
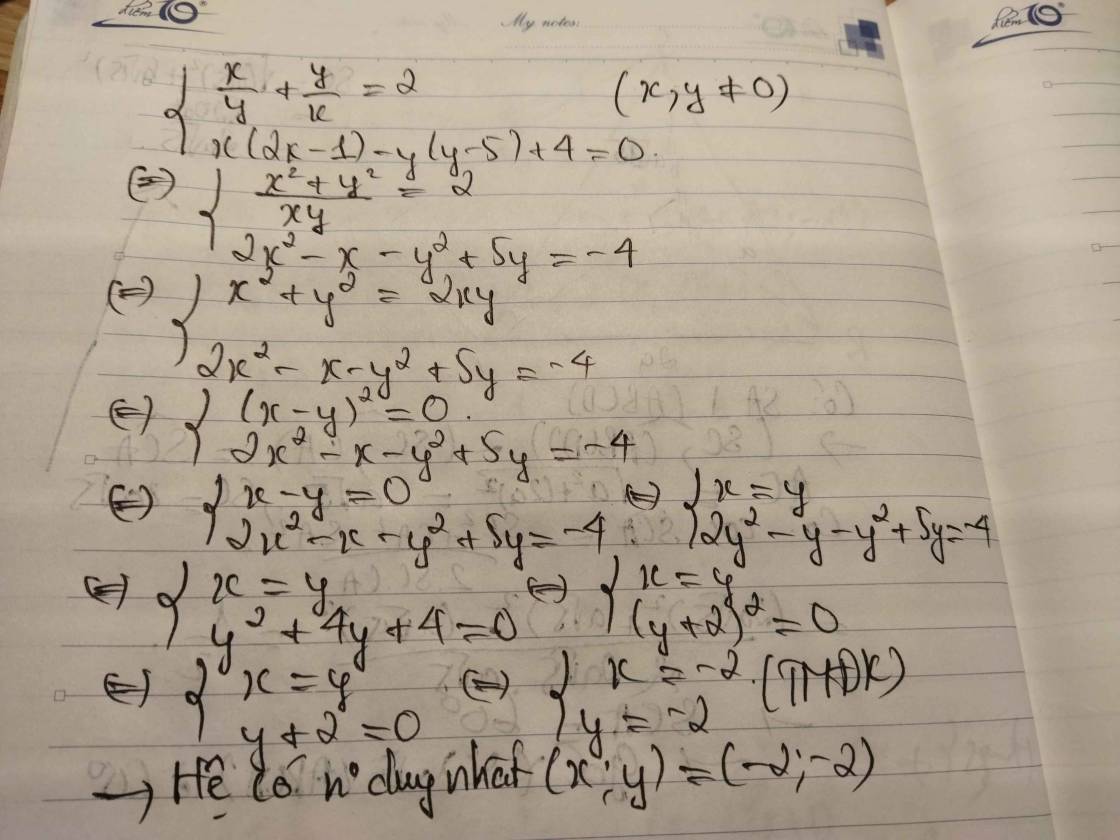
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

