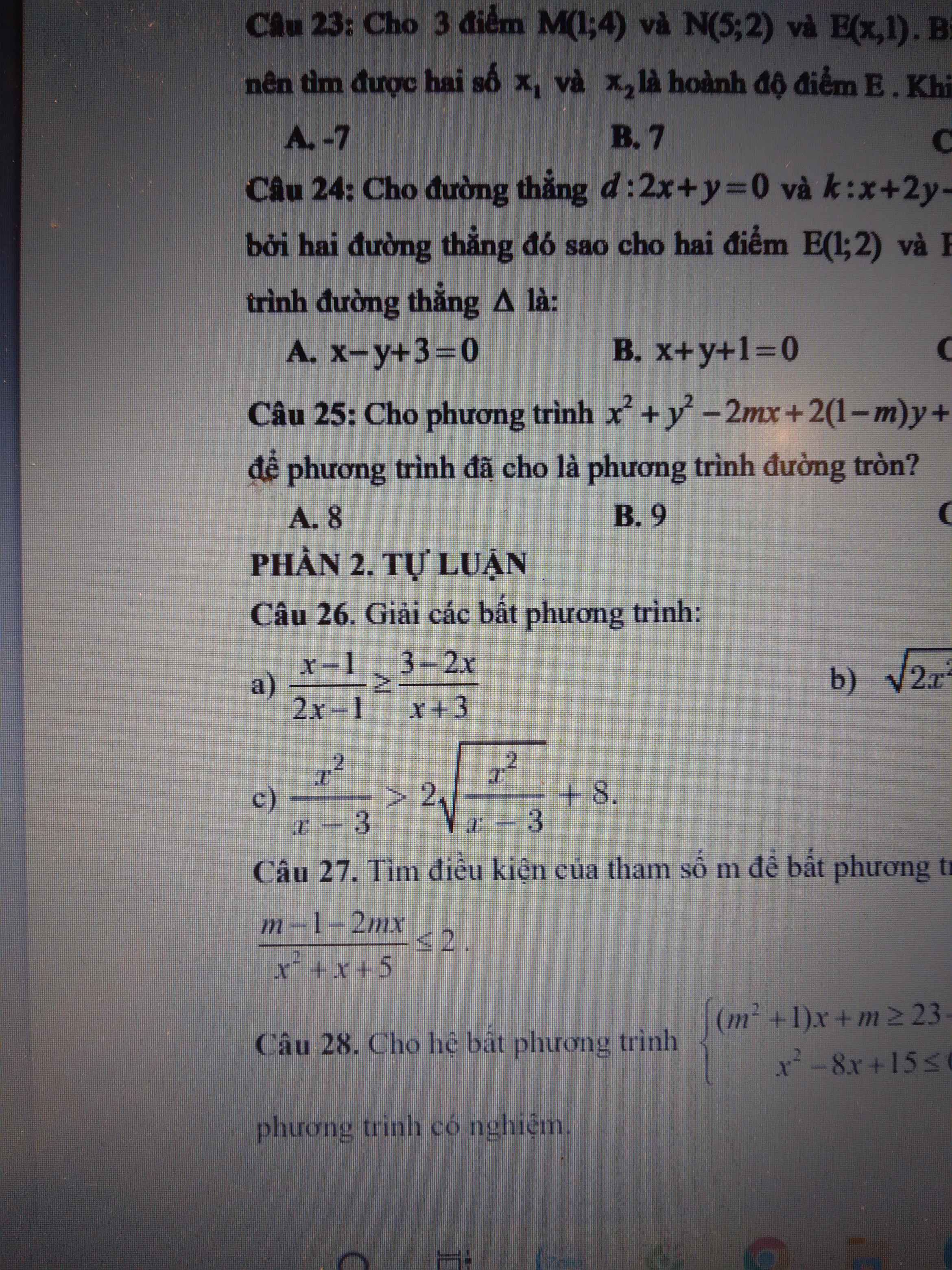Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


