Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

Giải:
Có \(y=f\left(x\right)=\dfrac{1}{2}x+5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow f\left(0\right)=\dfrac{1}{2}.0+5=0+5=5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow f\left(1\right)=\dfrac{1}{2}.1+5=\dfrac{1}{2}+5=\dfrac{11}{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow f\left(2\right)=\dfrac{1}{2}.2+5=1+5=6\)
\(\Leftrightarrow f\left(3\right)=\dfrac{1}{2}.3+5=\dfrac{3}{2}+5=\dfrac{13}{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow f\left(-2\right)=\dfrac{1}{2}.\left(-2\right)+5=-1+5=4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow f\left(-10\right)=\dfrac{1}{2}.\left(-10\right)+5=-5+5=0\)
Vậy ...
Chúc bạn học tốt!
\(y=f\left(x\right)=\dfrac{1}{2}x+5\)
Ta có : \(f\left(0\right)=\dfrac{1}{2}.0+5=5\)
\(f\left(1\right)=\dfrac{1}{2}.1+5=\dfrac{11}{2}=5,5\)
\(f\left(2\right)=\dfrac{1}{2}.2+5=6\)
\(f\left(3\right)=\dfrac{1}{2}.3+5=\dfrac{13}{2}=6,5\)
\(f\left(-2\right)=\dfrac{1}{2}.\left(-2\right)+5=4\)
\(f\left(-10\right)=\dfrac{1}{2}.\left(-10\right)+5=0\)
#HỌC TỐT ~~~

a: f(1)=-1,5
f(2)=-6
f(3)=-13,5
=>f(1)>f(2)>f(3)
b: \(f\left(-3\right)=-1,5\cdot9=-13,5\)
f(-2)=-1,5x4=-6
f(-1)=-1,5x1=-1,5
=>f(-3)<f(-2)<f(-1)
c: Hàm số này đồng biến khi x<0 và nghịch biến khi x>0

Ta có f(x) = 2015/[x(x + 2)]
=> f(1) = 2015/(1.3) = (2015/2)(1/1 - 1/2)
f(2) = 2015/(2.4) = (2015/2)(1/2 - 1/4)
f(3) = 2015/(3.5) = (2015/2)(1/3 - 1/5)
.........................................
=> S = f(1)+f(2)+f(3)+...+f(2015)
= (2015/2)(1 + 1/2 - 1/2016 - 1/2017)

c) Từ kết quả câu a, b ta được bảng sau:
Nhận xét:
- Các hàm số y = f(x) = 2/3 x và y = g(x) = 2/3 x + 3 là hai hàm số đồng biến vì khi x tăng thì y cũng nhận được các giá trị tương ứng tăng lên.
- Cùng một giá trị của biến x, giá trị của hàm số y = g(x) luôn luôn lớn hơn giá trị tương ứng của hàm số y = f(x) là 3 đơn vị.
a) Cho hàm số : \(y=f\left(x\right)=\dfrac{2}{3}x\)
Ta có : \(f\left(-2\right)=\dfrac{2}{3}.\left(-2\right)=-\dfrac{4}{3}\)
\(f\left(-1\right)=\dfrac{2}{3}.\left(-1\right)=-\dfrac{2}{3}\)
\(f\left(0\right)=\dfrac{2}{3}.0=0\)
\(f\left(\dfrac{1}{2}\right)=\dfrac{2}{3}.\dfrac{1}{2}=\dfrac{1}{3}\)
\(f\left(1\right)=\dfrac{2}{3}.1=\dfrac{2}{3}\)
\(f\left(2\right)=\dfrac{2}{3}.2=\dfrac{4}{3}\)
\(f\left(3\right)=\dfrac{2}{3}.3=2\)
b) Cho hàm số : \(y=g\left(x\right)=\dfrac{2}{3}x+3\)
\(g\left(-2\right)=\dfrac{2}{3}.\left(-2\right)+3=\dfrac{5}{3}\)
\(g\left(-1\right)=\dfrac{2}{3}.\left(-1\right)+3=\dfrac{7}{3}\)
\(g\left(0\right)=\dfrac{2}{3}.0+3=3\)
\(g\left(\dfrac{1}{2}\right)=\dfrac{2}{3}.\dfrac{1}{2}+3=\dfrac{10}{3}\)
\(g\left(1\right)=\dfrac{2}{3}.1+3=\dfrac{11}{3}\)
\(g\left(2\right)=\dfrac{2}{3}.2+3=\dfrac{13}{3}\)
\(g\left(3\right)=\dfrac{2}{3}.3+3=5\)
c) Khi \(x\)lấy cùng một giá trị thì giá trị của \(g\left(x\right)\) lớn hơn giá trị của \(f\left(x\right)\) là \(3\) đơn vị.

