
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


a) (2x + 1)(1 - 2x) + (1 - 2x)2 = 18
= ( 1 - 2x) \(\left[\left(2x+1+1-2x\right)\right]\) = 18
= 2(1 - 2x) - 18 = 0
= 2 - 4x - 18 = 0
= -16 - 4x = 0
= -4x = 16
= x = \(\dfrac{16}{-4}=-4\)
b) 2(x + 1)2 -(x - 3)(x + 3) - (x - 4)2 = 0
= 2 (x2 + 2x + 1) - (x2 - 9) - (x2 - 8x + 16) = 0
= 2x2 + 4x + 2 - x2 + 9 - x2 + 8x - 16 = 0
= 12x - 5 = 0
= 12x = 5
= x = \(\dfrac{5}{12}\)
c) (x - 5)2 - x(x - 4) = 9
= x2 - 10x + 25 - x2 + 4x - 9 = 0
= -6x + 16 = 0
= -6x = -16
= x = \(\dfrac{-16}{-6}=\dfrac{8}{3}\)
d) (x - 5)2 + (x - 4)(1 - x)
= x2 - 10x + 25 + 5x - x2 - 4 = 0
= -5x + 21 = 0
= -5x = -21
= x = \(\dfrac{-21}{-5}=\dfrac{21}{5}\)
Chúc bạn học tốt

b: =>4x^2+8x-8x^2+5x-10=0
=>-4x^2+13x-10=0
=>x=2 hoặc x=5/4
c: =>2x^2-5x+6x-15=2x^2+8x
=>x-15=8x
=>-7x=15
=>x=-15/7
d: =>3x^2+15x-2x-10-3x^2-12x=5
=>x-10=5
=>x=15
e: =>x^2-3x+2x^2+2x=3x^2-12
=>-x=-12
=>x=12

a) (x-2)3+6(x+1)2-x3+12=0
\(\Rightarrow\)x3-6x2+12x-8+6(x2+2x+1)-x3+12=0
\(\Rightarrow\)x3-6x2+12x-8+6x2+12x+6-x3+12=0
\(\Rightarrow\)24x+10=0
\(\Rightarrow\)24x=-10
\(\Rightarrow\)x=\(\dfrac{-10}{24}=\dfrac{-5}{12}\)
b)(x-5)(x+5)-(x+3)2+3(x-2)2=(x+1)2-(x-4)(x+4)+3x2
\(\Rightarrow\)x2-25-(x2+6x+9)+3(x2-4x+4)=x2+2x+1-(x2-16)+3x2
\(\Rightarrow\)x2-25-x2-6x-9+3x2-12x+12=x2+2x+1-x2+16+3x2
\(\Rightarrow\)3x2-18x-22=3x2+2x+17
\(\Rightarrow\)3x2-18x-22-3x2-2x-17=0
\(\Rightarrow\)-20x-39=0
\(\Rightarrow\)-20x=39
\(\Rightarrow\)x=\(-\dfrac{39}{20}\)

a: Ta có: \(\left(x+2\right)\left(x^2-2x+4\right)-x\left(x^2+2\right)=15\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3+8-x^3-2x=15\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x=-7\)
hay \(x=-\dfrac{7}{2}\)
b: Ta có: \(\left(x-2\right)^3-\left(x-4\right)\left(x^2+4x+16\right)+6\left(x+1\right)^2=49\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3-6x^2+12x-8-x^3+64+6\left(x+1\right)^2=49\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-6x^2+12x+56+6x^2+12x+6=49\)
\(\Leftrightarrow24x=-13\)
hay \(x=-\dfrac{13}{24}\)

a: Ta có: \(\left(x+2\right)\left(x+3\right)-\left(x-2\right)\left(x-5\right)=-4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+5x+6-x^2+7x-10=-4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow12x=0\)
hay x=0
b: Ta có: \(\left(x+1\right)\left(x^2-x+1\right)-x\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)=8\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3+1-x^3+9x=8\)
\(\Leftrightarrow9x=7\)
hay \(x=\dfrac{7}{9}\)
c: Ta có: \(4x^2-9=\left(3x+1\right)\left(2x-3\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(3x+1\right)\left(2x-3\right)-\left(2x-3\right)\left(2x+3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x-3\right)\left(3x+1-2x-3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x-3\right)\left(x-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{3}{2}\\x=2\end{matrix}\right.\)

