Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

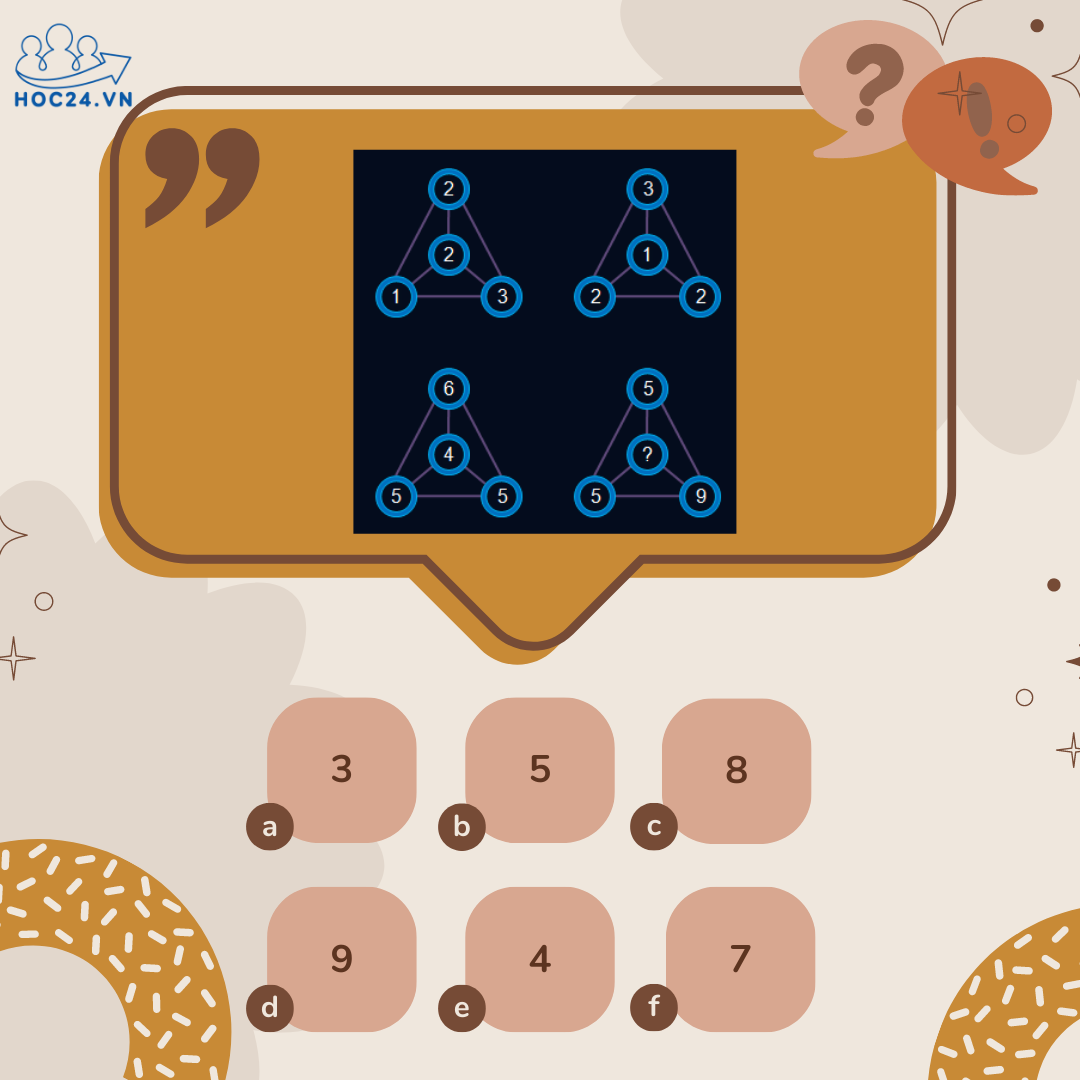
Ta có các quy luật sau:
\(\left(1+3\right)-2=2\)
\(\left(2+2\right)-3=1\)
\(\left(5+5\right)-6=4\)
Vậy dòng cuối là:
\(\left(5+9\right)-5=9\)
Số điền vào là 9
(Quy luật: lấy 2 số phía dưới cộng với nhau rồi trừ cho số phía trên sẽ ra được số ở giữa)

