Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

\(b,\) PT giao Ox và Oy:
\(y=0\Leftrightarrow x=2\Leftrightarrow A\left(2;0\right)\Leftrightarrow OA=2\\ x=0\Leftrightarrow y=-4\Leftrightarrow B\left(0;-4\right)\Leftrightarrow OB=4\)
Gọi H là chân đường cao từ O đến (d)
Áp dụng HTL: \(\dfrac{1}{OH^2}=\dfrac{1}{OA^2}+\dfrac{1}{OB^2}=\dfrac{1}{4}+\dfrac{1}{16}=\dfrac{5}{16}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow OH^2=\dfrac{16}{5}\Leftrightarrow OH=\dfrac{4}{\sqrt{5}}\left(cm\right)\)
Vậy k/c là \(\dfrac{4}{\sqrt{5}}\left(cm\right)\)
\(c,\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a=2;b\ne-4\\0a+b=3\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a=2\\b=3\end{matrix}\right.\)

a: 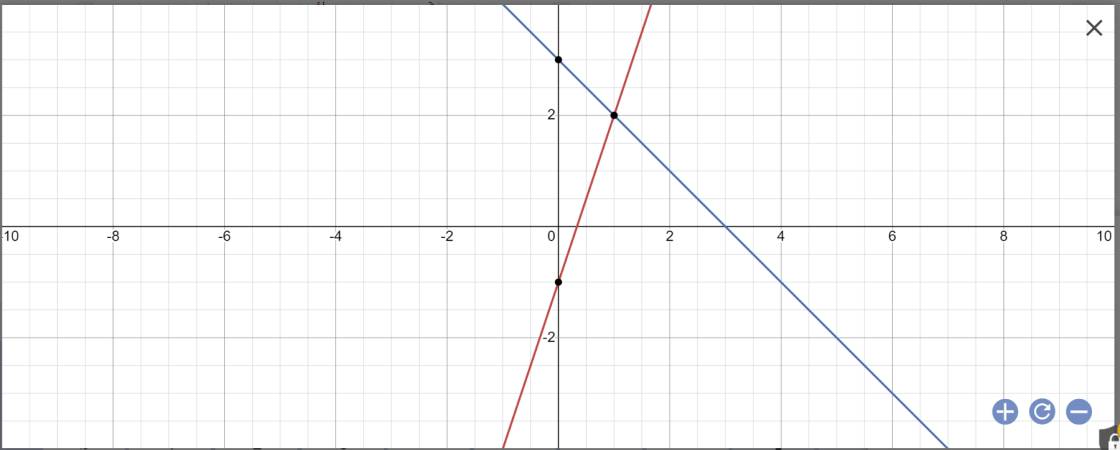
b: Tọa độ A là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\3x-1=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{1}{3}\\y=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: A(1/3;0)
Tọa độ B là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\-x+3=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\-x=-3\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\x=3\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: B(3;0)
Tọa độ C là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3x-1=-x+3\\y=3x-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}4x=4\\y=3x-1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\y=3\cdot1-1=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: C(1;2)
c: Gọi \(\alpha\) là góc tạo bởi (d1) với trục Ox
\(tan\alpha=a=3\)
=>\(\alpha\simeq71^033'\)