3.
Xét \(x^2-8x+7\le0\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x-7\right)\le0\Rightarrow1\le x\le7\)
Có tập nghiệm \(D_1=\left[1;7\right]\)
Xét \(x^2-\left(2m+1\right)x+m^2+m\le0\Leftrightarrow\left(x-m\right)\left(x-m-1\right)\le0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m\le x\le m+1\) có tập nghiệm là \(D_2=\left[m;m+1\right]\)
a. Hệ BPT vô nghiệm khi \(D_1\cap D_2=\varnothing\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}m>7\\m+1< 1\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}m>7\\m< 0\end{matrix}\right.\)
b. Do \(D_2\) là đoạn có độ dài bằng \(m+1-m=1\) nên hệ có tập nghiệm là 1 đoạn dài 1 trên trục số khi: \(D_2\subset D_1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m\ge1\\m+1\le7\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow1\le m\le6\)

5:
a: sin x=2*cosx
\(A=\dfrac{6cosx+2cosx-4\cdot8\cdot cos^3x}{cos^3x-2cosx}\)
\(=\dfrac{8-32cos^2x}{cos^2x-2}\)
b: VT=sin^4(pi/2-x)+cos^4(x+pi/2)+6*1/2*sin^22x+1/2*cos4x
=cos^4x+sin^4x+3*sin^2(2x)+1/2*(1-2*sin^2(2x))
=1-2*sin^2x*cos^2x+3*sin^2(2x)+1/2-sin^2(2x)
==3/2=VP

4b.
\(\dfrac{\pi}{2}< a< \pi\Rightarrow cosa< 0\Rightarrow cosa=-\sqrt{1-sin^2a}=-\dfrac{4}{5}\)
\(\Rightarrow tana=\dfrac{sina}{cosa}=-\dfrac{3}{4}\)
\(tan\left(a+\dfrac{\pi}{3}\right)=\dfrac{tana+tan\left(\dfrac{\pi}{3}\right)}{1-tana.tan\left(\dfrac{\pi}{3}\right)}=\dfrac{-\dfrac{3}{4}+\sqrt{3}}{1-\left(-\dfrac{3}{4}\right).\sqrt{3}}=...\)
c.
\(\dfrac{3\pi}{2}< a< 2\pi\Rightarrow cosa>0\Rightarrow cosa=\sqrt{1-sin^2a}=\dfrac{5}{13}\)
\(cos\left(\dfrac{\pi}{3}-a\right)=cos\left(\dfrac{\pi}{3}\right).cosa+sin\left(\dfrac{\pi}{3}\right).sina=\dfrac{1}{2}.\dfrac{5}{13}+\left(-\dfrac{12}{13}\right).\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}=...\)

4:
a: -90<a<0
=>cos a>0
cos^2a=1-(-4/5)^2=9/25
=>cosa=3/5
\(sin\left(45-a\right)=sin45\cdot cosa-cos45\cdot sina=\dfrac{\sqrt{2}}{2}\left(cosa-sina\right)\)
\(=\dfrac{\sqrt{2}}{2}\left(\dfrac{3}{5}-\dfrac{4}{5}\right)=\dfrac{-\sqrt{2}}{10}\)
b: pi/2<a<pi
=>cosa<0
cos^2a+sin^2a=0
=>cos^2a=16/25
=>cosa=-4/5
tan a=3/5:(-4/5)=-3/4
\(tan\left(a+\dfrac{pi}{3}\right)=\dfrac{tana+\dfrac{tanpi}{3}}{1-tana\cdot tan\left(\dfrac{pi}{3}\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{-\dfrac{3}{4}+\sqrt{3}}{1-\dfrac{-3}{4}\cdot\sqrt{3}}=\dfrac{48-25\sqrt{3}}{11}\)
c: 3/2pi<a<pi
=>cosa>0
cos^2a+sin^2a=1
=>cos^2a=25/169
=>cosa=5/13
cos(pi/3-a)
\(=cos\left(\dfrac{pi}{3}\right)\cdot cosa+sin\left(\dfrac{pi}{3}\right)\cdot sina\)
\(=\dfrac{5}{13}\cdot\dfrac{1}{2}+\dfrac{-12}{13}\cdot\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}=\dfrac{5-12\sqrt{3}}{26}\)

