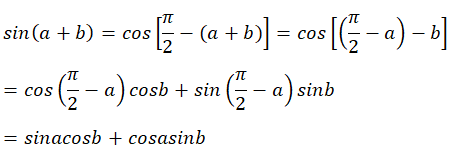Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Không mất tính tổng quát giả sử: \(A\ge B\ge C\)
=> \(tanA\ge tanB\ge tanC;cosA\le cosB\le cosC\)
Áp dụng BĐT Chebyshev ta có:
\(\left(\dfrac{tanA+tanB+tanC}{3}\right)\left(\dfrac{cosA+cosB+cosC}{3}\right)\ge\dfrac{tanA\cdot cosA+tanB\cdot cosB+tanC\cdot cosC}{3}\)
=> \(\dfrac{sinA+sinB+sinC}{cosA+cosB+cosC}\le\dfrac{tanA+tanB+tanC}{3}\)
mặt khác ta có: \(tanA+tanB+tanC=tanA\cdot tanB\cdot tanC\)
=> \(\dfrac{sinA+sinB+sinC}{cosA+cosB+cosC}\le\dfrac{tanA\cdot tanB\cdot tanC}{3}\left(đpcm\right)\)
đẳng thức xảy ra khi tam giác ABC đều
Đề sai.
\(tan90^o=\dfrac{1}{0}\) (không thể chia cho không) nên đề bài sai với trường hợp tam giác vuông rồi.

x1 ; x2 là 2 ngiệm của P(x) => P(x1) = P (x2) = 0
=> ax12 + bx1 + c = ax22 + bx2 + c = 0
=> ax12 + bx1 + c - ( ax22 + bx2 + c) = 0
<=> a. (x12 - x22 ) + b.(x1 - x2) = 0 <=> a. (x1 - x2). (x1 + x2) + b.(x1 - x2) = 0
<=> (x1 - x2). [ a.(x1 + x2) + b ] = 0 mà x1 ; x2 khác nhau nên a.(x1 + x2) + b = 0 => b = - a.(x1 + x2) (*)
+) ax12 + bx1 + c = 0 => c = - ( ax12 + bx1) = - x1. (ax1 + b) = - x1 . (-ax2) = ax1. x2 (Do (*))
vậy c = ax1.x2 (**)
Thay b ; c từ (*) và (**) vào P(x) ta được P(x) = ax2 -ax.(x1 + x2) + ax1.x2 = ax2 - ax.x1 - ax.x2 + ax1.x2
= ax. (x - x1) - ax2 . (x - x1) = (ax - ax2). (x - x1) = a. (x - x2). (x - x1) => ĐPCM

Ta có : \(a\left(a+2\right)< a\left(a+2\right)+1=a^2+2a+1=\left(a+1\right)^2\)
\(\Rightarrow\) \(a\left(a+2\right)< \left(a+1\right)^2\)
\(\Rightarrow\) đpcm
Ta có: \(a\left(a+2\right)< a\left(a+2\right)+1=a^2+2a+1=\left(a+1\right)^2\)
\(\Rightarrow a\left(a+2\right)< \left(a+1\right)^2\)

\(\text{a, Ta có :}\) \(M=\left(x^2+10x+16\right)\left(x^2+10x+24\right)+16\)
\(\text{Đặt }a=x^2+10x+16\)
\(\text{Ta có: }M=a\left(a+8\right)+16=a^2+8a+16=\left(a+4\right)^2\)
\(M=\left(x^2+10x+20\right)^2\)
\(\text{b, }\)\(\left|x+1\right|=\left|x\left(x+1\right)\right|\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left|x\left(x+1\right)\right|-\left|x+1\right|=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left|x\right|.\left|x+1\right|-\left|x+1\right|=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left|x+1\right|\left(\left|x\right|-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\left|x+1\right|=0\\\left|x\right|-1=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-1\\x=1\end{matrix}\right.\)

ta có : \(VP=x^3+3x^2+2x=x\left(x^2+3x+2\right)=x\left(x^2+x+2x+2\right)\)
\(=x\left(x\left(x+1\right)+2\left(x+1\right)\right)=x\left(x+2\right)\left(x+1\right)=VT\)
vậy \(x\left(x+1\right)\left(x+2\right)=x^3+3x^2+2x\) (đpcm)
Ta có \(VT\) :
\(x\left(x+1\right)\left(x+2\right)=x^3+2x^2+x^2+2x=x^3+3x^2+2x=VP\)
\(\Rightarrowđpcm\)

a: Vì 3 là số nguyên tố nên theo ĐỊnh lí nhỏ Fermat, ta được:
\(a^3-a⋮3\)
b: Vì 7 là số nguyên tố nên theo định lí nhỏ Fermat,ta được:
\(a^7-a⋮7\)