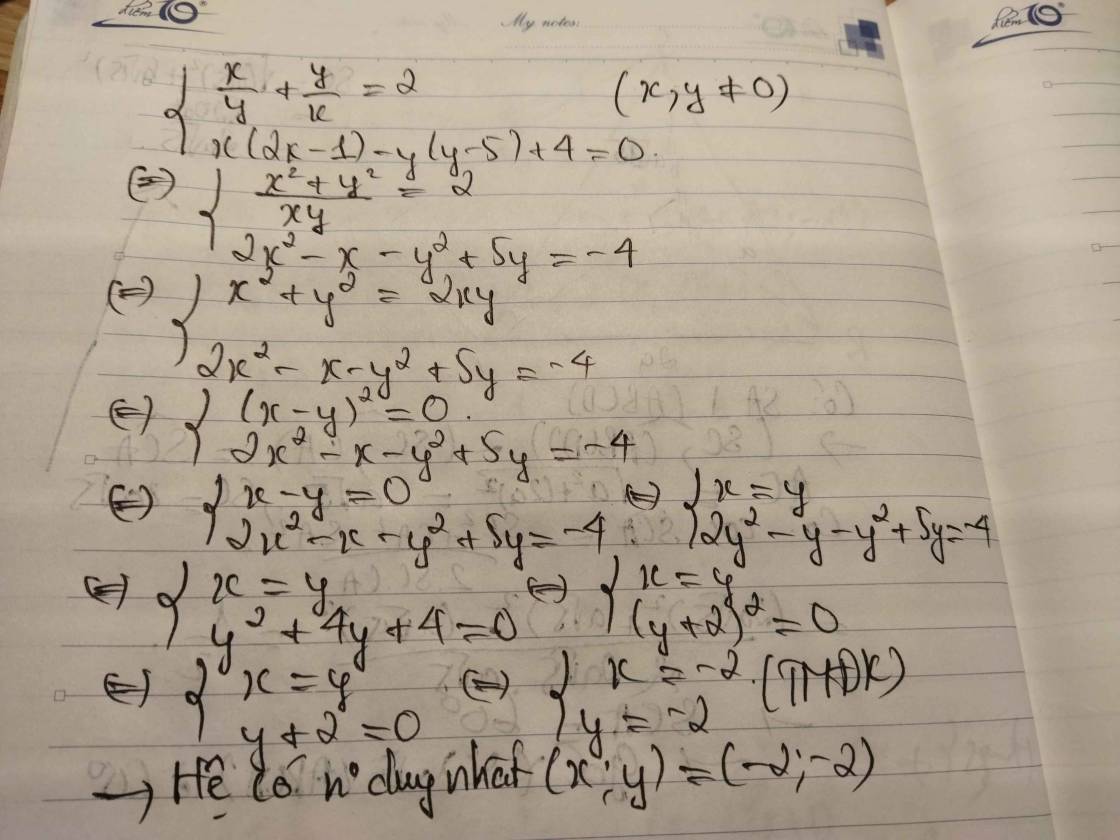

9) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{7}{2x+y}+\dfrac{4}{2x-y}=74\\\dfrac{3}{2x+y}+\dfrac{2}{2x-y}=32\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{21}{2x+y}+\dfrac{12}{2x-y}=222\\\dfrac{21}{2x+y}+\dfrac{14}{2x-y}=224\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{2}{2x-y}=2\\\dfrac{7}{2x+y}+\dfrac{4}{2x-y}=74\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x+y=\dfrac{1}{10}\\2x-y=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-2y=\dfrac{9}{10}\\2x+y=\dfrac{1}{10}\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=-\dfrac{9}{20}\\x=\dfrac{11}{40}\end{matrix}\right.\)
10) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=2y-1\\2x-y=5\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x-4y=-2\\2x-y=5\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=2y-1\\3y=7\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{11}{3}\\y=\dfrac{7}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
11) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3x-6=0\\2y-x=4\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3x=6\\y=\dfrac{x+4}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\y=3\end{matrix}\right.\)
12) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x+y=5\\x+7y=9\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x+y=5\\2x+14y=18\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x+y=5\\13y=13\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\y=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
13) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{3}{x}-\dfrac{4}{y}=2\\\dfrac{4}{x}-\dfrac{5}{y}=3\end{matrix}\right.\)(ĐKXĐ: \(x,y\ne0\))
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{12}{x}-\dfrac{16}{y}=8\\\dfrac{12}{x}-\dfrac{15}{y}=9\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{3}{x}-\dfrac{4}{y}=2\\\dfrac{1}{y}=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{1}{2}\left(tm\right)\\y=1\left(tm\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
14) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{1}{x}+\dfrac{1}{y}=\dfrac{1}{12}\\\dfrac{8}{x}+\dfrac{15}{y}=1\end{matrix}\right.\)(ĐKXĐ: \(x,y\ne0\))
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{8}{x}+\dfrac{8}{y}=\dfrac{2}{3}\\\dfrac{8}{x}+\dfrac{15}{y}=1\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{1}{x}+\dfrac{1}{y}=\dfrac{1}{12}\\\dfrac{7}{y}=\dfrac{1}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=28\left(tm\right)\\y=21\left(tm\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
15) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2\sqrt{x-1}-\sqrt{y-1}=1\\\sqrt{x-1}+\sqrt{y-1}=2\end{matrix}\right.\)(ĐKXĐ: \(x\ge1,y\ge1\))
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3\sqrt{x-1}=3\\\sqrt{x-1}+\sqrt{y-1}=2\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{x-1}=1\\\sqrt{y-1}=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-1=1\\y-1=1\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Leftrightarrow x=y=2\left(tm\right)\)

