Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

\(a) 2Fe + 6H_2SO_4 \to Fe_2(SO_4)_3 + 3SO_2 + 6H_2O\\ 2Al+ 6H_2SO_4 \to Al_2(SO_4)_3 + 3SO_2 + 6H_2O\\ b) n_{Fe} = a(mol) ; n_{Al} = b(mol) \Rightarrow 56a + 27b = 11(1)\\ n_{SO_2} = 1,5a + 1,5b = \dfrac{10,08}{22,4} = 0,45(2)\\ (1)(2) \Rightarrow a = 0,1 ; b = 0,2\\ \%m_{Fe} = \dfrac{0,1.56}{11}.100\% = 50,91\%\\ \%m_{Al} = 100\%-50,91\% = 49,09\%\)

Gọi số mol Cu, Fe là a, b (mol)
=> 64a + 56b = 17,6 (1)
\(n_{SO_2}=\dfrac{8,96}{22,4}=0,4\left(mol\right)\)
PTHH: 2Fe + 6H2SO4 --> Fe2(SO4)3 + 3SO2 + 6H2O
b-------------------------------->1,5b
Cu + 2H2SO4 --> CuSO4 + SO2 + 2H2O
a--------------------------->a
=> a + 1,5b = 0,4 (2)
(1)(2) => a = 0,1 (mol); b = 0,2 (mol)
=> \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\%m_{Cu}=\dfrac{0,1.64}{17,6}.100\%=36,36\%\\\%m_{Fe}=\dfrac{0,2.56}{17,6}.100\%=63,64\%\end{matrix}\right.\)

a) nFe = x mol ; nCu = y mol
Ta có: nSO2 = 0,4 mol
e cho: Fe0 - 3e → Fe3+
x mol → 3x mol → x mol
Cu0 - 2e → Cu2+
y mol → 2y mol → y mol
e nhận: S6+ + 2e → S4+
0,4 mol → 0,8 mol → 0,4 mol
- Theo định luật bảo toàn electron, ta có: tổng số mol e cho = tổng số mol e nhận
→ 3x + 2y = 0,8 (1)
- Khối lượng hỗn hợp ban đầu: mFe + mCu = 18,4 (g)
→ 56x + 64y = 18,4 (2)
Giải hệ hai phương trình (1) và (2), ta được: x = 0,18 mol ; y = 0,13 mol
mFe = 0,18 x 56 = 10,08 (g) → %mFe = 54,78% → %mCu = 100% - %mFe = 45,22%
b) Theo định luật bảo toàn electron, ta có: tổng số mol e cho = tổng số mol e nhận
→ ne nhận= 3x + 2y = 0,8
2H+ + 2e → H2
0,8 mol → 0,4 mol
VH2= 8,96 (l)

a) \(n_{H_2}=\dfrac{3,36}{22,4}=0,15\left(mol\right)\)
PTHH: 2Al + 3H2SO4 --> Al2(SO4)3 + 3H2
0,1<----------------------------0,15
=> \(\%m_{Al}=\dfrac{0,1.27}{7,5}.100\%=36\%\)
\(\%m_{Cu}=100\%-36\%=64\%\)
b) \(n_{Cu}=\dfrac{7,5-0,1.27}{64}=0,075\left(mol\right)\)
PTHH: Cu + 2H2SO4 --> CuSO4 + SO2 + 2H2O
0,075------------------------>0,075
2Al + 6H2SO4 --> Al2(SO4)3 + 3SO2 + 6H2O
0,1----------------------------->0,15
=> VSO2 = (0,075 + 0,15).22,4 = 5,04 (l)