\(a,x+5x^2=0\\ \Rightarrow a,x\left(1+5x\right)=0\\ \Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=-\dfrac{1}{5}\end{matrix}\right.\\ b,\left(x+3\right)^2+\left(4+x\right)\left(4-x\right)=0\\ \Rightarrow x^2+6x+9+16-x^2=0\\ \Rightarrow6x+25=0\\ \Rightarrow6x=-25\\ \Rightarrow x=-\dfrac{25}{6}\)
\(c,5x\left(x-1\right)=x-1\\ \Rightarrow c,5x\left(x-1\right)-\left(x-1\right)\\ \Rightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(5x-1\right)=0\\ \Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=\dfrac{1}{5}\end{matrix}\right.\\ d,x^2-2x-3=0\\ \Rightarrow\left(x^2-3x\right)+\left(x-3\right)=0\\ \Rightarrow x\left(x-3\right)+\left(x-3\right)=0\\ \Rightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left(x-3\right)=0\\ \Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-1\\x=3\end{matrix}\right.\)

a) \(\left(x-1\right)^3\)
\(=x^3-3x^2+3x-1\)
b) \(\left(2x-3y\right)^3\)
\(=\left(2x\right)^3-3\left(2x\right)^23y+3.2x\left(3y\right)^3+\left(3y\right)^3\)
\(=8x^3-36x^2y+54xy^2-27y^3\)
Bài 3:
a: Ta có: \(\left(x-2\right)^3-x^2\left(x-6\right)=5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3-6x^2+12x-8-x^3+6x^2=5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow12x=13\)
hay \(x=\dfrac{13}{12}\)
b: Ta có: \(\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)-x\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)=4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3-1-x^3+4x=4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x=5\)
hay \(x=\dfrac{5}{4}\)

b)(x+3)2-(x-4)(x+8)=1
\(\Rightarrow\)x2+6x+9-(x2+8x-4x-32)=1
⇒x2+6x+9-x2-8x+4x+32=1
⇒2x+41=1
\(\Rightarrow\)2x+41-1=0
\(\Rightarrow\)2x+40=0
⇒2x=-40
\(\Rightarrow\)x=\(\dfrac{-40}{2}\)
⇒x=-20

