Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

Với x >= 2 biểu thức có dạng :
\(B=x-2-3\left(2x+1\right)=x-2-6x-3=-5x-5\)
Với x < 2 biểu thức có dạng :
\(B=2-x-3\left(2x+1\right)=2-x-6x-3=-1-7x\)

bài 1 .
a. 3 x(5x2 – 2x -1) = 15x3 – 6x2 – 3x
b. (x2+2xy -3)(-xy) = – x3y – 2x2y2 + 3xy
c. 1/2 x2y ( 2x3 – 2/5 xy2 -1 )= x5y – 1/5 x3y3 – 1/2 x2y
bài 2 .
a) 2x^3-3x-5x^3-x^2+x^2=-3x-3x^3
b) 3x^2-6x-5x+5x^2-8x^2+24=-11x+24
c) 3x^3-3/2x^2-x^3-x/2+x/2+2=2x^3-3/2x^2+2
bài 3 .
?????????? bài 3 thì tui ko biết
Bài 3 :
\(P=5x\left(x^2-3\right)+x^2\left(7-5x\right)-7x^2\)
\(=5x^3-15x+7x^2-5x^3-7x^2=-15x\)
Thay x = -5 vào biểu thức trên ta được
\(-15.\left(-5\right)=75\)
Vậy x = -5 thì P = 75

Bài 2:
3x + 2(5 - x) = 0
<=> 3x + 10 - 2x = 0
<=> x + 10 = 0
<=> x = 0 - 10
<=> x = -10
=> x = -10
Bài 3:
6(3q + 4q) - 8(5p - q) + (p - q)
= 6.3p + 6.4q - 8.5p - (-8).q + p - q
= 18p + 24q - 40p + 8q + p - q
= (18p - 40p + p) + (24q + 8q - q)
= -21p + 31q

a) \(x\left(xy+1\right)+y\left(xy-1\right)-xy\left(x+y\right)\)
\(=X^2y+x+xy^2-y-x^2y-xy^2\)
\(=x-y\)

