tanx nhận giá trị bằng 1, đó là
chỉ có ba giá trị của x để hàm số y = tanx nhận giá trị bằng 1, đó là ![]() .
.
c) Phần phía trên trục hoành của đoạn đồ thị y = tanx (ứng với x ∈ ![]() ) gồm các điểm của đồ thị có hoành độ truộc một trong các khoảng
) gồm các điểm của đồ thị có hoành độ truộc một trong các khoảng ![]() . Vậy trên đoạn
. Vậy trên đoạn ![]() , các giá trị của x để hàm số y = tanx nhận giá trị dương là x ∈
, các giá trị của x để hàm số y = tanx nhận giá trị dương là x ∈ ![]() .
.
d) Phần phía dưới trục hoành của đoạn đồ thị y = tanx (ứng với x ∈ ![]() ) gồm các điểm của đồ thị có hoành độ thuộc một trong các khoảng
) gồm các điểm của đồ thị có hoành độ thuộc một trong các khoảng ![]() . Vậy trên đoạn
. Vậy trên đoạn ![]() , các giá trị của x để hàm số y = tanx nhận giá trị âm là x ∈
, các giá trị của x để hàm số y = tanx nhận giá trị âm là x ∈ ![]() .
.
a) \(\left\{-\pi;0;\pi\right\}\)
b) \(\left\{\dfrac{\pi}{4};\dfrac{\pi}{4}\pm\pi\right\}\)
c) \(\left(-\pi;-\dfrac{\pi}{2}\right)\cup\left(0;\dfrac{\pi}{2}\right)\cup\left(\pi;\dfrac{3\pi}{2}\right)\)
d) \(\left(-\dfrac{\pi}{2};0\right)\cup\left(\dfrac{\pi}{2};\pi\right)\)




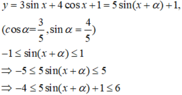
\(y=5\left[\dfrac{3}{5}sin\left(3x+\dfrac{\pi}{6}\right)+\dfrac{4}{5}cos\left(3x+\dfrac{\pi}{6}\right)\right]\)
\(y=5.sin\left(3x+\dfrac{\pi}{6}+a\right)\) với \(cosa=\dfrac{3}{5}\)
Do \(-1\le sin\left(3x+\dfrac{\pi}{6}+a\right)\le1\)
\(\Rightarrow-5\le y\le5\)