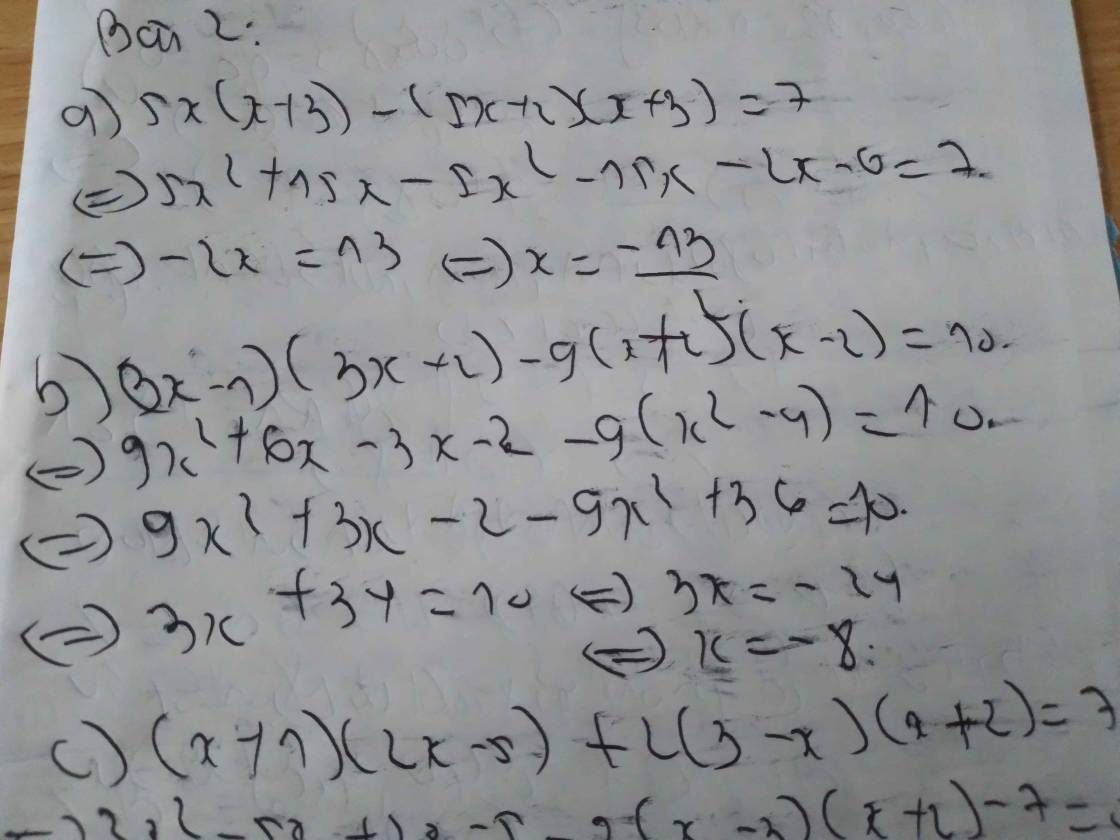


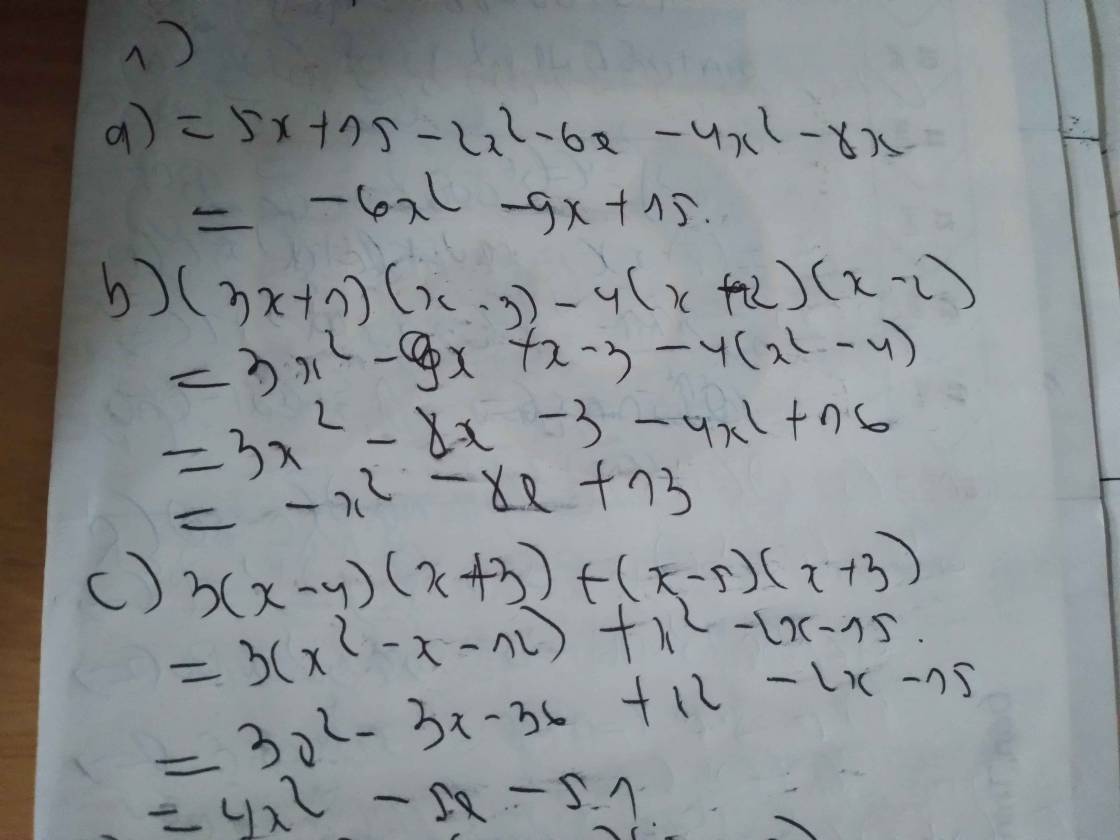
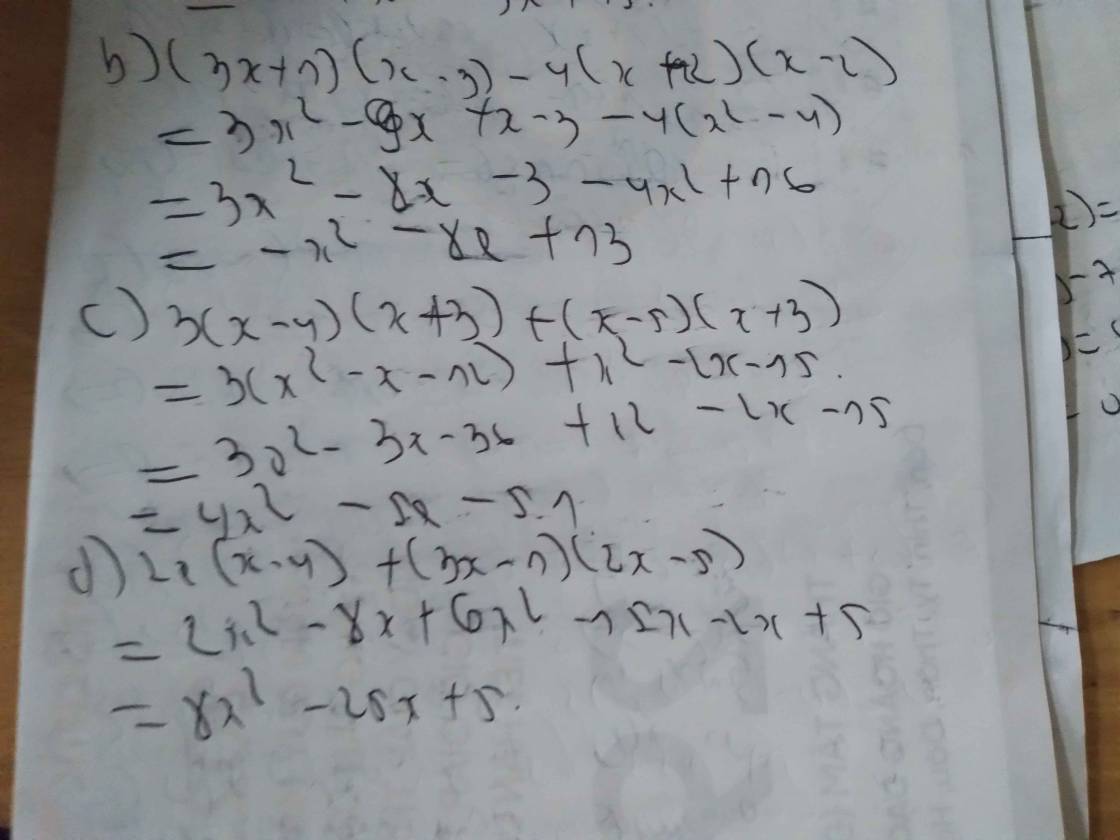
\(\frac{x}{2}-\frac{x}{3}=\frac{1}{4}\)
\(\frac{3x}{6}-\frac{2x}{6}=\frac{1}{4}\)
=> \(\frac{x}{6}=\frac{1}{4}\)
<=> 4x = 6
<=> x = \(\frac{3}{2}\)