a) Để hàm xác định thì \(\hept{\begin{cases}x\ge0\\\sqrt{x}-1\ne0\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x\ge0\\x\ne1\end{cases}}\)
b) Ta có: \(f\left(x\right)=\frac{\sqrt{x}+1}{\sqrt{x}-1}\)
\(\Rightarrow f\left(4-2\sqrt{3}\right)=\frac{\sqrt{4-2\sqrt{3}}+1}{\sqrt{4-2\sqrt{3}}-1}=\frac{\sqrt{\left(\sqrt{3}-1\right)^2}+1}{\sqrt{\left(\sqrt{3}-1\right)^2}-1}=\frac{\sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{3}-2}\)
và \(f\left(a^2\right)=\frac{\sqrt{a^2}+1}{\sqrt{a^2}-1}=\frac{\left|a\right|+1}{\left|a\right|-1}\)(với \(a\ne\pm1\))
* Nếu \(a\ge0;a\ne1\)thì \(f\left(a^2\right)=\frac{a+1}{a-1}\)
* Nếu \(a< 0;a\ne-1\)thì \(f\left(a^2\right)=\frac{a-1}{a+1}\)
c) \(f\left(x\right)=\frac{\sqrt{x}+1}{\sqrt{x}-1}=\frac{\sqrt{x}-1+2}{\sqrt{x}-1}=1+\frac{2}{\sqrt{x}-1}\)
Để f(x) nguyên thì \(\frac{2}{\sqrt{x}-1}\)nguyên hay \(2⋮\sqrt{x}-1\Rightarrow\sqrt{x}-1\inƯ\left(2\right)=\left\{\pm1;\pm2\right\}\)
Mà \(\sqrt{x}-1\ge-1\)nên ta xét ba trường hợp:
+) \(\sqrt{x}-1=-1\Rightarrow x=0\left(tmđk\right)\)
+) \(\sqrt{x}-1=1\Rightarrow x=4\left(tmđk\right)\)
+) \(\sqrt{x}-1=2\Rightarrow x=9\left(tmđk\right)\)
Vậy \(x\in\left\{0;4;9\right\}\)thì f(x) có giá trị nguyên
d) \(f\left(x\right)=\frac{\sqrt{x}+1}{\sqrt{x}-1}\); \(f\left(2x\right)=\frac{\sqrt{2x}+1}{\sqrt{2x}-1}\)
f(x) = f(2x) khi \(\frac{\sqrt{x}+1}{\sqrt{x}-1}=\frac{\sqrt{2x}+1}{\sqrt{2x}-1}\Leftrightarrow\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)\left(\sqrt{2x}-1\right)=\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)\left(\sqrt{2x}+1\right)\)\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{2}x+\sqrt{2x}-\sqrt{x}-1=\sqrt{2}x-\sqrt{2x}+\sqrt{x}-1\)\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{2x}-\sqrt{x}=-\sqrt{2x}+\sqrt{x}\Leftrightarrow2\sqrt{2x}=2\sqrt{x}\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{2x}=\sqrt{x}\Leftrightarrow x=0\)(tmđk)
Vậy x = 0 thì f(x) = f(2x)
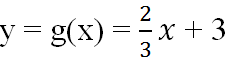
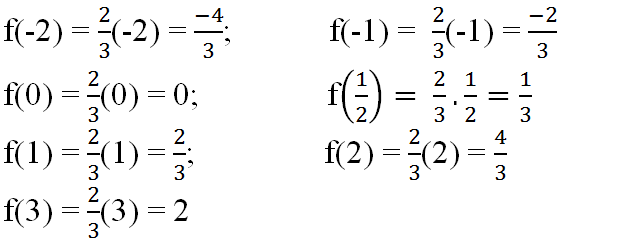
Ta có: