Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

a, \(6x^2-5x+3=2x-3x\left(3-2x\right)\)
⇔ \(6x^2-5x+3=2x-9x+6x^2\)
⇔ \(6x^2-5x+3-6x^2+9x-2x=0\)
⇔ \(2x+3=0\)
⇔ \(2x=-3\)
⇔ \(x=-\dfrac{3}{2}\)
b, \(\dfrac{2\left(x-4\right)}{4}-\dfrac{3+2x}{10}=x+\dfrac{1-x}{5}\)
⇔ \(\dfrac{20\left(x-4\right)}{4.10}-\dfrac{4\left(3+2x\right)}{4.10}=\dfrac{5x}{5}+\dfrac{1-x}{5}\)
⇔ \(\dfrac{20x-80}{40}-\dfrac{12+8x}{40}=\dfrac{5x+1-x}{5}\)
⇔ \(\dfrac{20x-80-12-8x}{40}=\dfrac{4x+1}{5}\)
⇔ \(\dfrac{12x-92}{40}-\dfrac{4x+1}{5}=0\)
⇔ \(\dfrac{12x-92}{40}-\dfrac{8\left(4x+1\right)}{40}=0\)
⇔ \(12x-92-8\left(4x+1\right)=0\)
⇔ 12x - 92 - 32x - 8 = 0
⇔ -100 - 20x = 0
⇔ 20x = -100
⇔ x = -100 : 20
⇔ x = -5

a: \(\Leftrightarrow1-x+3x+3=2x+3\)
=>2x+4=2x+3(vô lý)
b: \(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+2\right)^2-2x+3=x^2+10\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+4x+4-2x+3=x^2+10\)
=>4x+7=10
hay x=3/4
d: \(\Leftrightarrow\left(-2x+5\right)\left(3x-1\right)+3\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)=\left(x+2\right)\left(1-3x\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-6x^2+2x+15x-5+3\left(x^2-1\right)=\left(x+2\right)\left(1-3x\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-6x^2+17x-5+3x^2-3=x-3x^2+2-6x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-3x^2+17x-8=-3x^2-5x+2\)
=>22x=10
hay x=5/11

a) ĐKXĐ: x # -5
\(\dfrac{2x-5}{x+5}=3\) ⇔ \(\dfrac{2x-5}{x+5}=\dfrac{3\left(x+5\right)}{x+5}\)
⇔ 2x - 5 = 3x + 15
⇔ 2x - 3x = 5 + 20
⇔ x = -20 thoả ĐKXĐ
Vậy tập hợp nghiệm S = {-20}
b) ĐKXĐ: x # 0
\(\dfrac{x^2-6}{x}=x+\dfrac{3}{2}\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{2\left(x^2+6\right)}{2x}=\dfrac{2x^2+3x}{2x}\)
Suy ra: 2x2 – 12 = 2x2 + 3x ⇔ 3x = -12 ⇔ x = -4 thoả x # 0
Vậy tập hợp nghiệm S = {-4}.
c) ĐKXĐ: x # 3
\(\dfrac{\left(x^2+2x\right)-\left(3x+6\right)}{x-3}=0\) ⇔ x(x + 2) - 3(x + 2) = 0
⇔ (x - 3)(x + 2) = 0 mà x # 3
⇔ x + 2 = 0
⇔ x = -2
Vậy tập hợp nghiệm S = {-2}
d) ĐKXĐ: x # \(-\dfrac{2}{3}\)
\(\dfrac{5}{3x+2}=2x-1\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{5}{3x+2}=\dfrac{\left(2x-1\right)\left(3x+2\right)}{3x+2}\)
⇔ 5 = (2x - 1)(3x + 2)
⇔ 6x2 – 3x + 4x – 2 – 5 = 0
⇔ 6x2 + x - 7 = 0
⇔ 6x2 - 6x + 7x - 7 = 0
⇔ 6x(x - 1) + 7(x - 1) = 0
⇔ (6x + 7)(x - 1) = 0
⇔ x = \(-\dfrac{7}{6}\) hoặc x = 1 thoả x # \(-\dfrac{2}{3}\)
Vậy tập nghiệm S = {1;\(-\dfrac{7}{6}\)}.
a)ĐKXĐ:x≠-5
Khử mẫu:2x-5=3(x+5) (1)
giải phương trình (1),ta được:
(1)⇔2x-5=3x+15
⇔2x-3x=15+5
⇔-x=20⇔x=-20(TM)
vậy phương trình đã cho có nghiệm x=-20

b: \(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{7x+10}{x+1}\left(x^2-x-2-2x^2+3x+5\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(7x+10\right)\left(-x^2+2x+3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(7x+10\right)\left(x^2-2x-3\right)=0\)
=>(7x+10)(x-3)=0
hay \(x\in\left\{-\dfrac{10}{7};3\right\}\)
d: \(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{13}{2x^2+7x-6x-21}+\dfrac{1}{2x+7}-\dfrac{6}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{13}{\left(2x+7\right)\left(x-3\right)}+\dfrac{1}{\left(2x+7\right)}-\dfrac{6}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow26x+91+x^2-9-12x-14=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+14x+68=0\)
hay \(x\in\varnothing\)

