Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

BÀI 1:
a) \(ĐKXĐ:\) \(x-3\)\(\ne\)\(0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(x\)\(\ne\)\(3\)
b) \(A=\frac{x^3-3x^2+4x-1}{x-3}\)
\(=\frac{\left(x^3-3x^2\right)+\left(4x-12\right)+11}{x-3}\)
\(=\frac{x^2\left(x-3\right)+4\left(x-3\right)+11}{x-3}\)
\(=x^2+4+\frac{11}{x-3}\)
Để \(A\)có giá trị nguyên thì \(\frac{11}{x-3}\)có giá trị nguyên
hay \(x-3\)\(\notinƯ\left(11\right)=\left\{\pm1;\pm11\right\}\)
Ta lập bảng sau
\(x-3\) \(-11\) \(-1\) \(1\) \(11\)
\(x\) \(-8\) \(2\) \(4\) \(14\)
Vậy....

a: \(\dfrac{A}{B}=\dfrac{x^3+x^2+2x^2+2x+x+1-3}{x+1}=x^2+2x+1-\dfrac{3}{x+1}\)
b: Để A chia hết cho B thì \(x+1\in\left\{1;-1;3;-3\right\}\)
=>\(x\in\left\{0;-2;2;-4\right\}\)

Bài 1:
a) x≠2x≠2
Bài 2:
a) x≠0;x≠5x≠0;x≠5
b) x2−10x+25x2−5x=(x−5)2x(x−5)=x−5xx2−10x+25x2−5x=(x−5)2x(x−5)=x−5x
c) Để phân thức có giá trị nguyên thì x−5xx−5x phải có giá trị nguyên.
=> x=−5x=−5
Bài 3:
a) (x+12x−2+3x2−1−x+32x+2)⋅(4x2−45)(x+12x−2+3x2−1−x+32x+2)⋅(4x2−45)
=(x+12(x−1)+3(x−1)(x+1)−x+32(x+1))⋅2(2x2−2)5=(x+12(x−1)+3(x−1)(x+1)−x+32(x+1))⋅2(2x2−2)5
=(x+1)2+6−(x−1)(x+3)2(x−1)(x+1)⋅2⋅2(x2−1)5=(x+1)2+6−(x−1)(x+3)2(x−1)(x+1)⋅2⋅2(x2−1)5
=(x+1)2+6−(x2+3x−x−3)(x−1)(x+1)⋅2(x−1)(x+1)5=(x+1)2+6−(x2+3x−x−3)(x−1)(x+1)⋅2(x−1)(x+1)5
=[(x+1)2+6−(x2+2x−3)]⋅25=[(x+1)2+6−(x2+2x−3)]⋅25
=[(x+1)2+6−x2−2x+3]⋅25=[(x+1)2+6−x2−2x+3]⋅25
=[(x+1)2+9−x2−2x]⋅25=[(x+1)2+9−x2−2x]⋅25
=2(x+1)25+185−25x2−45x=2(x+1)25+185−25x2−45x
=2(x2+2x+1)5+185−25x2−45x=2(x2+2x+1)5+185−25x2−45x
=2x2+4x+25+185−25x2−45x=2x2+4x+25+185−25x2−45x
=2x2+4x+2+185−25x2−45x=2x2+4x+2+185−25x2−45x
=2x2+4x+205−25x2−45x=2x2+4x+205−25x2−45x
c) tự làm, đkxđ: x≠1;x≠−1

a: \(A=\left(2x-1\right)\left(4x^2+2x+1\right)-7\left(x^3+1\right)\)
\(=\left(2x\right)^3-1^3-7x^3-7\)
\(=8x^3-1-7x^3-7=x^3-8\)
b: Thay x=-1/2 vào A, ta được:
\(A=\left(-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^3-8=-\dfrac{1}{8}-8=-\dfrac{65}{8}\)

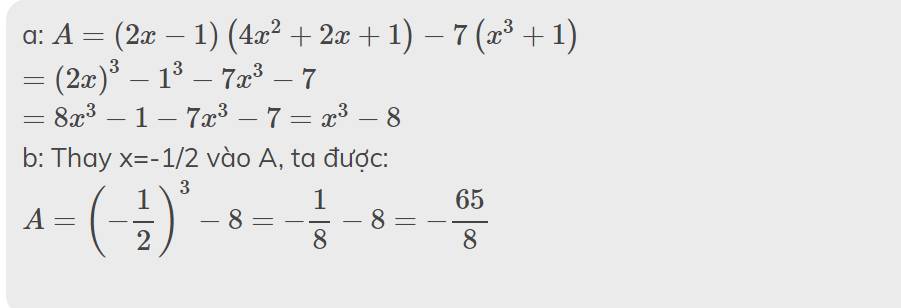
c: \(A=x^3-8=\left(x-2\right)\left(x^2+2x+4\right)\)
Để A là số nguyên tố thì x-2=1
=>x=3

