
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.



1.
\(DK:x\ge2\)
PT
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2+x\right)\sqrt{x-2}-\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+2\right)\sqrt{x-2}\left(1-\sqrt{x-2}\right)=0\)
Cho này thì ok ròi nhé
2.
\(DK:x\le\frac{5}{2}\)
Xet \(x\in\left[0;\frac{5}{2}\right]\)
PT
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-4x=5-2x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-2x-5=0\)
Ta co:
\(\Delta^`=\left(-1\right)^2-1.\left(-5\right)=6>0\)
\(\Rightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x_1=1+\sqrt{6}\left(l\right)\\x_2=1-\sqrt{6}\left(l\right)\end{cases}}\)
Xet \(x\le0\)
PT
\(4x-x^2=5-2x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-6x+5=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x-5\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=1\left(l\right)\\x=5\left(l\right)\end{cases}}\)
Vay PT vo nghiem

1.A. Ta thấy để hàm số xác định thì x-m\(\ne\)0 hay x\(\ne\)m mà vì x\(\in\)(0,1) nên để x\(\ne\)m thì m\(\notin\)(0,1)=>m>=1 hoặc m<=0
2A để A giao B khác 0 thì 2m-1<=m+3 hay m<=4
3C.A giao B =A khi \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m< =-1\\m+5>=3\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m< =1\\m>=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)

Mệnh đề nào sau đây đúng? Giải thích tại sao lại chọn đáp án đây.
A. Có duy nhất một vectơ cùng phương với mọi vectơ.
B. Có ít nhất hai vectơ có cùng phương với mọi vectơ.
C. Có vô số vectơ cùng phương với mọi vectơ.
D. Không có vectơ nào cùng phương với mọi vectơ
Vecto →0 là vecto duy nhất cùng phương với mọi vecto.
A nha . Vì
Ta có vectơ ⇀00⇀ cùng hướng với mọi vectơ nên nó cùng phương với mọi véc tơ.
Đáp án cần chọn là: A

a: Tọa độ đỉnh là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{3}{2}\\y=-\dfrac{\left(-3\right)^2-4\cdot1\cdot\left(-2\right)}{4}=-\dfrac{9+8}{4}=-\dfrac{17}{4}\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>Hàm số đồng biến khi x>3/2 và nghịch biến khi x<3/2
b: Tọa độ đỉnh là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{-b}{2a}=\dfrac{-3}{2\cdot\left(-2\right)}=\dfrac{3}{4}\\y=-\dfrac{3^2-4\cdot\left(-2\right)\cdot5}{4}=-\dfrac{9+40}{4}=-\dfrac{49}{4}\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>Hàm số nghịch biến khi x>3/4; đồng biến khi x<3/4

1, \(x^4-19x^2-10x+8=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+4\right)\left(x^3-4x^2-3x+2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+4\right)\left(x+1\right)\left(x^2-5x+2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+4=0\\x+1=0\\x^2-5x+2=0\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x_1=-4\\x_2=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
hoặc \(x^2-5x+2=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\Delta=17\left(CT:b^2-4ac\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x_3=\dfrac{5+\sqrt{17}}{2}\\x_4=\dfrac{5-\sqrt{17}}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy pt có 4 no là...........
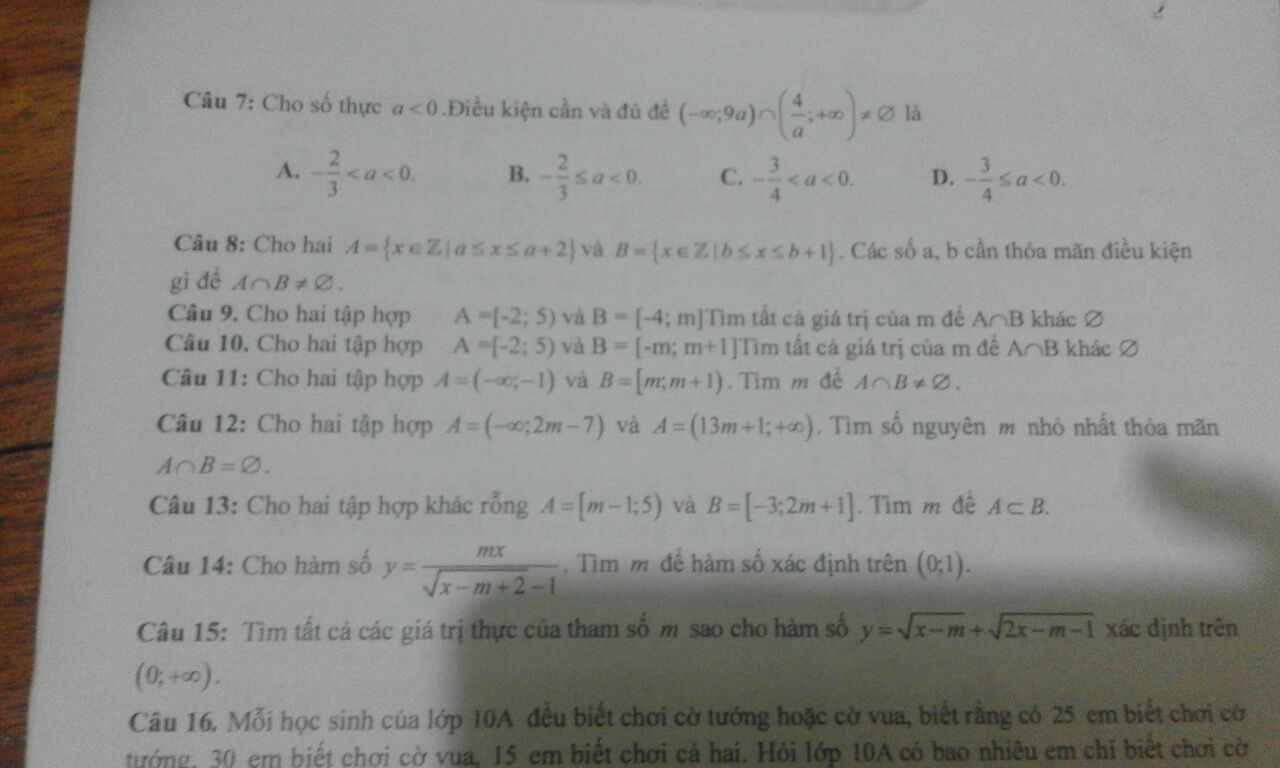 GIÚP MK VS!!! MAI MK PHẢI NỘP RỒI!!!!!!!!
GIÚP MK VS!!! MAI MK PHẢI NỘP RỒI!!!!!!!!