\(a,6x^2-5x+3=2x-3x\left(3-2x\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6x^2-5x+3=2x-9x+6x^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6x^2-5x+3=-7x+6x^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6x^2-5x+3+7x-6x^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x+3=0\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{-3}{2}\)
Vậy ....
b,\(\dfrac{2\left(x+4\right)}{4}-\dfrac{3+2x}{10}=x+\dfrac{1-x}{5}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{10\left(x-4\right)-2\left(3+2x\right)}{20}=\dfrac{20x+4\left(1-x\right)}{20}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow10x-40-6-4x=20x+4\left(1-x\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6x-46=16x+4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6x-16x=4+46\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-10x=50\Leftrightarrow x=-5\)
Vậy...
c,\(\dfrac{2x}{3}+\dfrac{3x-5}{4}=\dfrac{3\left(2x-1\right)}{2}-\dfrac{7}{6}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{8x+3\left(3x-5\right)}{12}=\dfrac{6\left(6x-3\right)-14}{12}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{8x+9x-15}{12}=\dfrac{36x-18-14}{12}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow17x-15=36x-32\)
\(\Leftrightarrow17x-36x=-32-15\)
\(\Leftrightarrow19x=-47\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{-47}{19}\)
Vậy...

a) 1x−1−3x2x3−1=2xx2+x+11x−1−3x2x3−1=2xx2+x+1
Ta có: x3−1=(x−1)(x2+x+1)x3−1=(x−1)(x2+x+1)
=(x−1)[(x+12)2+34]=(x−1)[(x+12)2+34] cho nên x3 – 1 ≠ 0 khi x – 1 ≠ 0⇔ x ≠ 1
Vậy ĐKXĐ: x ≠ 1
Khử mẫu ta được:
x2+x+1−3x2=2x(x−1)⇔−2x2+x+1=2x2−2xx2+x+1−3x2=2x(x−1)⇔−2x2+x+1=2x2−2x
⇔4x2−3x−1=0⇔4x2−3x−1=0
⇔4x(x−1



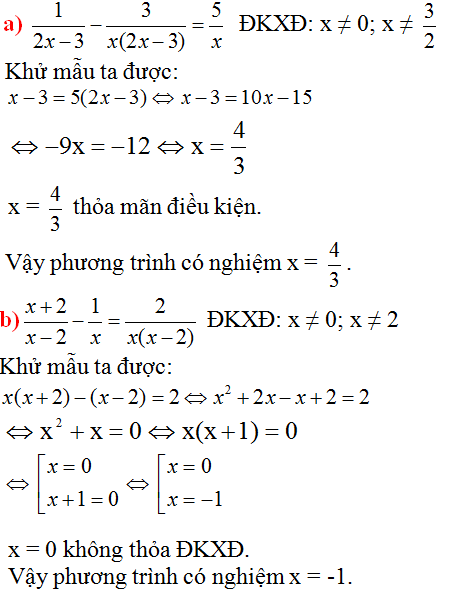

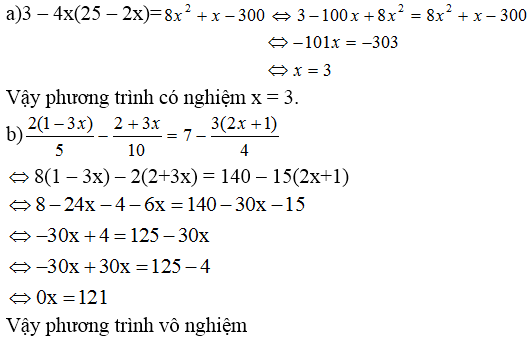

a: =>-3x=-12
=>x=4
b: =>3(3x+2)-3x-1=12x+10
=>9x+6-3x-1=12x+10
=>12x+10=6x+5
=>6x=-5
=>x=-5/6
c: =>x(x+1)+x(x-3)=4x
=>x^2+x+x^2-3x-4x=0
=>2x^2-6x=0
=>2x(x-3)=0
=>x=3(loại) hoặc x=0(nhận)