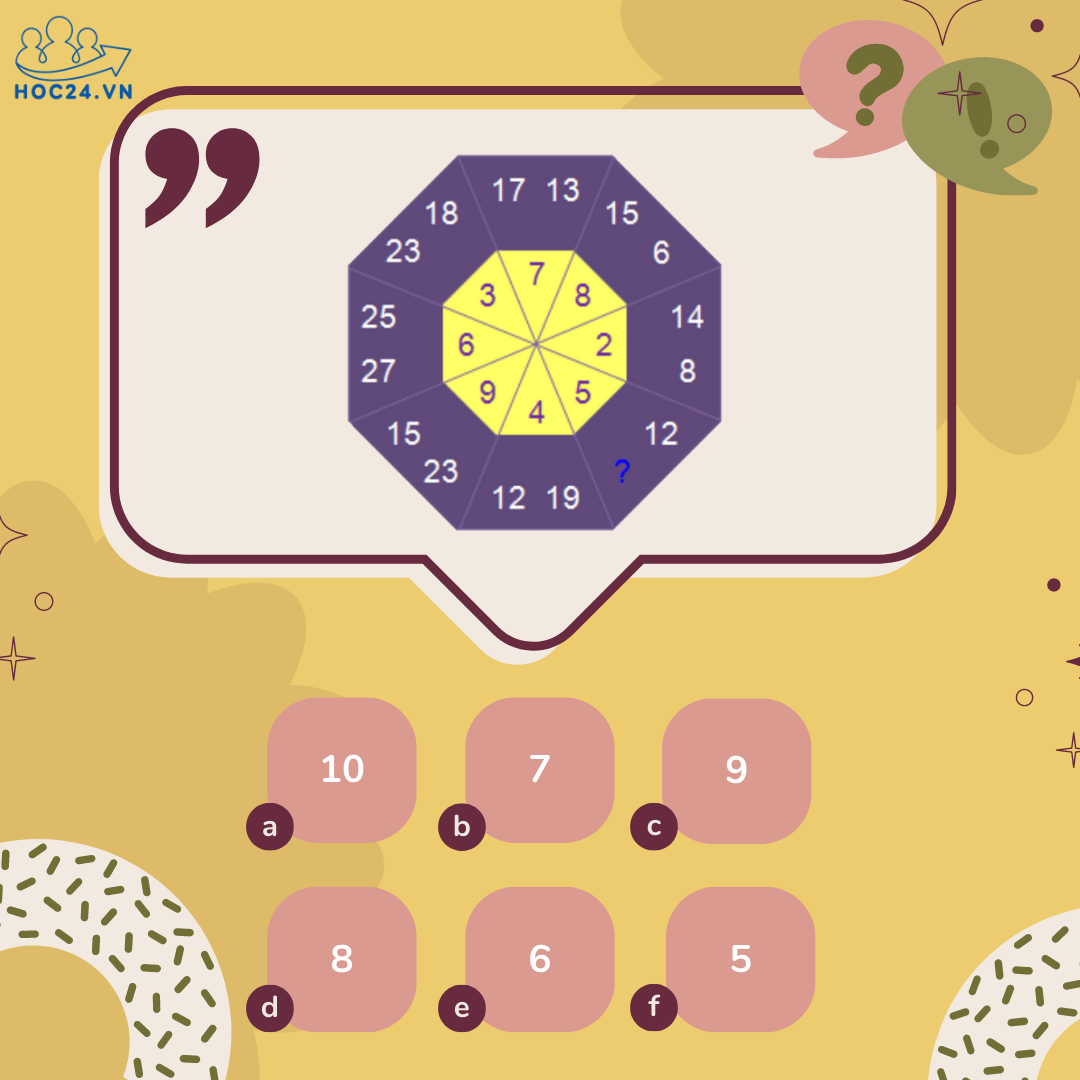
Quy luật: Hiệu của số lớn hơn trừ cho số nhỏ hơn trong mổi ô chính là kết quả của ô màu vàng đối diện
17-13=4
15-6=9
14-8=6
19-12=7
23-15=8
27-25=2
23-18=5
Suy ra: 12-x=3
=> x=12-3=9
Đáp án C
Giải thích: Mỗi số trong hình tam giác màu vàng bằng số lớn hơn của hình bình hành đối diện trừ đi số bé hơn ở hình bình hành đối diện.
