
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


\(\Leftrightarrow2x^3-2x+x^2-1-4x^2+2x+2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^3-3x^2+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^3-2x^2-x^2+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2\left(x-1\right)-\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(2x^2-x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(2x^2-2x+x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)^2\left(2x+1\right)=0\)
=>x=1 hoặc x=-1/2
\(\left(2x+1\right)\left(x^2-1\right)=4x^2-2x-2\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(2x+1\right)\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)=4x^2-4x+2x-2\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(2x+1\right)\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)=4x\left(x-1\right)+2\left(x-1\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(2x+1\right)\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)=\left(4x+2\right)\left(x-1\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(2x+1\right)\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)=2\left(2x+1\right)\left(x-1\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(2x+1\right)\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)-2\left(2x+1\right)\left(x-1\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(2x+1\right)\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1-2\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(2x+1\right)\left(x-1\right)^2=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\\x=1\end{matrix}\right.\)

Cách 1:
(x + 1)2 = 4(x2 – 2x + 1)
⇔ (x + 1)2 - 4(x2 – 2x + 1) = 0
⇔ (x + 1)2 - 22. (x -1)2 = 0
⇔ (x + 1)2 – [ 2(x – 1)]2 =0
⇔ [(x+ 1) + 2( x- 1)]. [(x+ 1) - 2( x- 1)]= 0
⇔ ( x+1+ 2x -2) . (x+1 – 2x + 2) =0
⇔ ( 3x- 1).( 3- x) = 0
⇔ 3x – 1 = 0 hoặc 3 – x= 0
+) 3x – 1 = 0 ⇔ 3x = 1 ⇔ x = 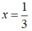
+) 3 – x = 0 ⇔ x= 3
Vậy tập nghiệm của phương trình đã cho là:
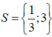
* Cách 2: Ta có:
(x + 1)2 = 4(x2 – 2x + 1)
⇔ (x + 1)2 - 4(x2 – 2x + 1) = 0
⇔ x2 + 2x +1- 4x2 + 8x – 4 = 0
⇔ - 3x2 + 10x – 3 = 0
⇔ (- 3x2 + 9x) + (x – 3) = 0
⇔ -3x (x – 3)+ ( x- 3) = 0
⇔ ( x- 3). ( - 3x + 1) = 0
⇔ x - 3 = 0 hoặc -3x + 1= 0
+) x - 3 = 0 x = 3
+) - 3x + 1 = 0 - 3x = - 1 ⇔ x = 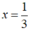
Vậy tập nghiệm của phương trình đã cho là:
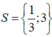
\(\left(x+1\right)^2=4\left(x^2-2x+1\right)\)
\(< =>\left(x+1\right)^2=\left(2x-2\right)^2\)
\(< =>\left(x+1-2x+2\right)\left(x+1+2x-2\right)=0\)
\(< =>\orbr{\begin{cases}-x+3=0\\3x-1=0\end{cases}}\)
\(< =>\orbr{\begin{cases}x=3\\x=\frac{1}{3}\end{cases}}\)

\(|x-6|=-5x+9\)
Xét \(x\ge6\)thì \(pt< =>x-6=-5x+9\)
\(< =>x-6+5x-9=0\)
\(< =>6x-15=0\)
\(< =>x=\frac{15}{6}\)(ktm)
Xét \(x< 6\)thì \(pt< =>x-6=5x-9\)
\(< =>4x-9+6=0\)
\(< =>4x-3=0< =>x=\frac{3}{4}\)(tm)
Vậy ...

\(\left(2x+1\right)\left(x^2+2\right)=0\)
\(< =>\orbr{\begin{cases}2x+1=0\\x^2+2=0\end{cases}}\)
Do \(x^2\ge0=>x^2+2\ge2=>x^2+2>0\)
Xét phương trình \(2x+1=0< =>x=-\frac{1}{2}\)

5 x - 2 2 - 2 x + 2 x - 1 2 = 1 - x 2 + x - 3 1 - x Đ K X Đ : x ≠ 1 ⇔ 5 x - 2 2 - 2 x + 2 x - 1 1 - x 2 1 - x = 2 1 - x 2 1 - x - 2 x 2 + x - 3 2 1 - x
⇔ 5x – 2 + (2x – 1)(1 – x) = 2(1 – x) – 2( x 2 + x – 3)
⇔ 5x – 2 + 2x – 2 x 2 – 1 + x – 2 + 2x + 2 x 2 + 2x – 6 = 0
⇔ 12x - 11 = 0
⇔ x = 11/12 (thoả mãn)
Vậy phương trình có nghiệm x = 11/12

a: =>(x^2-2x+1-1)^2+2(x-1)^2=1
=>(x-1)^4-2(x-1)^2+1+2(x-1)^2=1
=>(x-1)^4=0
=>x-1=0
=>x=1
b: =>(x^2+2)^2+3x(x^2+2)+2x^2-20x^2=0
=>(x^2+2)^2+3x(x^2+2)-18x^2=0
=>(x^2+2+6x)(x^2-3x+2)=0
=>\(x\in\left\{-3\pm\sqrt{7};1;2\right\}\)
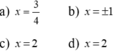


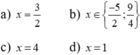
đk: 2x + 1 ≥ 0 <=> x ≥ -0,5
\(\left|x^2-1\right|=2x+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x^2-1=2x+1\\x^2-1=-2x-1\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x^2-2x-2=0\\x^2+2x=0\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}\left(x-1-\sqrt{3}\right)\left(x-1+\sqrt{3}\right)=0\left(1\right)\\x\left(x+2\right)=0\left(2\right)\end{cases}}\)
Giải 1:
\(\left(x-1-\sqrt{3}\right)\left(x-1+\sqrt{3}\right)=0\) \(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=1+\sqrt{3}\left(tm\right)\\x=1-\sqrt{3}\left(ktm\right)\end{cases}}\)
Giải 2:
\(x\left(x+2\right)=0\)\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=0\left(tm\right)\\x=-2\left(ktm\right)\end{cases}}\)
Vậy.....
P/s: (tm: thỏa mãn, ktm: không thỏa mãn)
lop 8 ha,tui moi hc lop 6 thui