a, \(n_{H_2}=\dfrac{4,48}{22,4}=0,2\left(mol\right)\)
PTHH: Fe + H2SO4 ---> FeSO4 + H2
0,2<---------------------------0,2
\(\rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m_{Fe}=0,2.56=11,2\left(g\right)\\m_{Cu}=16-11,2=4,8\left(g\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
b, \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}n_{Fe}=\dfrac{32}{16}.0,2=0,4\left(mol\right)\\n_{Cu}=\dfrac{4,8}{64}.\dfrac{32}{16}=0,15\left(mol\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
PTHH:
Cu + 2H2SO4 (đặc, nóng) ---> CuSO4 + SO2 + 2H2O
0,15--------------------------------------------->0,15
2Fe + 6H2SO4 (đặc, nóng) ---> Fe2(SO4)3 + 3SO2 + 6H2O
0,4------------------------------------------------------>0,6
=> VSO2 = (0,6 + 0,15).22,4 = 16,8 (l)
c, \(n_{NaOH}=0,375.2=0,75\left(mol\right)\)
\(T=\dfrac{0,75}{0,6+0,15}=1\) => tạo duy nhất muối axit (NaHSO3)
PTHH: NaOH + SO2 ---> NaHSO3
0,75----------------->0,75
=> mmuối = 0,75.104 = 78 (g)
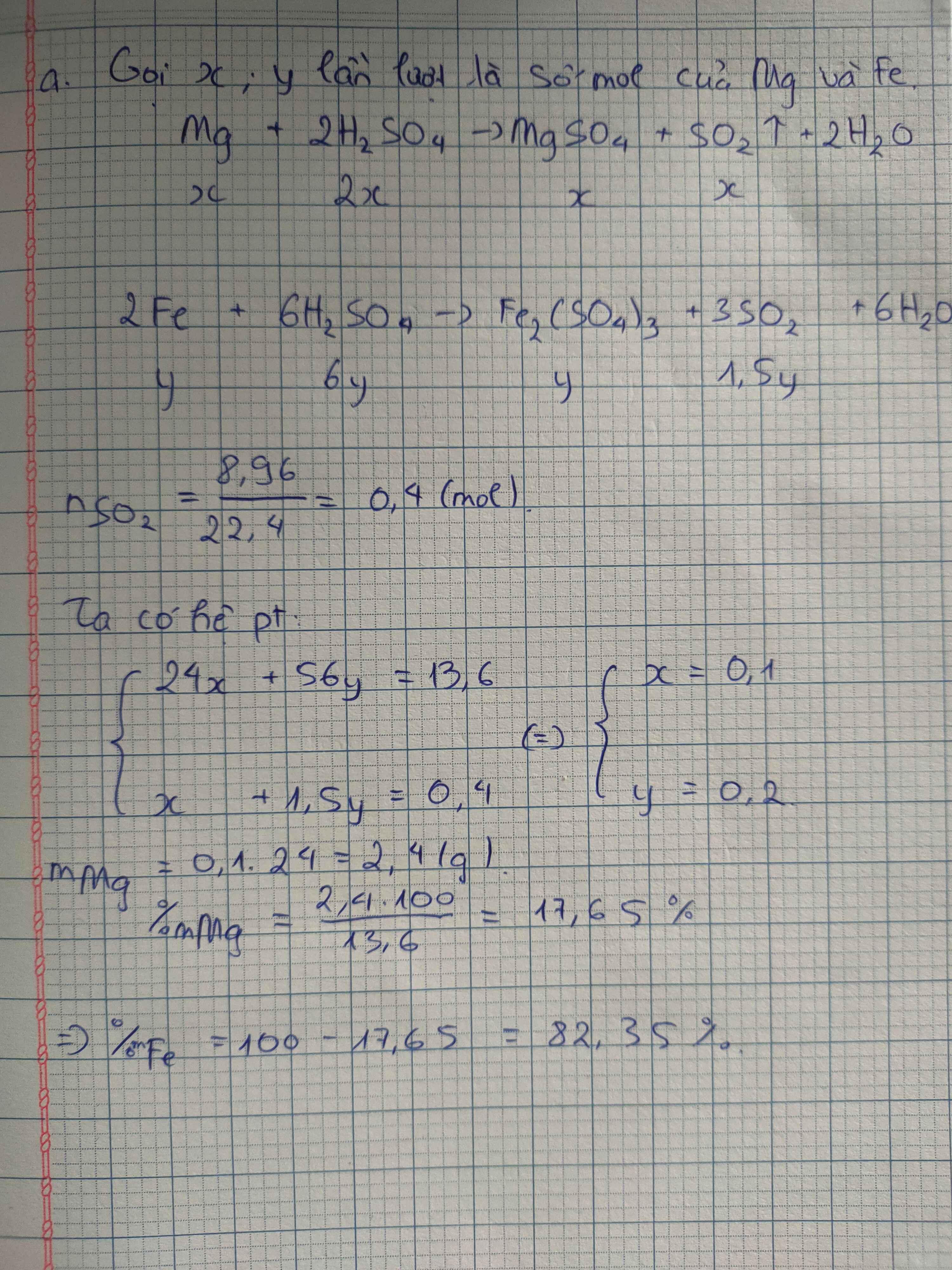

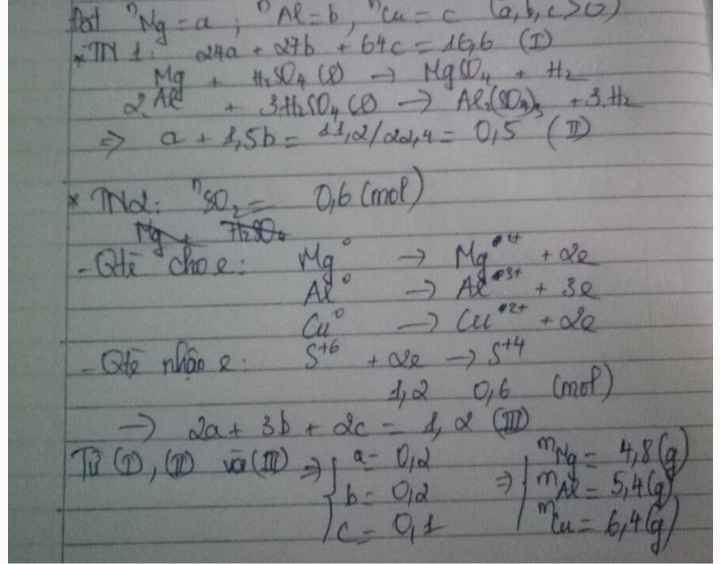


Nếu số lít SO2 =12.32 thì số mol sẽ là 0.55 nên Kl Cu =35.2(g).Không phù hợp yêu cầu của đề bài.
ca 3 cai fe cu va al deu td voi axit h2s04 dac nong