=> ? - 12 = 3 hoặc 12 - ? = 3
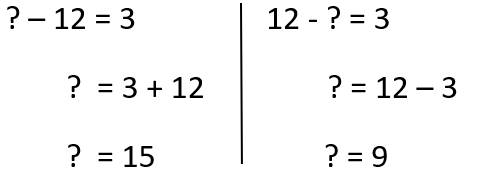
=> Đáp án là 15 hoặc 9
Đáp án: c
Bổ sung: Đáp án cũng có thể là 15

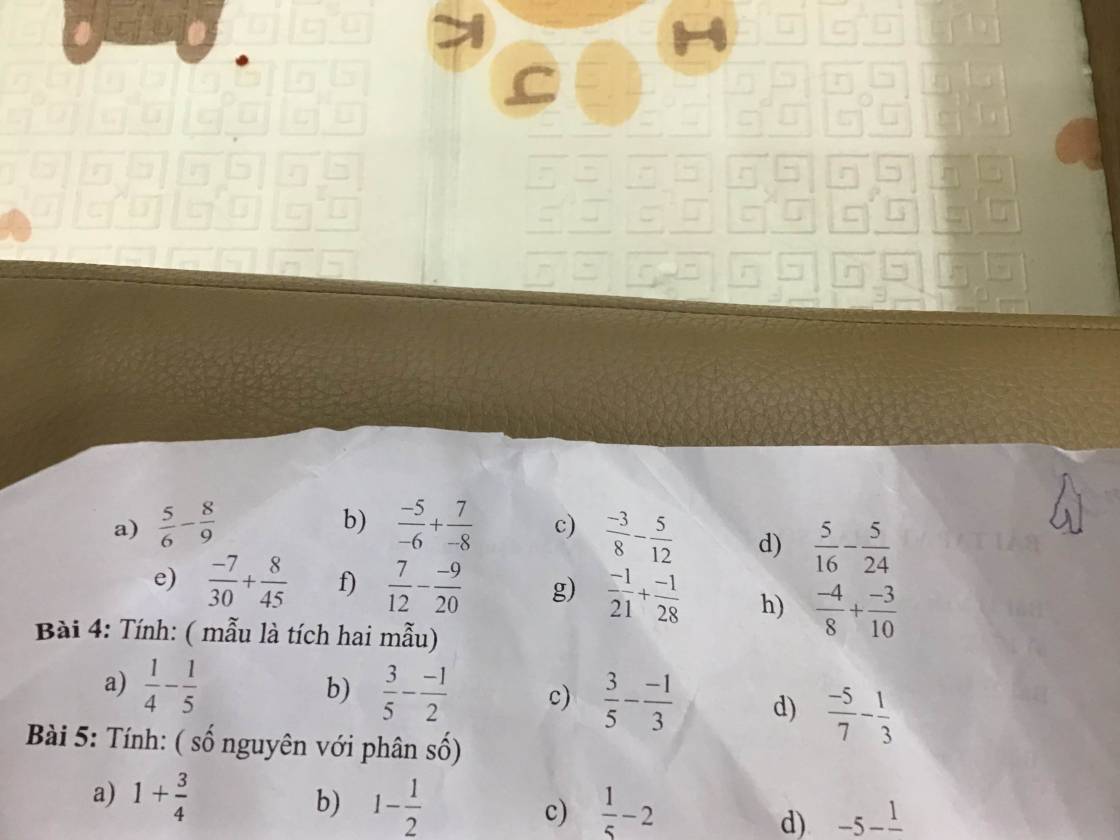
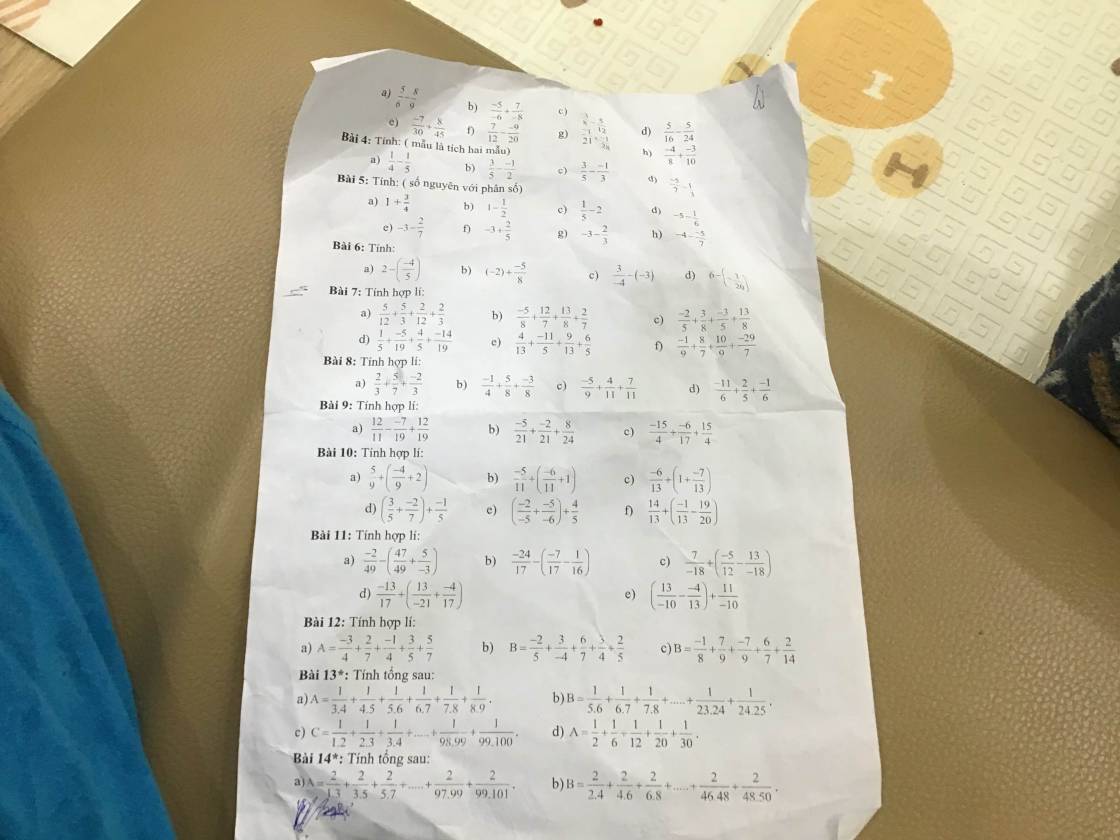
Bài 4:
a; \(\dfrac{1}{4}\) - \(\dfrac{1}{5}\) = \(\dfrac{5}{20}\) - \(\dfrac{4}{20}\) = \(\dfrac{1}{20}\)
b; \(\dfrac{3}{5}\) - \(\dfrac{-1}{2}\) = \(\dfrac{6}{10}\) + \(\dfrac{5}{10}\) = \(\dfrac{11}{10}\)
c; \(\dfrac{3}{5}\) - \(\dfrac{-1}{3}\) = \(\dfrac{9}{15}\) + \(\dfrac{5}{15}\) = \(\dfrac{14}{15}\)
d; \(\dfrac{-5}{7}\) - \(\dfrac{1}{3}\)= \(\dfrac{-15}{21}\) - \(\dfrac{7}{21}\)= \(\dfrac{-22}{21}\)
Bài 5
a; 1 + \(\dfrac{3}{4}\) = \(\dfrac{4}{4}\) + \(\dfrac{3}{4}\) = \(\dfrac{7}{4}\) b; 1 - \(\dfrac{1}{2}\) = \(\dfrac{2}{2}\) - \(\dfrac{1}{2}\) = \(\dfrac{1}{2}\)
c; \(\dfrac{1}{5}\) - 2 = \(\dfrac{1}{5}\) - \(\dfrac{10}{5}\) = \(\dfrac{-9}{5}\) d; -5 - \(\dfrac{1}{6}\) = \(\dfrac{-30}{6}\) - \(\dfrac{1}{6}\) = \(\dfrac{-31}{6}\)