Pt đầu chắc là sai đề (chắc chắn), bạn kiểm tra lại
Với pt sau:
Nhận thấy một ẩn bằng 0 thì 2 ẩn còn lại cũng bằng 0, do đó \(\left(x;y;z\right)=\left(0;0;0\right)\) là 1 nghiệm
Với \(x;y;z\ne0\)
Từ pt đầu ta suy ra \(y>0\) , từ đó suy ra \(z>0\) từ pt 2 và hiển nhiên \(x>0\) từ pt 3
Do đó:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=\dfrac{2x^2}{x^2+1}\le\dfrac{2x^2}{2x}=x\\z=\dfrac{3y^3}{y^4+y^2+1}\le\dfrac{3y^3}{3\sqrt[3]{y^4.y^2.1}}=y\\x=\dfrac{4z^4}{z^6+z^4+z^2+1}\le\dfrac{4z^4}{4\sqrt[4]{z^6z^4z^2}}=z\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y\le x\\z\le y\\x\le z\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow x=y=z\)
Dấu "=" xảy ra khi và chỉ khi \(x=y=z=1\)
Vậy nghiệm của hệ là \(\left(x;y;z\right)=\left(0;0;0\right);\left(1;1;1\right)\)

Tất cả các hpt này đều giải bằng PP đặt ẩn phụ
a) \(\begin{cases}2\left(x+y\right)+3\left(x-y\right)=4\\\left(x+y\right)+2\left(x-y\right)=5\end{cases}\)
Đặt \(x+y=a\) ; \(x-y=b\) ta được:
\(\begin{cases}2a+3b=4\\a+2b=5\end{cases}\) \(\Leftrightarrow\) \(\begin{cases}2a+3b=4\\2a+4b=10\end{cases}\)\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(\begin{cases}-b=-6\\2a+4b=10\end{cases}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(\begin{cases}b=6\\2a+4.6=10\end{cases}\) \(\Leftrightarrow\) \(\begin{cases}a=-7\\b=6\end{cases}\) \(\Leftrightarrow\) \(\begin{cases}x+y=6-7\\x-y=6-7\end{cases}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(\begin{cases}x-7=-1\\6-y=-1\end{cases}\) \(\Leftrightarrow\) \(\begin{cases}x=6\\y=-7\end{cases}\)
Lúc khác mình làm tiếp mấy câu kia
Tiếp nào!
b) \(\begin{cases}\dfrac{3}{x}-\dfrac{4}{y}=2\\\dfrac{4}{x}-\dfrac{5}{y}=3\end{cases}\) Đặt \(\dfrac{1}{x}=a\) ; \(\dfrac{1}{y}=b\) ta được:
\(\begin{cases}3a-4b=2\\4a-5b=3\end{cases}\) \(\Leftrightarrow\) \(\begin{cases}12a-16b=8\\12a-15b=9\end{cases}\) \(\Leftrightarrow\) \(\begin{cases}-1b=-1\\12a-15b=9\end{cases}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(\begin{cases}b=1\\a=2\end{cases}\)\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(\begin{cases}a=2\\b=1\end{cases}\) \(\Leftrightarrow\) \(\begin{cases}\dfrac{1}{a}=2\\\dfrac{1}{b}=1\end{cases}\) \(\Leftrightarrow\) \(\begin{cases}a=\dfrac{1}{2}\\b=1\end{cases}\)
c) Làm tương tự thay \(\dfrac{1}{2x-y}=a\) ; \(\dfrac{1}{x+y}=b\)

\(\left(x\ne-y;x>\dfrac{y}{2}\right)\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{4}{\sqrt{2x-y}}-\dfrac{21}{x+y}=\dfrac{1}{2}\\\dfrac{3}{\sqrt{2x-y}}+\dfrac{7-\left(x+y\right)}{x+y}=1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{4}{\sqrt{2x-y}}-\dfrac{21}{x+y}=\dfrac{1}{2}\\\dfrac{3}{\sqrt{2x-y}}+\dfrac{7}{x+y}=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(đặt:\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2x-y}}=a>0;\dfrac{1}{x+y}=b\)
\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}4a-21b=\dfrac{1}{2}\\3a+7b=2\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a=\dfrac{1}{2}\left(tm\right)\\b=\dfrac{1}{14}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2x-y}}=\dfrac{1}{2}\\\dfrac{1}{x+y}=\dfrac{1}{14}\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x-y=4\\x+y=14\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=6\\y=8\end{matrix}\right.\)(thỏa)

h) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{1}{x}+\dfrac{1}{y}=2\\\dfrac{3}{x}-\dfrac{4}{y}=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\left(1\right)\)\(\left(đk:x,y\ne0\right)\)
Đặt \(a=\dfrac{1}{x},b=\dfrac{1}{y}\)
\(\left(1\right)\Leftrightarrow\) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a+b=2\\3a-4b=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3a+3b=6\\3a-4b=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a+b=2\\7b=7\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Leftrightarrow a=b=1\)
Thay a,b:
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1}{x}=\dfrac{1}{y}=1\Leftrightarrow x=y=1\left(tm\right)\)