\(a\\ -5x^2+3x.\left(x+2\right)=-5x^2+3x^2+6x=-2x^2+6x\\ b\\ -2x.\left(1-x^2\right)-2x^3=-2x+2x^3-2x^3=-2x\\ c\\ 4x.\left(x-1\right)-4.\left(x^2+2x-1\right)\\ =4x^2-4x-4x^2-8x+4=-12x+4\)
\(d\\ 6x^3-2x^2.\left(-x^2-3x\right)=6x^3+2x^4+6x^3=2x^4+12x^3\\ e\\ 3x.\left(x-1\right)-\left(1+2x\right).5x\\ =3x^2-3x-5x-10x^2=-7x^2-8x\\ f\\ -5x^2-\left(x-6\right).\left(-2x^2\right)=-5x^2+2x^3-12x^2=2x^3-17x^2\)
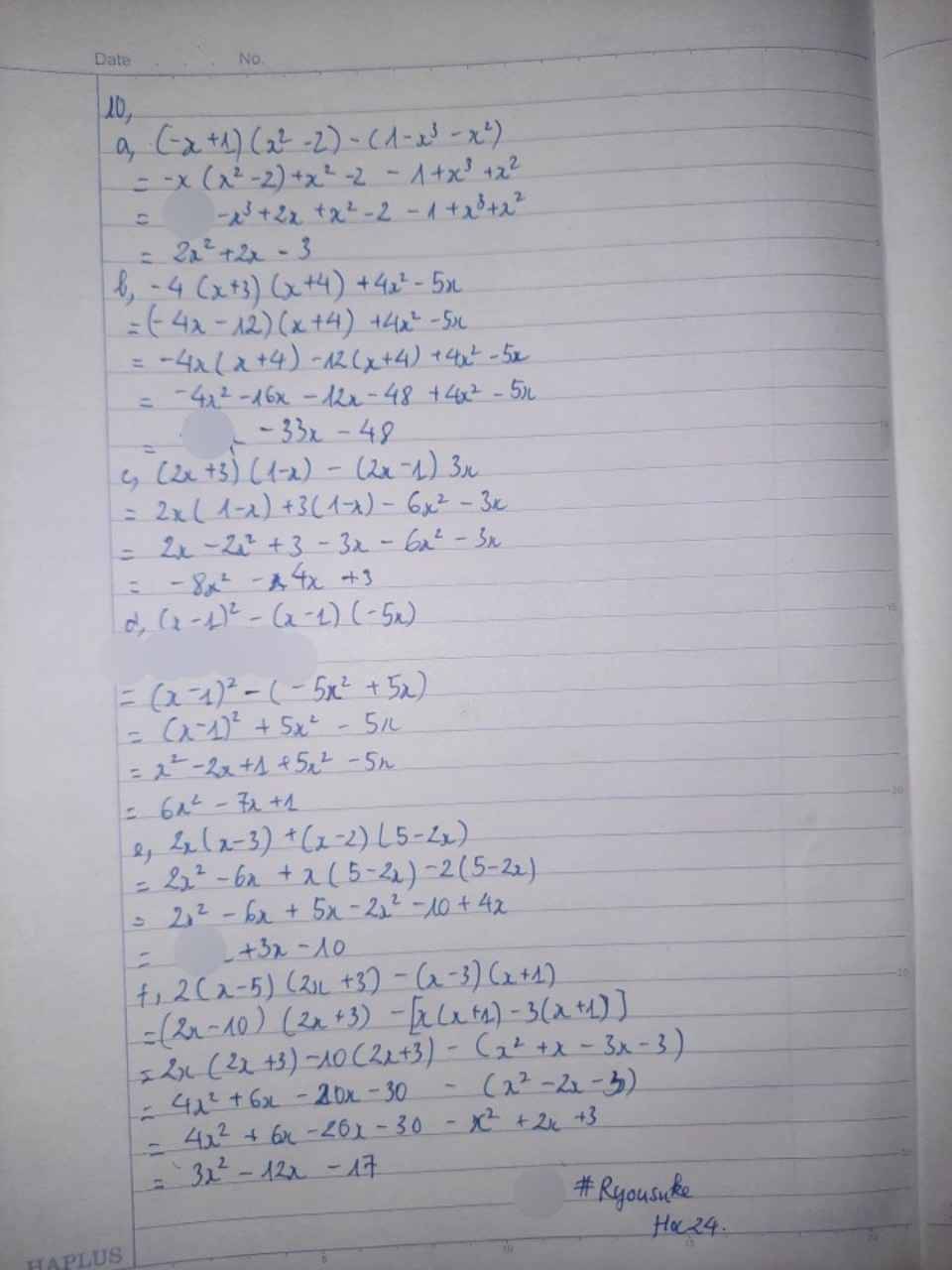
\(\left(x-2\right)\left(2x^3-x^2+1\right)+\left(x-2\right).x^2.\left(1-2x\right)\)
\(=\left(x-2\right)\left(2x^3-x^2+1\right)+\left(x-2\right)\left(x^2-2x^3\right)\)
\(=\left(x-2\right)\left(2x^3-x^2+1+x^2-2x^3\right)\)
\(=\left(x-2\right).1\)
\(=x-2\)
Ta có:
\(\left(x-2\right)\left(2x^3-x^2+1\right)+\left(x-2\right)x^2\left(1-2x\right)\)
\(=\left(x-2\right)\left(2x^3-x^2+1\right)+\left(x-2\right)\left(x^2-2x^3\right)\)
\(=\left(x-2\right)\left[\left(2x^3-x^2+1\right)+\left(x^2-2x^3\right)\right]\)
\(=\left(x-2\right)\left(2x^3-x^2+1+x^2-2x^3\right)\)
\(=\left(x-2\right).1\)
\(=x-2\)