Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

\(2\left(x+1\right)^2+3y^2=21\)
x+1=3k
\(2.3k^2+y^2=7\)
y phải lẻ <3
y=+-1=> k=+-1
vậy số cặp (x,y) thỏa mãn là: 4

Đặt tính \(2n^2-n+2\) : \(2n+1\) sẽ bằng n - 1 dư 3
Để chia hết thì 3 phải chia hết cho 2n + 1 hay 2n + 1 là ước của 3
Ư(3) = {\(\pm\) 3; \(\pm\) 1}
\(2n+1=1\Leftrightarrow2n=0\Leftrightarrow n=0\)
\(2n+1=-1\Leftrightarrow2n=-2\Leftrightarrow n=-1\)
\(2n+1=3\Leftrightarrow2n=2\Leftrightarrow n=1\)
\(2n+1=-3\Leftrightarrow2n=-4\Leftrightarrow n=-2\)
Vậy \(n=\left\{0;-2;\pm1\right\}\)

\(A=\left(2n-1\right)^3-2n+1\)
\(A=8n^3-6n+6n-1-2n+1\)
\(A=8n^3-2n=2n\left(4n^2-1\right)\)
\(A=2n\left(2n+1\right)\left(2n-1\right)\)
\(A=\left(2n-1\right)2n\left(2n+1\right)⋮6\) ( 3 số tự nhiên liên tiếp)

Câu 4:
a: ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{0;-5\right\}\)
b: \(A=\dfrac{x^2+2x}{2\left(x+5\right)}+\dfrac{x-5}{x}+\dfrac{50-5x}{2x\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^3+2x^2}{2x\left(x+5\right)}+\dfrac{2\left(x^2-25\right)}{2x\left(x+5\right)}+\dfrac{50-5x}{2x\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^3+2x^2+2x^2-50+50-5x}{2x\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^3+4x^2-5x}{2x\left(x+5\right)}=\dfrac{x\left(x^2+4x-5\right)}{2x\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x\left(x+5\right)\left(x-1\right)}{2x\left(x+5\right)}=\dfrac{x-1}{2}\)
c: Để A=-3 thì x-1=-6
hay x=-5(loại)

Điều kiện:
\(x-1\ne0\Rightarrow x\ne1\)
\(x^3+x\ne0\Leftrightarrow x\ne0\)

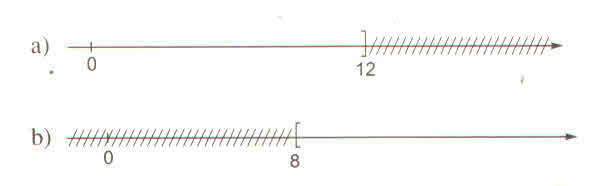
a) Hình a biểu diễn tập nghiệm của bất phương trình x ≤ 6
b) Hình b biểu diễn tập nghiệm của bất phương trình x > 2
c) Hình c biểu diễn tập nghiệm của bất phương trình x ≥ 5
d) Hình d biểu diễn tập nghiệm của bất phương trình x < -1



Chọn A