Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

b: Tọa độ giao điểm là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}4-2x=3x+1\\y=3x+1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{3}{5}\\y=\dfrac{9}{5}+1=\dfrac{14}{5}\end{matrix}\right.\)

a: 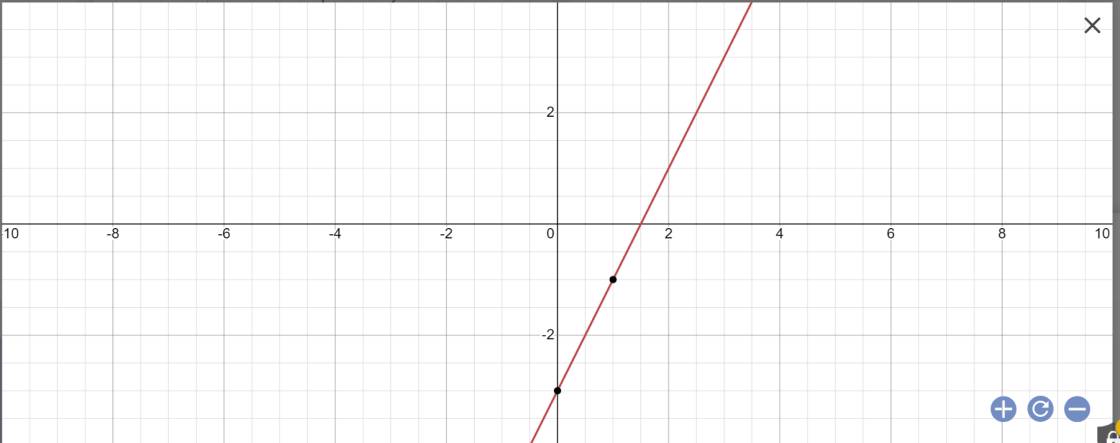
b: Phương trình hoành độ giao điểm là:
\(2x-3=\dfrac{1}{2}x+3\)
=>\(2x-\dfrac{1}{2}x=3+3=6\)
=>\(\dfrac{3}{2}x=6\)
=>\(x=6:\dfrac{3}{2}=4\)
Thay x=4 vào y=2x-3, ta được:
\(y=2\cdot4-3=5\)
Vậy: M(4;5)

a:
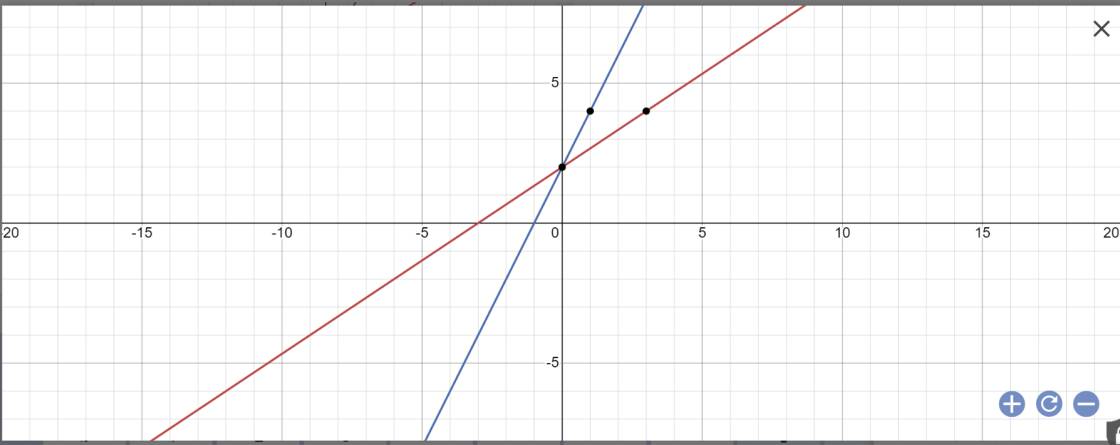
b: Tọa độ A là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\\dfrac{2}{3}x+2=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\\dfrac{2}{3}x=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\x=-2:\dfrac{2}{3}=-2\cdot\dfrac{3}{2}=-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
Tọa độ B là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\2x+2=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\2x=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=-1\\y=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
Tọa độ C là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{2}{3}x+2=2x+2\\y=2x+2\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-\dfrac{4}{3}x=0\\y=2x+2\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\y=2\cdot0+2=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: A(-3;0); B(-1;0); C(0;2)

b: Tọa độ giao điểm là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x-2=-x+1\\y=-x+1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\y=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
a)
 b, Gọi giao điểm của 2 đường thẳng trên là M(x1;y1)
b, Gọi giao điểm của 2 đường thẳng trên là M(x1;y1)
tọa độ giao điểm của (d1) và (d2) là nghiệm của hpt
{y1=2x1−7y1=−x1−1{y1=2x1−7y1=−x1−1<=>{x1=2y1=−3{x1=2y1=−3
Vậy...
c, phương trình đường thẳng (d3) có dạng y=ax+b
Vì đt(d3) song song với (d2) và cắt đường thẳng (d1) tại một điểm nằm trên trục tung nên ta được a=-1, x=0,y=-7
=> b=-7
Thay a=-1, b=-7 vào cths y=ax+b ta được
y=-x-7

\(b,\) PT hoành độ giao điểm: \(3x+2=x-2\Leftrightarrow x=-2\Leftrightarrow y=-4\Leftrightarrow A\left(-2;-4\right)\)
Vậy \(A\left(-2;-4\right)\) là tọa độ giao điểm

b: Tọa độ A là:
y=0 và 1/2x+2=0
=>x=-4 và y=0
Tọa độ B là:
y=0 và -x+2=0
=>B(2;0)
Tọa độ C là:
1/2x+2=-x+2 và y=-x+2
=>x=0 và y=2
d: A(-4;0); B(2;0); C(0;2)
\(AB=\sqrt{\left(2+4\right)^2}=6\)
\(AC=\sqrt{\left(0+4\right)^2+\left(2-0\right)^2}=2\sqrt{5}\)
\(BC=\sqrt{\left(0-2\right)^2+\left(2-0\right)^2}=2\sqrt{2}\)
\(P=\dfrac{6+2\sqrt{5}+2\sqrt{2}}{2}=3+\sqrt{5}+\sqrt{2}\left(cm\right)\)
=>S=6(cm2)
a/ bạn tự làm
b/ \(\Rightarrow y=0\Rightarrow\dfrac{1}{2}x+2=0\) giải PT tìm hoành độ x
c/ \(\Rightarrow x=0\Rightarrow y=0+2=2\)
d/ \(\Rightarrow\dfrac{1}{2}x+2=-x+2\) Giải PT tìm hoành độ x của C rồi thay vào d1 hoặc d2 để tìm tung độ y của C