
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


+ Với \(m-1=0\Leftrightarrow m=1\), pt trở thành : \(-x^2=0\Leftrightarrow x=0\)( loại)
+ Với \(m-1\ne0\Leftrightarrow m\ne1\)
Đặt \(t=x^2\left(t\ge0\right)\)
pt trở thành \(\left(m-1\right)t^2-mt+m^2-1=0\left(1\right)\)
pt có 3 nghiệm phân biệt \(\Leftrightarrow\left(1\right)\) có 2 nghiệm \(t_1,t_2\left(t_1=0< t_2\right)\)
Khi \(t_1=0\Rightarrow m=\pm1\). Vì có 2 nghiệm phân biệt nên \(m\ne1\)
Với \(m=-1\Rightarrow t_2=\dfrac{1}{2}\) ( nhận)
Vậy m=-1 thì pt đã cho có 3 nghiệm phân biệt

a) \(d\left(A;\Delta\right)=\dfrac{\left|4.1-3.3+2\right|}{\sqrt{4^2+\left(-3\right)^2}}=\dfrac{3}{5}\)
b) \(\overrightarrow{AB}=\left(-3;-2\right)\) là VTCP của đường thẳng d
PT tham số của d: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=1-3t\\y=3-2t\end{matrix}\right.\left(t\in R\right)\)
c) Đường tròn (C) có bán kính \(R=AB=\sqrt{\left(1+2\right)^2+\left(3-1\right)^2}=\sqrt{13}\)
PT đường tròn (C): \(\left(x-1\right)^2+\left(y-3\right)^2=13\)



\(\dfrac{\pi}{2}< a< \pi\Rightarrow cosa< 0\)
\(\Rightarrow cosa=-\sqrt{1-sin^2a}=-\sqrt{1-\dfrac{9}{16}}=-\dfrac{\sqrt{7}}{4}\)
\(tana=\dfrac{sina}{cosa}=-\dfrac{3\sqrt{7}}{7}\) ; \(cota=\dfrac{1}{tana}=-\dfrac{\sqrt{7}}{3}\)
Bây giờ bạn chỉ cần thay số và bấm máy tính
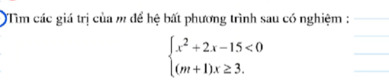
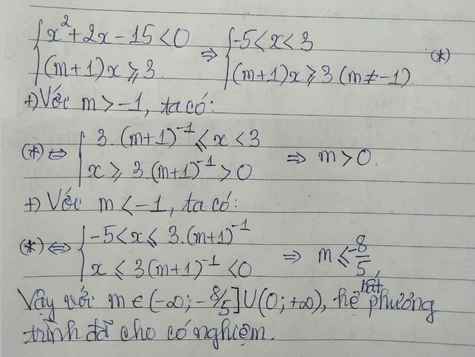