a, A xác định
\(\Leftrightarrow3x^3-19x^2+33x-9\ne0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x^3-x^2-18x^2+6x+27x-9\ne0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2\left(3x-1\right)-6x\left(3x-1\right)+9\left(3x-1\right)\ne0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(3x-1\right)\left(x-3\right)^2\ne0\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x\ne\frac{1}{3}\\x\ne3\end{cases}}\)
b, \(\frac{3x^3-14x^2+3x+36}{3x^2-19x^2+33x-9}=\frac{3x^2\left(x-3\right)-5x\left(x-3\right)-12\left(x-3\right)}{\left(3x-1\right)\left(x-3\right)^2}\)
\(=\frac{\left(3x^2-5x-12\right)\left(x-3\right)}{\left(3x-1\right)\left(x-3\right)^2}=\frac{\left(3x+4\right)\left(x-3\right)^2}{\left(3x-1\right)\left(x-3\right)^2}=\frac{3x+4}{3x-1}\)
\(A=0\Leftrightarrow\frac{3x+4}{3x-1}=0\Leftrightarrow3x+4=0\Leftrightarrow x=-\frac{4}{3}\) (thỏa mãn ĐKXĐ)
c, \(A=\frac{3x+4}{3x-1}=1+\frac{5}{3x-1}\in Z\Rightarrow5⋮\left(3x-1\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow3x-1\inƯ\left(5\right)=\left\{-5;-1;1;5\right\}\)
\(\Rightarrow x\in\left\{-\frac{4}{3};0;\frac{2}{3};2\right\}\)
Mà \(x\in Z,x\ne\left\{\frac{1}{3};3\right\}\Rightarrow x\in\left\{0;2\right\}\)
Bài của Hùng rất thông minh
Đang định có cách khác mà dài hơn cách Hùng nên thui
^^ 2k5 kết bạn nhé

Ta có:
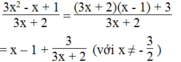
Vì x là số nguyên nên x – 1 là số nguyên.
Để biểu thức đã cho là số nguyên thì 3 ⋮ (3x + 2) và x ≠ -2/3
Suy ra: 3x + 2 ∈ Ư(3) = {-3; -1; 1; 3}
Ta có: 3x + 2 = -3 ⇒ x = -5/3 ∉ Z (loại)
3x + 2 = -1 ⇒ x = - 1
3x + 2 = 1 ⇒ x = -1/3 ∉ Z (loại)
3x + 2 = 3 ⇒ x = 1/3 ∉ Z (loại)
x = -1 khác -3/2
Vậy với x = - 1 thì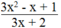 có giá trị nguyên.
có giá trị nguyên.

a,ĐK: \(\hept{\begin{cases}x\ne0\\x\ne\pm3\end{cases}}\)
b, \(A=\left(\frac{9}{x\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)}+\frac{1}{x+3}\right):\left(\frac{x-3}{x\left(x+3\right)}-\frac{x}{3\left(x+3\right)}\right)\)
\(=\frac{9+x\left(x-3\right)}{x\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)}:\frac{3\left(x-3\right)-x^2}{3x\left(x+3\right)}\)
\(=\frac{x^2-3x+9}{x\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)}.\frac{3x\left(x+3\right)}{-x^2+3x-9}=\frac{-3}{x-3}\)
c, Với x = 4 thỏa mãn ĐKXĐ thì
\(A=\frac{-3}{4-3}=-3\)
d, \(A\in Z\Rightarrow-3⋮\left(x-3\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow x-3\inƯ\left(-3\right)=\left\{-3;-1;1;3\right\}\Rightarrow x\in\left\{0;2;4;6\right\}\)
Mà \(x\ne0\Rightarrow x\in\left\{2;4;6\right\}\)
Ta có: \(B=x^3+3x^2+3x+9\)
\(=x^2\left(x+3\right)+3\left(x+3\right)\)
\(=\left(x+3\right)\left(x^2+3\right)\)
Để B là số nguyên tố thì: \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+3=1\\x^2+3=1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-2\\x^2=-2\left(voli\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Thay \(x=-2\) vào B ta được:
\(B=\left(-2+3\right)\left[\left(-2\right)^2+3\right]=7\) là số nguyên tố.
Vậy \(x=-2\)