15:
b: Gọi I(a;b)
Theo đề, ta có: d(I;d)=d(I;d')=căn 5
=>3a-b+3=căn 5*căn 10=5*căn 2 và a-3b+9=5căn 2
=>|3a-b+3|=|a-3b+9|
=>2a+2b=6 và 2a-4b=12
=>a=1 và b=2
=>I(1;2)
Phương trình (C) là:
(x-1)^2+(y-2)^2=5
c: (C): x^2+y^2+4x-y+4=0
=>(x+2)^2+(y-1/2)^2=1/4
=>I(-2;1/2);R=1/2
=>I'(2;1/2)
Phương trình (C') là:
(x-2)^2+(y-1/2)^2=1/4

Gọi \(M\left(x;y\right)\) là điểm bất kì thuộc mp, M nằm trên đường phân giác góc tạo bởi 2 đường thẳng đã cho khi và chỉ khi:
\(d\left(M;d\right)=d\left(M;k\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\left|2x+y\right|}{\sqrt{2^2+1^2}}=\dfrac{\left|x+2y-3\right|}{\sqrt{1^2+2^2}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left|2x+y\right|=\left|x+2y-3\right|\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x+y=x+2y-3\\2x+y=-x-2y+3\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-y+3=0\\x+y-1=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
Thế tọa độ E, F lần lượt vào 2 đường thẳng ta thấy cả 2 đều thỏa mãn (cho 2 giá trị cùng dấu dương)
Vậy đề bài sai, đáp án A và D đều đúng hết

