
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


\(=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow-1}\dfrac{\dfrac{x+2017-\left(2015-x\right)}{\sqrt[3]{\left(x+2017\right)^2}+\sqrt[3]{\left(x+2017\right)\left(2015-x\right)}+\sqrt[3]{\left(2015-x\right)^2}}}{\dfrac{2000+x-\left(1998-x\right)}{\sqrt{2000+x}+\sqrt{1998-x}}}\)
\(=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow-1}\dfrac{\sqrt{2000+x}+\sqrt{1998-x}}{\sqrt[3]{\left(x+2017\right)^2}+\sqrt[3]{\left(x+2017\right)\left(2015-x\right)}+\sqrt[3]{\left(2015-x\right)^2}}\)
\(=\dfrac{\sqrt{1999}+\sqrt{1999}}{\sqrt[3]{2016^2}+\sqrt[3]{2016^2}+\sqrt[3]{2016^2}}=\dfrac{2\sqrt{1999}}{3.24\sqrt[3]{294}}=\dfrac{\sqrt{1999}}{36\sqrt[3]{294}}\)
\(\Rightarrow a+b=1999+294\)

Rất đơn giản, điểm \(A\left(1;-2\right)\) có \(x=1;y=-2\)
Do đó ảnh của nó qua phép biến hình \(f\) sẽ có tọa độ: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_{A'}=-x=-1\\y_{A'}=\dfrac{y}{2}=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow A'\left(-1;-1\right)\)

\(f'\left(x\right)=2x^2-x\)
\(f'\left(x\right)\ge0\Leftrightarrow2x^2-x\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(2x-1\right)\ge0\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x\ge\dfrac{1}{2}\\x\le0\end{matrix}\right.\)

Đặt \(cosx-sinx=t\Rightarrow-\sqrt{2}\le t\le\sqrt{2}\)
\(t^2=1-2sinx.cosx\Rightarrow sinx.cosx=\dfrac{1-t^2}{2}\)
Pt trở thành:
\(t\left(1+\dfrac{1-t^2}{2}\right)+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow t^3-3t-2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(t-2\right)\left(t+1\right)^2=0\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}t=2\left(loại\right)\\t=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow cosx-sinx=-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt[]{2}cos\left(x+\dfrac{\pi}{4}\right)=-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow cos\left(x+\dfrac{\pi}{4}\right)=-\dfrac{\sqrt{2}}{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow cos\left(x+\dfrac{\pi}{4}\right)=cos\left(\dfrac{3\pi}{4}\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow...\)

cos x = cos\(\dfrac{\pi}{6}\)
x = \(\dfrac{\pi}{6}\) + k2\(\pi\) (1)
x = - \(\dfrac{\pi}{6}\) + k2\(\pi\) (2)
(1) thế k = -1 -> x = \(\dfrac{-11\pi}{6}\) (loại) *k= -2, k =-3,... loại luôn*
thế k = 0 -> x = \(\dfrac{\pi}{6}\) (nhận)
thế k = 1 -> x = \(\dfrac{13\pi}{6}\) (loại) *k=2, k=3,... loại luôn*
vậy (1) có 1 nghiệm
(2) thế k = - 1 -> x = \(\dfrac{-13\pi}{6}\) ( loại)
thế k = 0 -> x = \(\dfrac{-\pi}{6}\) (nhận)
thế k = 1 -> x = \(\dfrac{11\pi}{6}\) ( loại)
vậy tổng nghiệm (1) + (2) là 2 -> Đáp án câu D
#Chúc em học tốt