e; - 3 - \(\dfrac{2}{7}\)= \(\dfrac{-21}{7}\) - \(\dfrac{2}{7}\)= \(\dfrac{-23}{7}\) f; - 3 + \(\dfrac{2}{5}\) = \(\dfrac{-15}{5}\) + \(\dfrac{2}{5}\)= - \(\dfrac{13}{5}\)
g; - 3 - \(\dfrac{2}{3}\) = \(\dfrac{-9}{3}\) - \(\dfrac{2}{3}\) = \(\dfrac{-11}{3}\) h; - 4 - \(\dfrac{-5}{7}\) = \(\dfrac{-28}{7}\)+ \(\dfrac{5}{7}\) = - \(\dfrac{23}{7}\)

a; \(\dfrac{x-1}{12}\) = \(\dfrac{5}{3}\)
\(x-1\) = \(\dfrac{5}{3}\) \(\times\) 12
\(x\) - 1 = 20
\(x\) = 20 + 1
\(x\) = 21
b; \(\dfrac{-x}{8}\) = \(\dfrac{-50}{x}\)
-\(x\).\(x\) = -50.8
-\(x^2\) = -400
\(x^2\) = 400
\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-20\\x=20\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy \(x\) \(\in\) {-20; 20}
c; \(\dfrac{x}{3}\) = \(\dfrac{14}{x+1}\)
\(x\).(\(x\)+1) = 14.3
\(x^2\) + \(x\) = 42
\(x^2\) + \(x\) - 42 = 0
\(x^2\) - 6\(x\) + 7\(x\) - 42 = 0