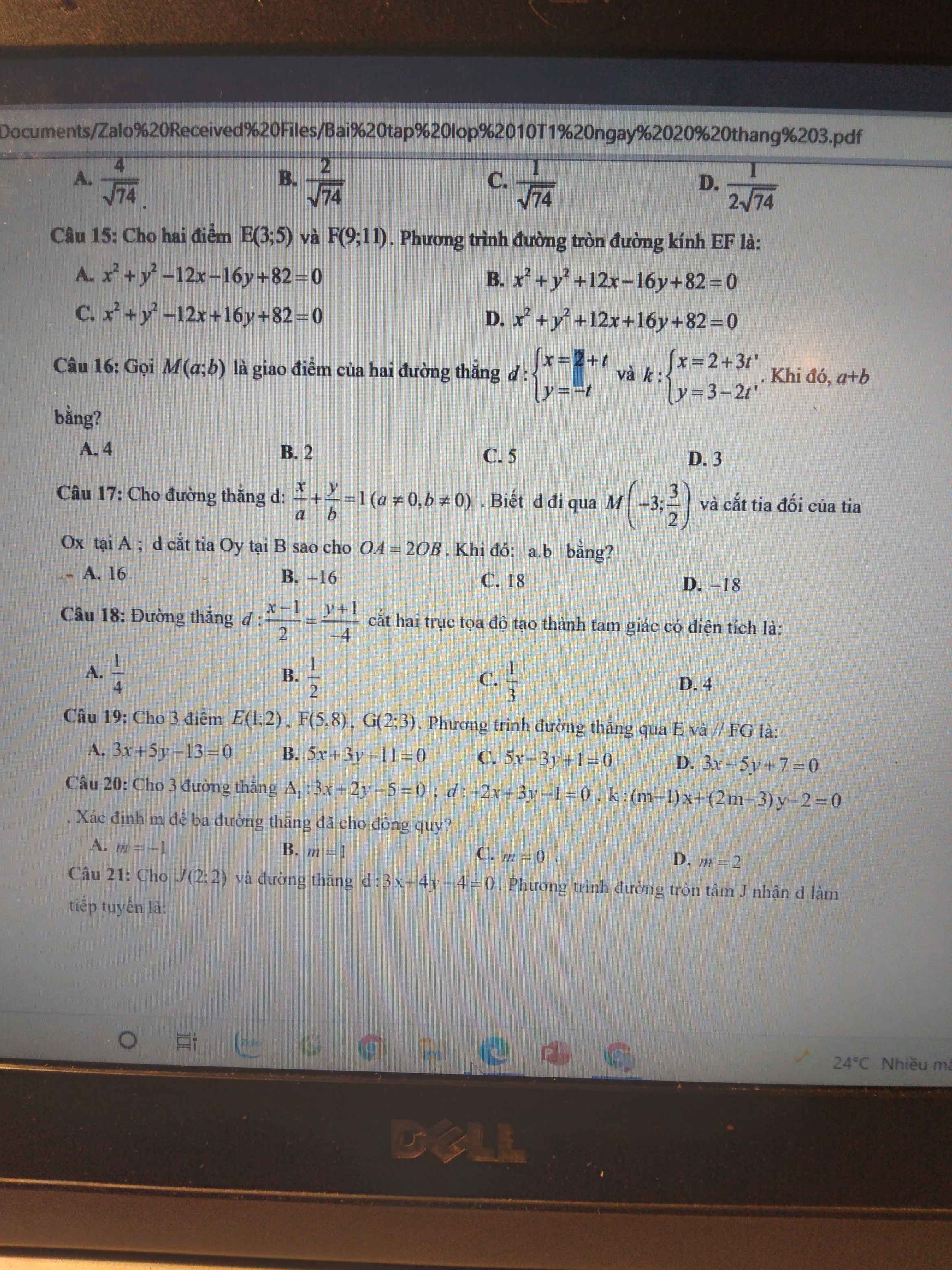
16.
Hệ tọa độ giao điểm: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2+t=2+3t'\\-t=3-2t'\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}t=-9\\t'=-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
Thay \(t=-9\) vào pt d ta được: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a=-7\\b=9\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow a+b=2\)
17.
Do d qua M nên: \(\dfrac{-3}{a}+\dfrac{3}{2b}=1\) (1)
d cắt tia đối Ox tại A \(\Rightarrow a< 0\) và \(OA=-a\)
d cắt Oy tại b \(\Rightarrow b>0\) và \(OB=b\)
\(OA=2OB\Rightarrow-a=2b\)
Thế vào (1): \(\dfrac{-3}{a}+\dfrac{3}{-a}=1\Rightarrow a=-6\Rightarrow b=\dfrac{-a}{2}=3\)
\(\Rightarrow ab=-18\)
18.
Gọi A là giao điểm của d với Ox
\(\Rightarrow y_A=0\Rightarrow\dfrac{x_A-1}{2}=\dfrac{0+1}{-4}\Rightarrow x_A=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(\Rightarrow OA=\left|x_A\right|=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
Gọi B là giao điểm của d với Oy
\(\Rightarrow x_B=0\Rightarrow\dfrac{0-1}{2}=\dfrac{y_B+1}{-4}\Rightarrow y_B=1\)
\(\Rightarrow OB=\left|y_B\right|=1\)
\(S=\dfrac{1}{2}OA.OB=\dfrac{1}{4}\)

Đặt \(\sqrt{\dfrac{x^2}{x-3}}=a\left(a>=0\right)\)
Theo đề, ta có bất phương trình:
\(a^2>2a+8\)
=>(a-4)(a+2)>0
=>a-4>0
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x^2}{x-3}>16\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-16x+48>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\in R\)
Vậy: S=R\{3}