Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

Lời giải của bạn Nhật Linh đúng rồi, tuy nhiên cần thêm điều kiện để A có nghĩa: \(x\ne\pm2\)

a,ĐK: \(\hept{\begin{cases}x\ne0\\x\ne\pm3\end{cases}}\)
b, \(A=\left(\frac{9}{x\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)}+\frac{1}{x+3}\right):\left(\frac{x-3}{x\left(x+3\right)}-\frac{x}{3\left(x+3\right)}\right)\)
\(=\frac{9+x\left(x-3\right)}{x\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)}:\frac{3\left(x-3\right)-x^2}{3x\left(x+3\right)}\)
\(=\frac{x^2-3x+9}{x\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)}.\frac{3x\left(x+3\right)}{-x^2+3x-9}=\frac{-3}{x-3}\)
c, Với x = 4 thỏa mãn ĐKXĐ thì
\(A=\frac{-3}{4-3}=-3\)
d, \(A\in Z\Rightarrow-3⋮\left(x-3\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow x-3\inƯ\left(-3\right)=\left\{-3;-1;1;3\right\}\Rightarrow x\in\left\{0;2;4;6\right\}\)
Mà \(x\ne0\Rightarrow x\in\left\{2;4;6\right\}\)

A=(xx2−4+22−x+1x+2):((x−2)+10−x2x+2)A=(xx2−4+22−x+1x+2):((x−2)+10−x2x+2)
=(x(x−2)(x+2)−2x−2+1x+2):(x−2)(x+2)+10−x2x+2(x(x−2)(x+2)−2x−2+1x+2):(x−2)(x+2)+10−x2x+2
=x−2(x+2)+x−2(x−2)(x+2):x2−4+10−x2x+2x−2(x+2)+x−2(x−2)(x+2):x2−4+10−x2x+2
=x−2(x+2)+x−2(x−2)(x+2)−6(x−2)(x+2):6x+2:x2−4+10−x2x+2x−2(x+2)+x−2(x−2)(x+2)−6(x−2)(x+2):6x+2:x2−4+10−x2x+2
=−6(x−2)(x+2).x+26−6(x−2)(x+2).x+26
=−1x−2=12−x−1x−2=12−x
b) Giá trị của A tại |x|=12|x|=12
Nếu x=12x=12 thì A=12−12=132=23A=12−12=132=23
Nếu x=−12x=−12 thì A=12−(−12)=12+12=152=25A=12−(−12)=12+12=152=25
c) A < 0 khi 2 – x < 0 hay x > 2
d)Để A=0

A=\(\left(\dfrac{x}{x^2-4}+\dfrac{2}{2-x}+\dfrac{1}{x+2}\right):\left(x-2+\dfrac{10-x^2}{x+2}\right)\)
Rút gọn được kết quả : A=\(\dfrac{-1}{x-2}\)
b, |x| = \(\dfrac{1}{2}\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{1}{2}\) hoặc \(x=\dfrac{-1}{2}\Rightarrow A=\dfrac{4}{3}\) hoặc \(A=\dfrac{4}{5}\)
c, A<0 \(\Leftrightarrow\) x>2
d, A\(\in Z\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{-1}{x-2}\in Z...\Rightarrow x\in\left\{1;3\right\}\)

a) P xác định \(\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}2x+10\ne0\\x\ne0\\2x\left(x+5\right)\ne0\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow x\ne\left\{-5;0\right\}}\)
b) \(P=\frac{x^2+2x}{2x+10}+\frac{x-5}{x}+\frac{50-5x}{2x\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(P=\frac{x^2\left(x+2\right)}{2x\left(x+5\right)}+\frac{2\left(x-5\right)\left(x+5\right)}{2x\left(x+5\right)}+\frac{5\left(10-x\right)}{2x\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(P=\frac{x^3+2x^2+2x^2-50+50-5x}{2x\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(P=\frac{x^3+4x^2-5x}{2x\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(P=\frac{x^3+5x^2-x^2-5x}{2x\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(P=\frac{x^2\left(x+5\right)-x\left(x+5\right)}{2x\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(P=\frac{\left(x+5\right)\left(x^2-x\right)}{2x\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(P=\frac{x\left(x-1\right)}{2x}\)
\(P=\frac{x-1}{2}\)
c) Để P = 0 thì \(x-1=0\Leftrightarrow x=1\)( thỏa mãn ĐKXĐ )
Để P = 1/4 thì \(\frac{x-1}{2}=\frac{1}{4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4\left(x-1\right)=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x-4=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x=6\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\frac{3}{2}\)( thỏa mãn ĐKXĐ )
d) Để P > 0 thì \(\frac{x-1}{2}>0\)
Mà 2 > 0, do đó để P > 0 thì \(x-1>0\Leftrightarrow x>1\)
Để P < 0 thì \(\frac{x-1}{2}< 0\)
Mà 2 > 0, do đó để P < 0 thì \(x-1< 0\Leftrightarrow x< 1\)
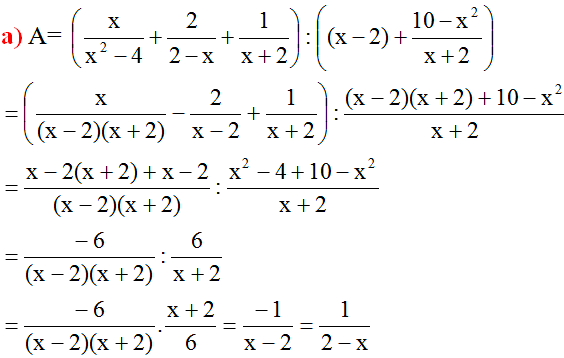
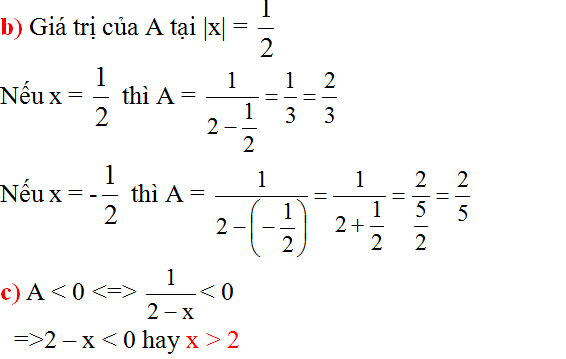
A= \(\left(\dfrac{x}{x^2-4}+\dfrac{2}{2-x}+\dfrac{1}{x+2}\right):\left(x-2+\dfrac{10-x^2}{x+2}\right)\)
\(=\dfrac{-6}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)}:\dfrac{6}{x+2}\)
\(=\dfrac{-1}{x-2}\)
b) \(\left|x\right|=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{1}{2};x=\dfrac{-1}{2}\)
Thay \(x=\dfrac{1}{2}\) (Thỏa mãn ĐKXĐ \(x\ne2;x\ne-2\) )
\(A=\dfrac{-1}{\dfrac{1}{2}-2}=\dfrac{2}{3}\)
Thay \(x=\dfrac{-1}{2}\) (Thỏa mãn ĐKXĐ \(x\ne2;x\ne-2\) )
\(A=\dfrac{-1}{\dfrac{-1}{2}-2}=\dfrac{2}{5}\)
c) \(\dfrac{-1}{x-2}< 0\)
\(\Rightarrow x-2>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x>2\)
Vậy x > 2 để A < 0