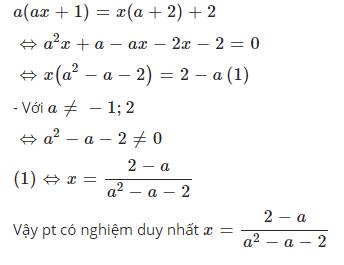Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.



\(a\left(ax+1\right)\text{=}x\left(a+2\right)+2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow a^2x-ax-2x\text{=}2-a\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(a^2-a-2\right)\text{=}2-a\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(a+1\right)\left(a-2\right)\text{=}2-a\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\text{=}\dfrac{-1}{a+1}\)
em mới có lớp 8 nên là em không chắc nữa

1)
<=> \(x^2-3x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x-3\right)=0\)
x= 0
x = 3
2) <=> \(x\left(x-3\right)=4\)
=> \(x=\dfrac{4}{x}+3\)
\(2,x^2-3x=4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-3x-4=0\)
\(\Delta=b^2-4ac=\left(-3\right)^2-4\left(-4\right)=25>0\)
\(\Rightarrow\)Pt có 2 nghiệm pb
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1=\dfrac{-b+\sqrt{\Delta}}{2a}=\dfrac{3+5}{2}=4\\x_2=\dfrac{-b-\sqrt{\Delta}}{2a}=\dfrac{-3-5}{2}=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy \(S=\left\{4;-1\right\}\)
\(3,x^4-5x^2+6=0\)
Đặt \(t=x^2\left(t\ge0\right)\)
Pt trở thành
\(t^2-5t+6=0\)
\(\Delta=b^2-4ac=\left(-5\right)^2-4.6=1>0\)
\(\Rightarrow\)Pt ó 2 nghiệm pb
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1=\dfrac{-b+\sqrt{\Delta}}{2a}=\dfrac{5+1}{2}=3\\x_2=\dfrac{-b-\sqrt{\Delta}}{2a}=\dfrac{-5-1}{2}-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow t=x^2\Leftrightarrow t=\pm\sqrt{3}\)
Vậy \(S=\left\{\pm\sqrt{3}\right\}\)

phân tích ta được T=\(\frac{1}{a}\)
suy ra với a=1 hoặc a=-1 thi với mọi x thì t=a.
Nếu a<>1 va a<>-1 thì ko có x.

Lời giải:
a)
\(3x^2-5x+1=2x-3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow 3x^2-5x+1-2x+3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow 3x^2-7x+4=0\) (\(a=3; b=-7; c=4)\)
b)
\(\frac{3}{5}x^2-4x-3=3x+\frac{1}{3}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow \frac{3}{5}x^2-4x-3-3x-\frac{1}{3}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow \frac{3}{5}x^2-7x-\frac{10}{3}=0(a=\frac{3}{5};b=-7; c=\frac{-10}{3})\)
c)
\(\Leftrightarrow -\sqrt{3}x^2+x-5-\sqrt{3}x-\sqrt{2}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow -\sqrt{3}x^2+(1-\sqrt{3})x-(5+\sqrt{2})=0\)
(\(a=-\sqrt{3}; b=1-\sqrt{3}; c=-(5+\sqrt{2}))\)
d)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-5(m+1)x+m^2-2=0\)
(\(a=1;b=-5(m+1); c=m^2-2)\)

Không biết câu 1 đề là m2x hay là mx ta ? Bởi nếu đề như vậy đenta sẽ là bậc 4 khó thành bình phương lắm
Làm câu 2 trước vậy , câu 1 để sau
a, pt có nghiệm \(x=2-\sqrt{3}\)
\(\Rightarrow pt:\left(2-\sqrt{3}\right)^3+a\left(2-\sqrt{3}\right)^2+b\left(2-\sqrt{3}\right)-1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow26-15\sqrt{3}+7a-4a\sqrt{3}+2b-b\sqrt{3}-1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{3}\left(4a+b+15\right)=7a+2b+25\)
Vì VP là số hữu tỉ
=> VT là số hữu tỉ
Mà \(\sqrt{3}\)là số vô tỉ
=> 4a + b + 15 = 0
=> 7a + 2b + 25 = 0
Ta có hệ \(\hept{\begin{cases}4a+b=-15\\7a+2b=-25\end{cases}}\)
Dễ giải được \(\hept{\begin{cases}a=-5\\b=5\end{cases}}\)
b, Với a = -5 ; b = 5 ta có pt:
\(x^3-5x^2+5x-1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2-4x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=1\\x^2-4x+1=0\left(1\right)\end{cases}}\)
Giả sử x1 = 1 là 1 nghiệm của pt ban đầu
x2 ; x3 là 2 nghiệm của pt (1)
Theo Vi-ét \(\hept{\begin{cases}x_2+x_3=4\\x_2x_3=1\end{cases}}\)
Có: \(x_2^2+x_3^2=\left(x_2+x_3\right)^2-2x_2x_3=16-2=14\)
\(x_2^3+x_3^3=\left(x_2+x_3\right)\left(x^2_2-x_2x_3+x_3^2\right)=4\left(14-1\right)=52\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x_2^2+x_3^2\right)\left(x_2^3+x_3^3\right)=728\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x_2^5+x_3^5+x_2^2x_3^2\left(x_2+x_3\right)=728\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^5_2+x_3^5+4=728\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x_2^5+x_3^5=724\)
Có \(S=\frac{1}{x_1^5}+\frac{1}{x_2^5}+\frac{1}{x_3^5}\)
\(=1+\frac{x_2^5+x_3^5}{\left(x_2x_3\right)^5}\)
\(=1+724\)
\(=725\)
Vậy .........
Câu 1 đây , lừa người quá
Giả sử pt có 2 nghiệm x1 ; x2
Theo Vi-ét \(\hept{\begin{cases}x_1+x_2=m^2\\x_1x_2=2m+2\end{cases}}\)
\(Do\text{ }m\inℕ^∗\Rightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}S=m^2>0\\P=2m+2>0\end{cases}\Rightarrow}x_1;x_2>0\)
Lại có \(x_1+x_2=m^2\inℕ^∗\)
Mà x1 hoặc x2 nguyên
Nên suy ra \(x_1;x_2\inℕ^∗\)
Khi đó : \(\left(x_1-1\right)\left(x_2-1\right)\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x_1x_2-\left(x_1+x_2\right)+1\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2m+2-m^2+1\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-1\le m\le3\)
Mà \(m\inℕ^∗\Rightarrow m\in\left\{1;2;3\right\}\)
Thử lại thấy m = 3 thỏa mãn
Vậy m = 3