\(x\).(\(x\) - 6) + 7.(\(x\) - 6) = 0
(\(x\) - 6).(\(x\) + 7) = 0
\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-6=0\\x+7=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=6\\x=-7\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy \(x\) \(\in\) {-7; 6}
d; \(x-\dfrac{2}{9}\) = \(\dfrac{1}{6}\)
\(x\) = \(\dfrac{1}{6}\) + \(\dfrac{2}{9}\)
\(x\) = \(\dfrac{7}{18}\)
Vậy \(x\) = \(\dfrac{7}{18}\)

Bài 5:
a. Gọi $d=ƯCLN(n-2, n+1)$
$\Rightarrow n-2\vdots d; n+1\vdots d$
$\Rightarrow (n+1)-(n-2)\vdots d$
$\Rightarrow 3\vdots d\Rightarrow d\in \left\{1; 3\right\}$
Để ps tối giản thì $n-2\not\vdots 3$
$\Leftrightarrow n\neq 3k+2$ với $k$ là số tự nhiên bất kỳ.
b.
Gọi $d=ƯCLN(n+5, n-2)$
$\Rightarrow n+5\vdots d; n-2\vdots d$
$\Rightarrow (n+5)-(n-2)\vdots d$
$\Rightarrow 7\vdots d$
$\Rightarrow d\in \left\{1; 7\right\}$
Để ps tối giản thì $n-2\not\vdots 7$
$\Rightarrow n\neq 7k+2$ với $k$ là số tự nhiên bất kỳ.