 giúp mình 5 câu này với ạ
giúp mình 5 câu này với ạ giúp mình 2 câu này với ạ
giúp mình 2 câu này với ạ giúp mình mấy câu này với mình cảm ơn nhìu ạ
giúp mình mấy câu này với mình cảm ơn nhìu ạ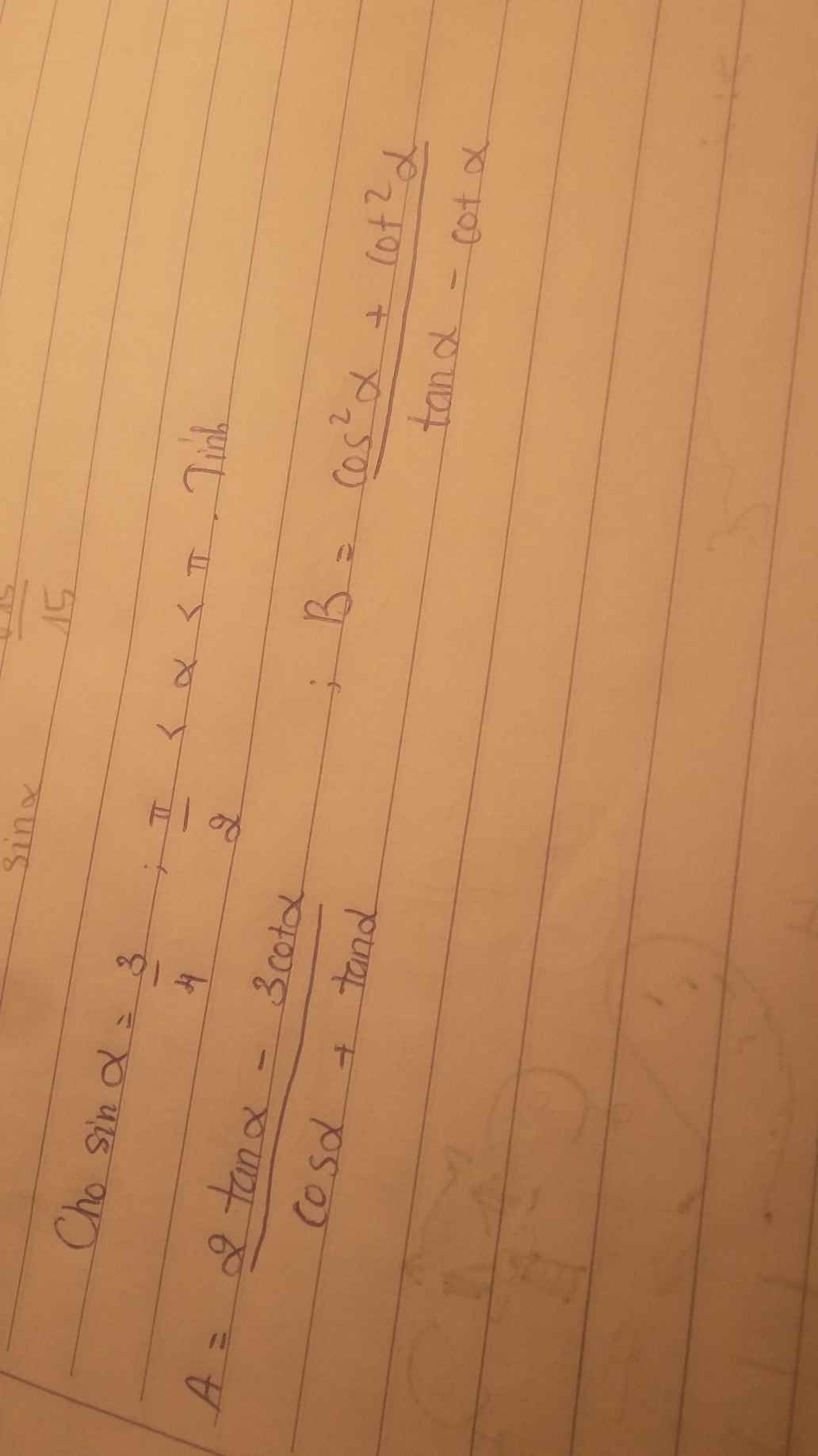
Pt tương đương: \(a=2\left|x^2-5x+4\right|-\left(x^2-5x\right)\)
Xét hàm \(f\left(x\right)=2\left|x^2-5x+4\right|-\left(x^2-5x\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow f\left(x\right)=\left[{}\begin{matrix}-3x^2+15x-8\left(\text{ với }1\le x\le4\right)\\x^2-5x+8\left(\text{ với }\left[{}\begin{matrix}x\ge4\\x\le1\end{matrix}\right.\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Do đó ta có BBT của \(f\left(x\right)\) như sau:
Từ BBT ta thấy pt có 4 nghiệm pb khi và chỉ khi: \(4< a< \dfrac{43}{4}\)