29.
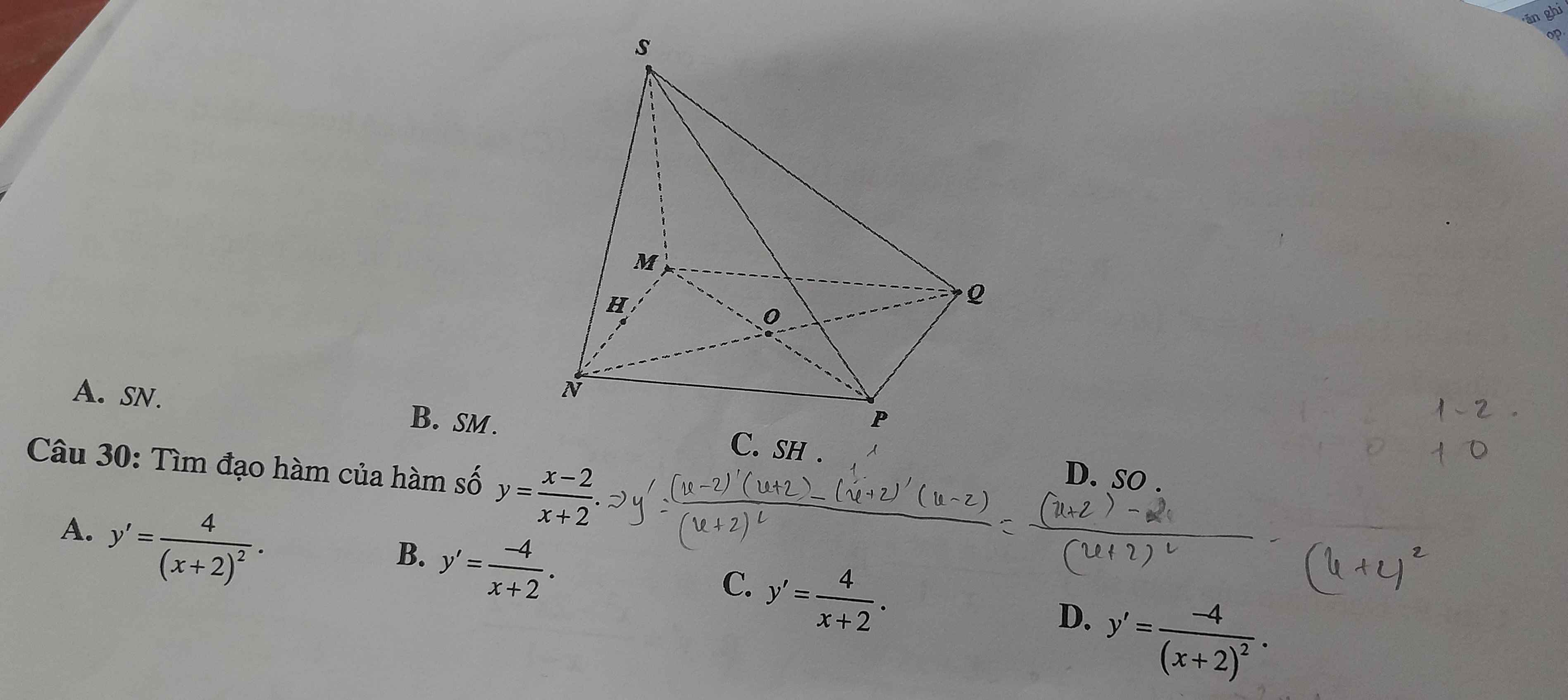
SMN cân tại S \(\Rightarrow SH\perp MN\) (trung tuyến đồng thời là đường cao trong tam giác cân)
Mà \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}MN=\left(SMN\right)\cap\left(MNPQ\right)\\\left(SMN\right)\perp\left(MNPQ\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow SH\perp\left(MNPQ\right)\)
Hay SH là đường cao của chóp

Hi bạn, câu 29 này mình có cái cách này dùng cho các bài lim khi rơi vào trường hợp vô định thì bạn dùng quy tắc L'Hospital làm cho nhanh với trường hợp các bài trắc nghiệm như thế này
Ở bài 29 này đang rơi vào dạng \(\dfrac{0}{0}\) nên dùng quy tắc L'Hospital được nè. Bạn làm như sau:
ĐKXĐ: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\ne1\\x\ge-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
Bước 1: Đạo hàm tử mẫu, ta được: \(\dfrac{\dfrac{1}{2}\left(x+3\right)^{-\dfrac{1}{2}}}{1}\)
Bước 2: Thay điểm cần tính giới hạn: (x=1)
ta sẽ được \(\dfrac{1}{4}\)
Vậy \(lim_{x\rightarrow1}\dfrac{\sqrt{x+3}-2}{x-1}=\dfrac{1}{4}\)
\(\Rightarrow a=1;b=4\)
Vậy S=4a-b=0

29.
\(y'=\dfrac{1}{3}x^3-\dfrac{1}{2}\left(m^2+1\right)x^2+\left(m^2-7m+12\right)x\)
\(y''=x^2-\left(m^2+1\right)x+m^2-7m+12\)
Pt \(y''=0\) có 2 nghiệm trái dấu khi và chỉ khi:
\(1.\left(m^2-7m+12\right)< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3< m< 4\)
\(\Rightarrow\) Không có giá trị nguyên nào của m thỏa mãn
30.
\(y'=x^2-2\left(2m+1\right)x-m\ge0;\forall x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\Delta'=\left(2m+1\right)^2+m\le0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4m^2+5m+1\le0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-1\le m\le-\dfrac{1}{4}\)
\(\Rightarrow\) Có 1 giá trị nguyên của m thỏa mãn (\(m=-1\))








\(f'\left(x\right)=\dfrac{-3}{\left(x-1\right)^2}\) ; \(f''\left(x\right)=\dfrac{6}{\left(x-1\right)^3}\)
\(f'\left(x\right)+f''\left(x\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{-3}{\left(x-1\right)^2}+\dfrac{6}{\left(x-1\right)^3}=0\) (\(x\ne1\))
\(\Leftrightarrow-3\left(x-1\right)+6=0\Rightarrow x=3\)