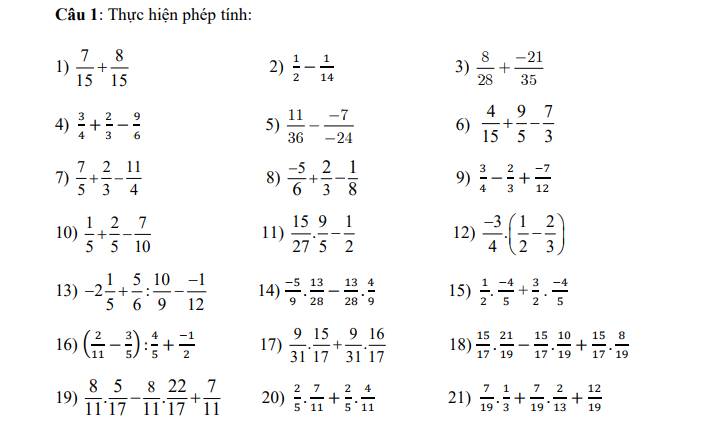
1; \(\dfrac{7}{15}\) + \(\dfrac{8}{15}\) = \(\dfrac{7+8}{15}\) = \(\dfrac{15}{15}\) = 1
2; \(\dfrac{1}{2}\) - \(\dfrac{1}{14}\) = \(\dfrac{1.7}{2.7}\) - \(\dfrac{1}{14}\) = \(\dfrac{7-1}{14}\) = \(\dfrac{6}{14}\) = \(\dfrac{3}{7}\)
3; \(\dfrac{8}{28}\) + \(\dfrac{-21}{35}\) = \(\dfrac{2}{7}\) + \(\dfrac{-21}{35}\)= \(\dfrac{10}{35}\) + \(\dfrac{-21}{35}\) = \(\dfrac{-11}{35}\)
4; \(\dfrac{3}{4}\) + \(\dfrac{2}{3}\) - \(\dfrac{9}{6}\) = \(\dfrac{9}{12}\) + \(\dfrac{8}{12}\) - \(\dfrac{18}{12}\) = \(\dfrac{9+8-18}{12}\) = \(\dfrac{-1}{12}\)
5; \(\dfrac{11}{36}\)- \(\dfrac{-7}{-24}\) = \(\dfrac{22}{72}\) + \(\dfrac{21}{72}\) = \(\dfrac{53}{72}\)
6; \(\dfrac{4}{15}\) + \(\dfrac{9}{5}\) - \(\dfrac{7}{3}\) = \(\dfrac{4}{15}\) + \(\dfrac{27}{15}\) - \(\dfrac{35}{15}\) = \(\dfrac{-4}{15}\)

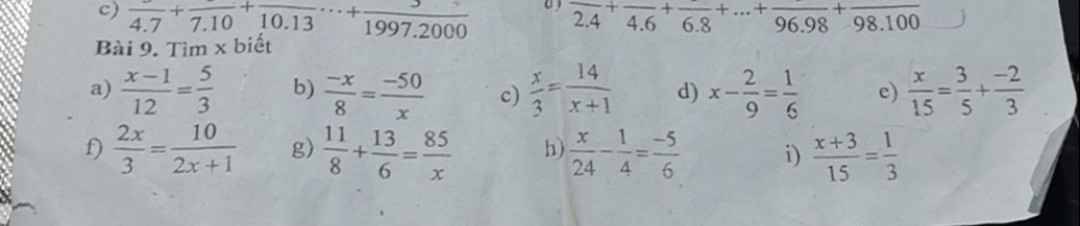

233.
Gọi số tự nhiên cần tìm là $a$. ĐK: $0\leq a< 500$
Theo bài ra: $a-8\vdots 15, a-13\vdots 35$
$\Rightarrow a-8+15.2\vdots 15; a-13+35\vdots 35$
$\Rightarrow a+22\vdots 15, a+22\vdots 35$
$\Rightarrow a+22\vdots 15; 35$
$\Rightarrow a+22=BC(15,35)$
Để $a$ nhỏ nhất thì $a+22$ nhỏ nhất. Do đó $a+22=BCNN(15,35)$
$\Rightarrow a+22=105$
$\Rightarrow a=83$
234a.
Gọi số tự nhiên cần tìm là $a(999\geq a\geq 100$). Theo bài ra ta có:
$a-1\vdots 2; a-2\vdots 3; a-3\vdots 4; a-4\vdots 5; a-5\vdots 6$
$\Rightarrow a+1\vdots 2,3,4,5,6$
$\Rightarrow a+1=BC(2,3,4,5,6)$
$\Rightarrow a+1\vdots BCNN(2,3,4,5,6)$
$\Rightarrow a+1\vdots 60$
$\Rightarrow a+1=60k$ với $k$ tự nhiên.
Vì $a\leq 999$ nên: $60k-1\leq 999$
$\Rightarrow k\leq 16,67$
Để $a$ lớn nhất thì $k$ lớn nhất. Do đó $k=16$
Khi đó: $a=60.16-1=959$